Home | 7 Days | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12
2021: 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07
Dear friends of COVID Reference,
Today, on 7 January 2022, 21 months after the first CR edition and after 649 daily updates, we have decided to stop working on CR and return to our previous projects.
It has been a pleasure to discover COVID-19 with you.
All the best,
Christian Hoffmann, Rob Camp & Bernd Sebastian Kamps
.
Contact:
![]()
7 January
Epidemiology
Kupferschmidt K, Vogel G. Omicron cases are exploding. Scientists still don’t know how bad the wave will be. Science 2022, published 4 January. https://www.science.org/content/article/omicron-cases-are-exploding-scientists-still-don-t-know-how-bad-wave-will-be
While Omicron may cause less severe disease and death, it might nonetheless overwhelm our hospitals. A short overview.
Transmission
Eyre DW, Taylor D, Purver M, et al. Effect of Covid-19 Vaccination on Transmission of Alpha and Delta Variants. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jan 5. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34986294. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116597
Vaccination was associated with a smaller reduction in transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant than of the Alpha variant, and the effects of vaccination decreased over time.
Clinical
Kozlov M. Omicron’s feeble attack on the lungs could make it less dangerous. Nature 2022, published 5 January. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-00007-8
Omicron seems to multiply less readily in lung tissue. But in people infected with previously circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants, lungs can already be badly damaged.
Collateral Damage
Pai M, Kasaeva T, Swaminathan S. Covid-19’s Devastating Effect on Tuberculosis Care – A Path to Recovery. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jan 5. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34986295. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2118145
A 15% reduction in the number of people treated for drug-resistant tuberculosis; a 21% decrease in people receiving preventive treatment for tuberculosis infection, and a decrease (from $5.8 billion to $5.3 billion) in global tuberculosis spending from 2019 to 2020.
Treatment
Lowe D. Making Paxlovid. Science 2022, published 5 January. https://www.science.org/content/blog-post/making-paxlovid
Paxlovid (PF-07321332), Pfizer’s protease inhibitor drug for SARS-CoV-2 infection, will soon be available, but at first only in limited amounts. Derek Lowe describes the complexities of producing the drug to scale. Like with vaccines, there are supply chain problems.
Thread of the Day
Grifoni A. Go T cells! Twitter 2022, posted 5 January. https://twitter.com/Alba_Grifoni/status/1478788717900972039
Optimistic summary by Alba Grifoni who presents the latest papers on COVID-19 T cell immunology. The bottom line: T cell responses are largely preserved even in the context of Omicron.
Beyond COVID
Larsen J, Raisen CL, Ba X, et al. Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics. Nature (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04265-w
The authors show that particular lineages of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus—a notorious human pathogen—appeared in European hedgehogs in the pre-antibiotic era.
6 January
Vaccination
Lipkind HS, Vazquez-Benitez G, DeSilva M, et al. Receipt of COVID-19 Vaccine During Pregnancy and Preterm or Small-for-Gestational-Age at Birth — Eight Integrated Health Care Organizations, United States, December 15, 2020–July 22, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022;71. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7101e1
“In this retrospective cohort of >40,000 pregnant women, COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with preterm birth or small-for-gestational-age at birth overall, stratified by trimester of vaccination, or number of vaccine doses received during pregnancy, compared with unvaccinated pregnant women.”
Immunology
Willett BJ, Grove J, MacLean O, et al. The hyper-transmissible SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant exhibits significant antigenic change, vaccine escape and a switch in cell entry mechanism. medRxiv 2022, posted 3 January. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.03.21268111
The authors show that “immunity from natural infection (without vaccination) is more protective than two doses of vaccine but inferior to three doses.”
Virology
van der Straten K, Guerra D, van Gils M, et al. Mapping the antigenic diversification of SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv 2022, posted 3 January. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.03.21268582
Omicron is different. After studying SARS-CoV-2 antigenic drift by assessing neutralizing activity against variants-of-concern (VOCs), the authors conclude that “Omicron forms a new antigenic cluster associated with immune escape and likely require(es) vaccine updates to ensure vaccine effectiveness.”
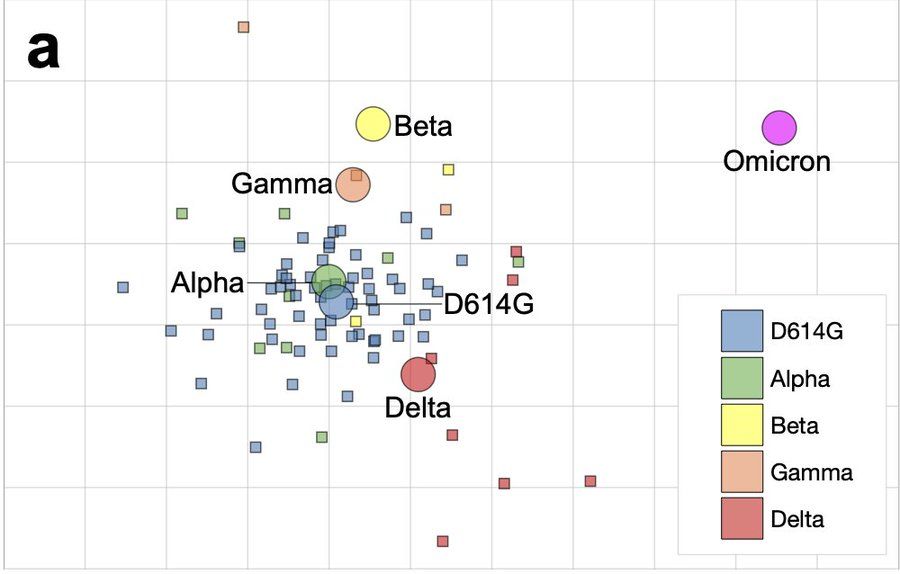
Figure 2. SARS-CoV-2 antigenic cartography. Antigenic map of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs based on post-SARS-CoV-2 infection sera. SARS-CoV-2 VOCs are shown as circles and sera are indicated as squares. Each square corresponds to sera of one individual and is coloured by the infecting SARS-CoV-2 variant. Both axes of the map are antigenic distance and each grid square (1 antigenic unit) represents a two-fold change in neutralization titre. The distance between points in the map can be interpreted as a measure of antigenic similarity of similarity in reactivity where closer together points are more similar.
Clinical
Iversen KK, Afzal S, Ahlström MG, et al. Lung function decline in relation to COVID-19 in the general population: a matched cohort study with pre-pandemic assessment of lung function. J Infect Dis. 2022 Jan 3:jiab636. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34979029. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab636
COVID-19 related decline of dynamic lung volumes in the general population not requiring hospitalization were small but measurable.
Pediatrics
Shuffrey LC, Firestein MR, Kyle MH, et al. Association of Birth During the COVID-19 Pandemic With Neurodevelopmental Status at 6 Months in Infants With and Without In Utero Exposure to Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Jan 4:e215563. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34982107. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.5563
Birth during the COVID-19 pandemic, but not maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection, might be associated with differences in neurodevelopment at age 6 months. A cohort study of 255 infants born between March and December 2020.
5 January
Immunology
Gao Y, Cai C, Grifoni A, et al. Ancestral SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells cross-recognize Omicron (B.1.1.529). Research Square 2022, posted 3 January. https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1217466/v1
SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induced by prior infection and, more extensively, by mRNA vaccination, provide comprehensive heterologous immune reactivity against B.1.1.529 (Omicron).
Carreño JM, Alshammary H, Tcheou J, et al. Activity of convalescent and vaccine serum against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Nature 2021, published 31 December. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03846-z
Neutralizing activity of sera from convalescent and double vaccinated participants was undetectable to very low against B.1.1.529 (Omicron) while neutralizing activity of sera from individuals who had been exposed to spike three or four times was maintained, although at significantly reduced levels. The data confirm that previously infected individuals may benefit from vaccination.
Epidemiology
Cuschieri S, Pallari E, Hatziyianni A, Sigurvinsdottir R, Sigfusdottir ID, Sigurðardóttir ÁK. A year of Covid-19: Experiences and lessons learnt by small European island states: Cyprus, Iceland, and Malta. Eur J Public Health. 2022 Jan 3:ckab217. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34978569. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckab217
How small islands manage COVID-19. Cyprus and Malta contained the COVID-19 spread better than Iceland during the first wave. However, a significantly higher viral spread and mortality rates were observed in Malta during the second wave.
Diagnostic
HMG20210301. COVID-19 Self-Test.
HM Government 2021, posted 1 March. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S9XR8RZxKNo
The Omicron wave may be a good time to update your swabbing technique. Swab both your nose and throat. Watch the video to see how at 3:40.
Prevention
> 100 public health experts, clinicians, scientists. Covid-19: An urgent call for global “vaccines-plus” action. BMJ 2022, published 3 January. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.o1
The current UK government under Prime Minister Boris Johnson has shown repeatedly that they are unfit and unable to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, more than 100 researchers and healthcare workers call for a global “vaccines-plus” action. See also the Twitter thread by Adam Hamdy: https://twitter.com/adamhamdy/status/1477934985185169408. #9: “The history of public health is littered with examples of vested interests resisting calls for better sanitation, better workplace safety, cleaner air, etc., because such things disrupt the status quo and require investment. They would rather trade your life for their money.” (italics ours)
Thread of the Day
Spencer C. Just leaving the ER. It was a long day. Twitter 2022, posted 4 January. https://twitter.com/Craig_A_Spencer/status/1478217081959108614
Craig Spencer describes the challenges he and his colleagues are facing with the current Omicron surge in New York City.
4 January
Epidemiology
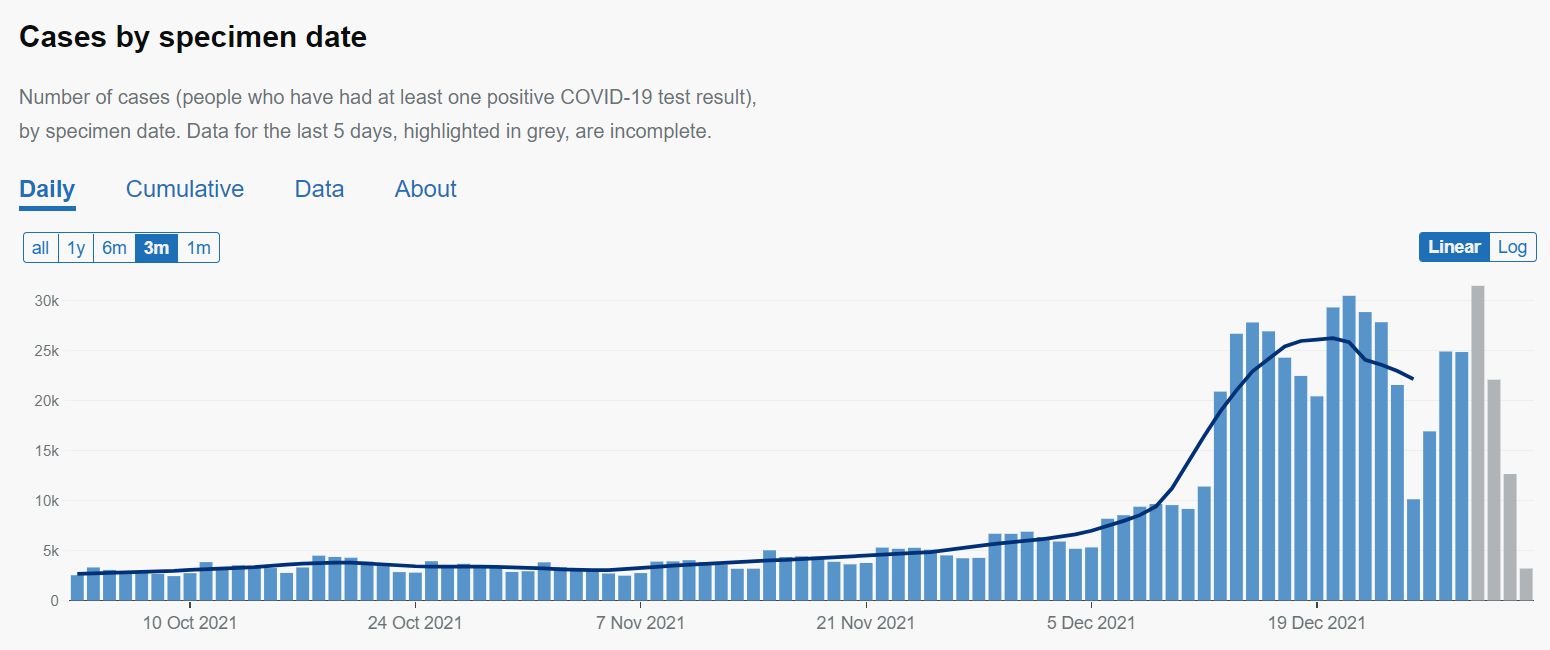
GOV.UK20220101. Cases in London. GOV.UK Coronavirus in the UK 2022, update 1 January. https://coronavirus.data.gov.uk/details/cases?areaType=region&areaName=London
Infections in London appear to have reached a peak. Hopefully.
Vaccines
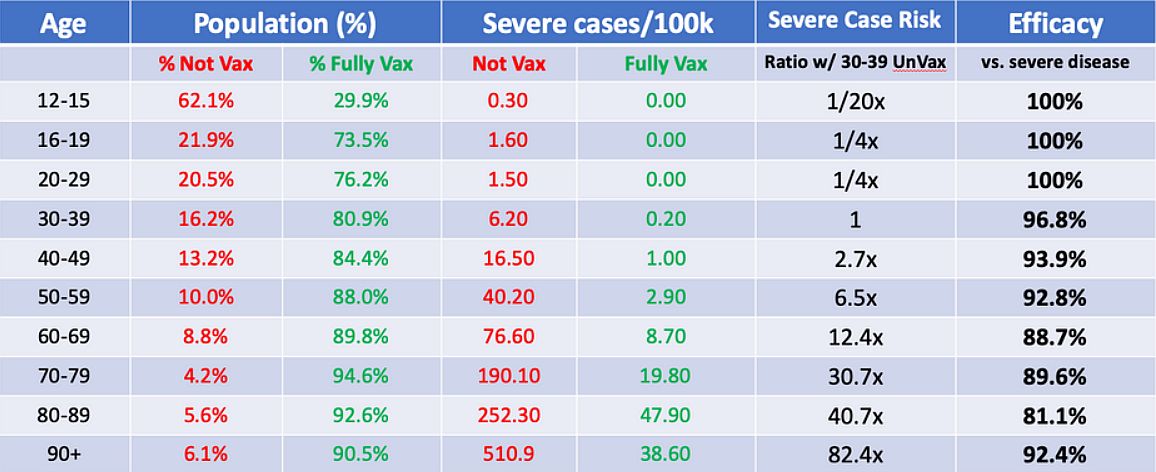
UKHSA 20211231. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England Technical briefing: Update on hospitalisation and vaccine effectiveness for Omicron VOC-21NOV-01 (B.1.1.529). UK Health Security Agency 2021, published 31 December. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1044481/Technical-Briefing-31-Dec-2021-Omicron_severity_update.pdf
Paper of the Day. After the third vaccine dose, there was 88% protection against hospitalization due to infection with Omicron. In comparison, 6 months after the second dose, protection was only 52% (see table). The authors also found that the risk of presentation to emergency care or hospital admission with Omicron was approximately half of that for Delta. In addition, the risk of hospital admission from emergency departments with Omicron was approximately one-third of that for Delta.
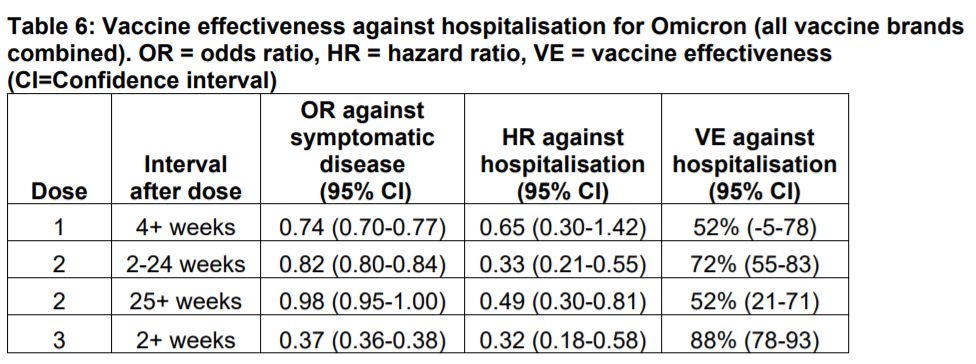
Table 6 – Vaccine effectiveness against hospitalisation for Omicron (all vaccine brands combined). OR = odds ratio, HR = hazard ratio, VE = vaccine effectiveness (CI = Confidence interval)
Immunology
Perugino CA, Liu H, Feldman J, et al. Preferential expansion of cross-reactive pre-existing switched memory B cells that recognize the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant Spike protein. medRxiv 2022, posted 1 January. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.30.21268554
How memory B cells adapt to the Omicron variant after a third vaccine dose.
Miyamoto S, Arashiro T, Adachi Y, et al. Vaccination-infection interval determines cross-neutralization potency to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron after breakthrough infection by other variants. medRxiv 2022, posted 1 January. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.28.21268481
In this small study, Omicron was highly resistant to neutralization in fully vaccinated individuals without a history of breakthrough infections. However, cross-neutralization against Omicron was induced in vaccinees that experienced breakthrough infections. Interestingly, it was the time interval between vaccination and infection, rather than the variant types of infection, that was correlated with the magnitude and potency of Omicron-neutralizing antibodies.
Bradshaw R. VOC Fitness Landscape. Twitter 2022, posted 2 January. https://twitter.com/Forensic_Stats/status/1477698508132077572
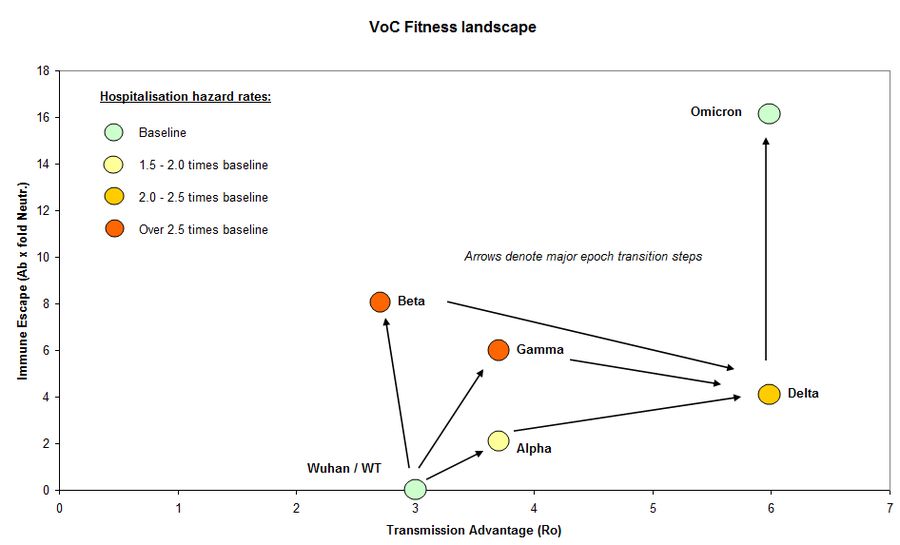
Prevention
MPG 20211202. How well masks protect. Max-Planck-Gesellschaft 2021, published 2 December. https://www.mpg.de/17916867/coronavirus-masks-risk-protection
Omicron times are good for revising mask habits. Three meters is not enough to ensure protection. Even at that distance, it takes less than five minutes for an unvaccinated person standing in the breath of a person with COVID-19 to become infected with almost 100 percent certainty. Fortunately, FFP2 masks work.
3 January
Vaccination
Hause AM, Baggs J, Marquez P, et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Safety in Children Aged 5-11 Years – United States, November 3-December 19, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Dec 31;70(5152):1755-1760. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34968370. Full text: https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm705152a1
After approximately 8 million doses administered to children ages 5-11, the most common reported side effects were pain at the injection site, fatigue and headache. These reactions seem to be more common after the second dose.
Immunology
Schmidt F, Muecksch F, Weisblum Y, et al. Plasma neutralization properties of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. N Engl J Med 2021, published 30 December. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2119641
Yet another study showing that the Omicron variant shows an unprecedented degree of neutralizing antibody escape, but that boosting will provide additional protection against infection with the variant and subsequent disease.
Clinical
Maslo C, Friedland R, Toubkin M, Laubscher A, Akaloo T, Kama B. Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized Patients in South Africa During the COVID-19 Omicron Wave Compared With Previous Waves. JAMA. 2021 Dec 30. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34967859. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.24868
A Dutch study showing that 68% – 69% of patients presenting to the emergency department with a positive COVID-19 result were admitted to the hospital in the first 3 waves vs 41.3% in wave 4 (Omicron). Patients hospitalized during wave 4 were also younger, with a higher proportion of females, and significantly fewer patients with co-morbidities admitted.
Rodríguez-Flores M, Goicochea-Turcott EW, Mancillas-Adame L, et al. The utility of the Edmonton Obesity Staging System for the prediction of COVID-19 outcomes: a multi-centre study. Int J Obes (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-021-01017-8
In this study from Mexico, the authors show that the performance of the Edmonton Obesity Staging System (EOSS) was associated with adverse COVID-19 outcomes, and it distinguished risks beyond body mass index (BMI). In patients with a BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, the risk for intubation increased with progressive EOSS stages.
Treatment
Diaz R, Orlandini A, Castellana N, et al. Effect of Colchicine vs Usual Care Alone on Intubation and 28-Day Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2141328. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34964849. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41328
Nothing new. Compared with usual care, colchicine did not significantly reduce mechanical ventilation or 28-day mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia.
2 January
Happy New Year!
1 January
Vaccines
Nemet I, Kliker L, Lustig Y, et al. Third BNT162b2 Vaccination Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infection. N Engl J Med. 2021 Dec 29. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34965337. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2119358
Obviously, three Pfizer doses are better than two. With just two doses, there was significantly lower neutralization efficiency against Beta, Delta, and Omicron than against the wild-type virus.
McGrew S, Taylor HA. Adolescents, Parents, and Covid-19 Vaccination – Who Should Decide? N Engl J Med. 2021 Dec 29. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34965336. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp2116771
Allowing adolescents to independently consent to COVID-19 vaccination could substantially increase vaccine uptake in this population. The authors “believe that allowing adolescents to independently consent to Covid-19 vaccination is on par with allowing independent consent to any intervention that is in adolescents’ best interest and supports an important public health goal.”
Transmission
Fox-Lewis A, Williamson F, Harrower J, et al. Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant within Tightly Monitored Isolation Facility, New Zealand (Aotearoa). Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 29;28(3). PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34965365. Full text: https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2803.212318
Evidence for airborne spread of SARS-CoV-2 from an asymptomatic patient to group of 3 people who were staying in separate nonadjacent rooms 2 meters apart. The four individuals had no direct contact with each other or with any shared objects, as corroborated by security camera footage. However, security camera showed simultaneous door openings of the rooms 4 times, for 3-5 seconds each time.
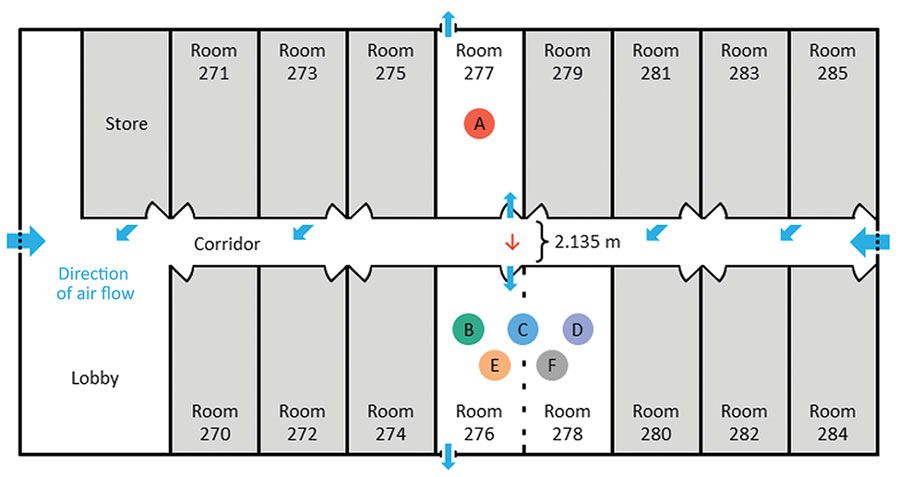
Figure 2. Layout of managed isolation facility block 2, New Zealand, in which airborne transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Delta variant occurred between separate nonadjacent rooms. Colored circles indicate persons A–F. Person A occupied room 277 and travel group BCDEF occupied adjoining rooms 276 and 278 on the opposite side of the corridor, 2.135 m apart. Red arrow indicates direction of probable airborne transmission of Delta variant from person A to persons B, C, and D. Blue arrows indicate direction of airflow.
Clinical
Jassat W, Abdool Karim S, Mudara C, et al. Clinical Severity of COVID-19 Patients Admitted to Hospitals in Gauteng, South Africa During the Omicron-Dominant Fourth Wave. Lancet Preprints 2021, posted 29 December. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3996320 Best clinical paper on Omicron so far. Omicron led to less severe disease – at least in the Gauteng province of South Africa. In this analysis of 41,046, 33,423, and 133,551 SARS-CoV-2 cases in the second, third and fourth South African COVID-19 waves, about 4.9% of cases were admitted to hospital during the fourth (Omicron-dominated) wave compared to 18.9% and 13.7% during the second (Beta-dominated) and third (Delta-dominated) waves (p < 0.001). During the fourth wave, 28.8% of admissions were severe disease compared to 60.1% and 66.9% in the second and third waves. Importantly, patients admitted to hospital in the Omicron-dominated fourth wave were 73% less likely to have severe disease than patients admitted during the third wave. The authors caution that “since any combination of a less-virulent virus, co-morbidities, high immunity from prior infection(s) or vaccination may be important contributors to this clinical presentation, care should be taken in extrapolating this to other populations with different co-morbidity profiles, prevalence of prior infection and vaccination coverage.”
Treatment
Heskin J, Pallett SJC, Mughal N, et al. Caution required with use of ritonavir-boosted PF-07321332 in COVID-19 management. Lancet 2022, published 1 January. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02657-X
Paxlovid, the new Pfizer anti-COVID drug, is a combination of PF-07321332 and ritonavir. Ritonavir is an old acquaintance from HIV treatment – as a potent inhibitor of the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, it is used widely to enhance plasma drug concentrations of other drugs. There is a potential for clinically significant drug–drug interactions and the authors recommend “that all prescribing clinicians become familiar with potential interactions by use of dedicated reference guides, such as the University of Liverpool antiretroviral drug interaction checker and existing antiretroviral treatment guidelines, and by liaising closely with colleagues experienced in the treatment of HIV infection, to reduce the potential for clinically significant iatrogenic adverse or life-threatening events.”
31 December
Vaccines
Collie S, Champion J, Moultrie H, Bekker LG, Gray G. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 Vaccine against Omicron Variant in South Africa. N Engl J Med. 2021 Dec 29. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34965358. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2119270
Reduced-but-maintained effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine against hospital admission for COVID-19 in people with Omicron infection (70% vs 93% for those with Delta) in South Africa. “The addition of a booster dose of vaccine may mitigate this reduction in vaccine effectiveness”.
Immunology
Tarke A, Coelho CH, Zhang Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination induces immunological memory able to cross-recognize variants from Alpha to Omicron. medRxiv 2021, posted 28 December. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.28.474333v1
There is a high degree of T cell preservation against COVID variants in people vaccinated with the Pfizer, Moderna, J&J and Novavax vaccines.
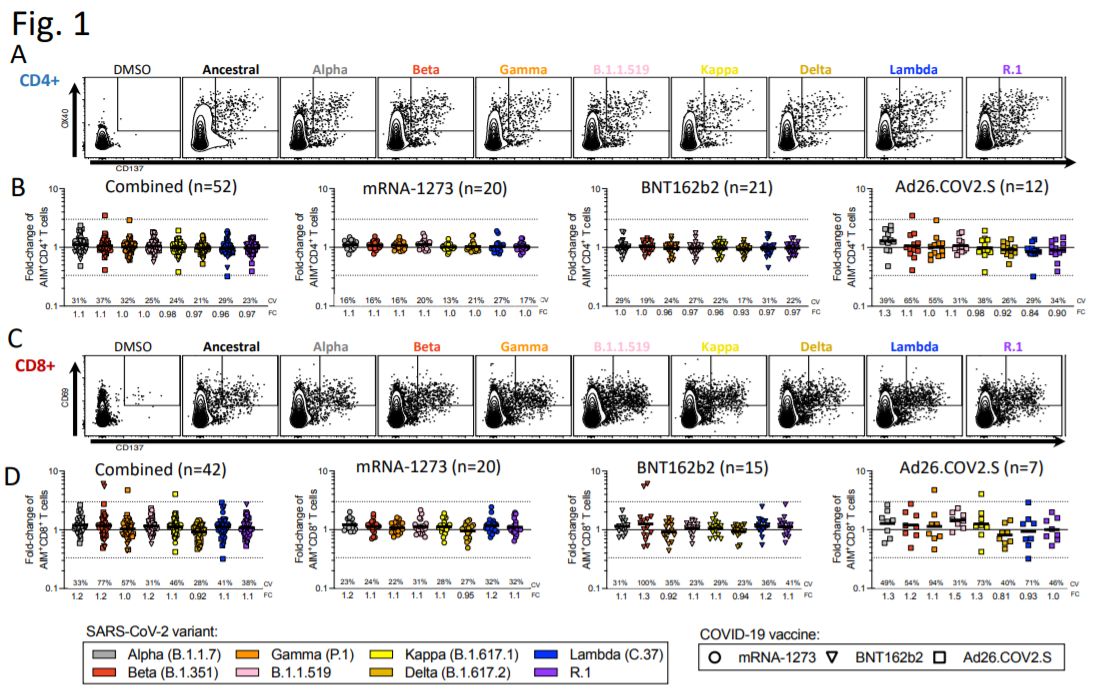
Figure 1. Impact of variant associated mutations on spike-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The Virus Monologues 2021. We describe T cell responses to #Omicron… Twitter 2021, posted 29 December. Link: https://twitter.com/virusmonologues/status/1476221654007173125
Excellent thread explaining T cell responses to the Omicron variant in people who received one or two injections of the J&J vaccine or two Pfizer doses. The authors show that despite Omicron’s reduced susceptibility to neutralizing antibodies, the majority of the T cell response, induced either by vaccination or by natural infection, cross-recognizes the Omicron variant. “Well-preserved T cell immunity to Omicron is likely to contribute to protection from severe COVID-19, supporting early clinical observations from South Africa.”
Keeton R, Tincho MB, Ngomti A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike T cell responses induced upon vaccination or infection remain robust against Omicron. medRxiv 2021, posted 28 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.26.21268380
The paper re: the Twitter thread above. While antibodies prevent the virus from growing and spreading, T cells kill infected cells and minimize tissue damage.
Figure from https://twitter.com/virusmonologues/status/1476221672495751173
Transmission
Mortensen LH, Denwood MJ, Christiansen LE, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC Transmission in Danish Households. medRxiv 2021, posted 27 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.27.21268278
Strong evidence of immune evasiveness of the Omicron variant. When comparing households infected with the Omicron vs the Delta VOC, the authors found a 1.17 times higher secondary attack rate (SAR) for those unvaccinated, 2.61 times higher for those fully vaccinated and 3.66 times higher for booster-vaccinated individuals.
30 December
Vaccines
Lu L, Mok BWY, Chen L, et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by sera from BNT162b2 or Coronavac vaccine recipients. medRxiv 2021, posted 14 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.13.21267668
Bad news for the Coronavac vaccine. When testing the neutralization susceptibility of different variants (including Omicron) to sera from 25 Pfizer vaccine and 25 Coronavac vaccine recipients, only 20% and 24% of the Pfizer vaccine recipients had detectable neutralizing antibody against two Omicron variants, respectively. Importantly, none of the Coronavac recipients had detectable neutralizing antibody titers against the Omicron isolates. If the Chinese lockdown measures don’t work against Omicron, the country may be in trouble.
Saksela K, Mäkelä A, Ugurlu H, et al. Intranasal inhibitor blocks omicron and other variants of SARS-CoV-2. Research Square 2021, posted 28 December. https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1196079/v1
The authors describe a human nephrocystin SH3 domain-derived antibody mimetic targeted against a conserved region in the receptor-binding domain of the Spike which neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 and its variants of concern, including Delta and Omicron.
Epidemiology
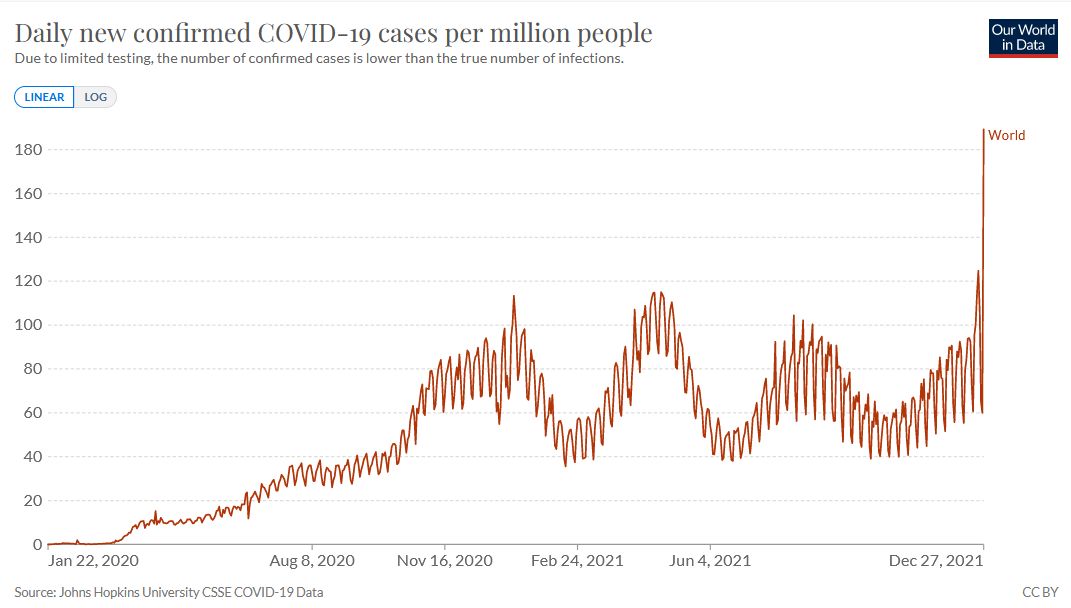
Our World in Data 2021. World. Daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases per million people. https://bit.ly/3FH2OL6
Omicron is different.
Immunology
Sun J, Zheng Q, Madhira V, et al. Association Between Immune Dysfunction and COVID-19 Breakthrough Infection After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in the US. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Dec 28. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34962505. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.7024
Persons with immune dysfunction (i.e., HIV infection, rheumatoid arthritis, and solid organ transplant) may have higher rates for COVID-19 breakthrough infections and worse outcomes after full or partial vaccination, compared to persons without immune dysfunction. The authors suggest that these persons “should use non-pharmaceutical interventions (eg, mask wearing) and alternative vaccination approaches (eg, additional dose or immunogenicity testing) even after full vaccination.”
Transmission
Jansen L, Tegomoh B, Lange K, et al. Investigation of a SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant Cluster — Nebraska, November–December 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 28 December 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm705152e3
Transmission of the Omicron variant to 5 (all!) household numbers, most previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. None required hospitalization.
Pediatrics
Ryan L, Plötz FB, van den Hoogen A, et al. Neonates and COVID-19: state of the art : Neonatal Sepsis series. Pediatr Res. 2021 Dec 28. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34961785. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01875-y
Read about proportionately higher SARS-CoV-2 infection in premature neonates, long-term data on outcomes for affected babies, recommendations for reduction of viral transmission to neonates, and the negative impact of severe visitation restrictions implemented early in the pandemic.
29 December
Vaccines
ICNARC 20211224. ICNARC report on COVID-19 in critical care: England, Wales and Northern Ireland. Published 24 December 2021. https://www.icnarc.org/Our-Audit/Audits/Cmp/Reports
Data from the pre-Omicron world showing that 60- to 70-year-old double-vaccinated people had a 60-fold lower risk of ending up in intensive care compared to unvaccinated people (37.3 per 100,000, compared to 0.6 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per week among those who were vaccinated).
Hansen CH, Schelde AB, Mousten-Helm IR, et al. Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Omicron or Delta variants. medRxiv 2021, posted 22 December. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.20.21267966
In this pre-print from Denmark, vaccine efficacy (VE) against the Omicron variant of 55.2% and 36.7% for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, respectively, in the first month after primary vaccination. The VE rapidly declined over just a few months. VE was re-established upon re-vaccination with the Pfizer vaccine.
Gruell H, Vanshylla K, Tober-Lau P, et al. mRNA booster immunization elicits potent neutralizing serum activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Research Square 2021, posted 27 December. https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1168453/v1
mRNA booster immunizations are critical, even in vaccinated and convalescent individuals. The authors report a near-complete lack of neutralizing activity against Omicron after two doses, whereas mRNA booster immunizations (a third dose) resulted in a significant increase of serum neutralizing activity against Omicron.
Pathogenesis
Abdelnabi R, Fo CSY, Zhang X, et al. The omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern does not readily infect Syrian hamsters. bioRxiv 2021, posted 26 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.24.474086
In the Syrian hamster model, with the Omicron variant, a 3 log10 lower viral RNA load was detected in the lungs as compared to animals infected with D614G, and no infectious virus was detectable in the lungs. In this model, no signs of peri-bronchial inflammation or bronchopneumonia.
Immunology
Khan K, Karim F, Cele S, et al. Omicron infection enhances neutralizing immunity against the Delta variant. Preprint, posted 27 December 2021. https://secureservercdn.net/50.62.198.70/1mx.c5c.myftpupload.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/MEDRXIV-2021-268439v1-Sigal.pdf
Omicron infection might enhance neutralizing immunity against the Delta variant, especially in individuals who were vaccinated. If Omicron is less pathogenic than Delta, it could help decrease severe disease from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
28 December
Vaccines
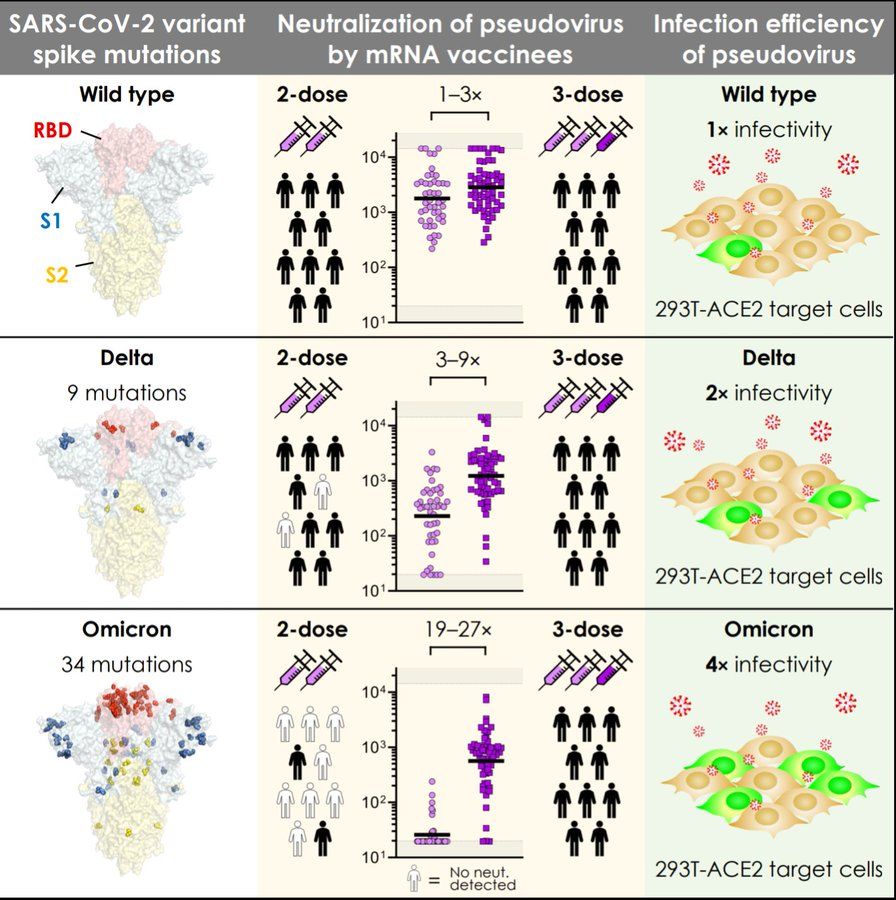
Garcia-Beltran WF, St Denis KJ, Hoelzemer A, et al. mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell 2021, 23 December. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01496-3
Paper describing the importance of COVID-19 vaccine boosters. Three mRNA vaccine doses elicit potent variant cross-neutralization, including Omicron.
Graphical abstract:
Immunology
Wolter N, Jassat W, Walaza S, et al. Early assessment of the clinical severity of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in South Africa. medRxiv 2021, posted 21 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.21.21268116
Early analyses suggesting a reduced risk of hospitalization and severe disease among probable Omicron cases in South Africa. It is not yet clear if these results will be reproduced in countries with older populations (mean age in South Africa: 28 years; in Germany: 46 years).
Meng B, Ferreira IATM, Abdullahi A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike mediated immune escape, infectivity and cell-cell fusion. bioRxiv 2021, posted 21 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.17.473248
Tentative evidence for reduced severity of Omicron infections: reduced spike cleavage efficiency, lower infectivity of lung cells, impaired ability to form syncytia, etc.
Epidemiology
ONS 20211224. Interim results from the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Infection Survey, UK: 24 December 2021. Office for National Statistics 2021, published 24 December. https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/conditionsanddiseases/bulletins/coronaviruscovid19infectionsurveypilot/24december2021
Omicron in the UK: Interim data showing that between 13 and 19 December 2021, in England, the percentage of people testing positive for coronavirus was 2.83% for a total of 1,544,600 people having COVID-19, equating to around 1 in 35 people. Find also the data for Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales.
Beyond COVID
Editors. Nature’s 10. Ten people who helped shape science in 2021. Nature 2021, published 15 December. https://www.nature.com/immersive/d41586-021-03621-0/index.html
Some of the people behind the year’s biggest research stories, including an Omicron investigator and a Mars explorer | Winnie Byanyima: Vaccine warrior | Friederike Otto: Weather detective | Zhang Rongqiao: Mars explorer | Timnit Gebru: AI ethics leader | Tulio de Oliveira: Variant tracker | John Jumper: Protein predictor | Victoria Tauli-Corpuz: Indigenous defender | Guillaume Cabanac: Deception sleuth | Meaghan Kall: COVID communicator | Janet Woodcock: Drug chief
27 December
Vaccines
Maimon N, Mizrahi A, Belbshtein U, et al. Effects of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine Booster in Long-Term Care Facilities in Israel. N Engl J Med 2021, published 22 December. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2117385
In July 2021, during a surge in COVID-19 cases in Israel, booster injections of the Pfizer vaccine were rapidly deployed in long-term care facilities. Compared to people 60 years of age or older in the general population, infection rates in long-term care facilities decreased by 71%, and hospitalization rates fell by 80%.
Jyssum I, Kared H, Tran TT, et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses to two and three doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in rituximab-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective, cohort study. Lancet 2021, published 23 December. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00394-5
in rituximab-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis, there may be a divergent humoral and cellular response to two and three doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. The authors found that 53% of patients had CD4+ T cell responses and 74% had CD8+ T cell responses after two vaccine doses. They conclude that even if a third vaccine dose given 6–9 months after a rituximab infusion might not induce a serological response, it could be considered to boost the cellular immune response.
Lacy J, Pavord S, Brown KE. VITT and Second Doses of Covid-19 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2021, published 22 December. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2118507
No recurrence of AstraZeneca vaccine-induced VITT (vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia) in 40 persons who were given a second dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, generally the Pfizer vaccine BNT162b2.
Halperin SA, Ye L, MacKinnon-Cameron D, et al. Final efficacy analysis, interim safety analysis, and immunogenicity of a single dose of recombinant novel coronavirus vaccine (adenovirus type 5 vector) in adults 18 years and older: an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, published 23 December. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02753-7
Final efficacy and interim safety analysis of the Phase III trial of a the Ad5-nCoV vaccine by CanSino Biologics and the Beijing Institute of Biotechnology. Vaccine efficacy against severe disease exceeded 90% in the study population.
Treatment
ACTIV-3/Therapeutics for Inpatients with COVID-19 (TICO) Study Group. Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, published 23 December. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00751-9
A total of 546 patients randomly assigned to sotrovimab (n = 184), BRII-196 plus BRII-198 (n = 183), or placebo (n = 179). Neither sotrovimab (Vir Biotechnology and GlaxoSmithKline) nor BRII-196 plus BRII-198 (Brii Biosciences) showed efficacy for improving clinical outcomes among adults hospitalized with COVID-19.
25 December
Immunology
Planas D, Maes P, Guivel-Benhassine F, et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, published 23 December. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03827-2
The authors examined the sensitivity of Omicron to 9 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) clinically approved or in development, and to antibodies present in 115 sera from COVID-19 vaccine recipients or convalescent individuals. Omicron was totally or partially resistant to neutralization by all mAbs tested. Read more about 1) sera from Pfizer or AstraZeneca vaccine recipients, 2) sera from COVID-19 convalescent patients collected 6 or 12 months post symptoms and 3) neutralizing response after administration of a booster Pfizer dose and of previously-infected individuals.
Mudd PA, Minervina AA, Pogorelyy MV, et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits a robust and persistent T follicular helper cell response in humans. Cell 2021, published 22 December. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01489-6
Robust TFH cell responses play a key role in establishing robust long term immunity via the Pfizer vaccine and will probably help to prevent severe disease from all variants, including Omicron.
Thorne LG, Bouhaddou M, Reuschl AK, et al. Evolution of enhanced innate immune evasion by SARS-CoV-2. Nature (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04352-y
The authors found that the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant increased sub-genomic RNA and protein levels of N, Orf9b and Orf6, all known innate immune antagonists.
Epidemiology
Hale VL, Dennis PM, McBride DS, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04353-x
SARS-CoV-2 virus was detected by rRT-PCR in more than one-third (129/360, 35.8%) of nasal swabs obtained from free-ranging white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in northeast Ohio (USA) during January-March 2021. Deer in 6 locations were infected with 3 SARS-CoV-2 lineages (B.1.2, B.1.582, B.1.596).
Clinical
Public Health England 20211223. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England| Technical briefing 33. UK Government 2021, 23 September. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1043807/technical-briefing-33.pdf
Vaccine efficacy (VE) was ~70% 1 week after a Pfizer booster, dropping to ~45% after 10+ weeks. VE after a Moderna (mRNA-1273) booster stayed around 70-75% up to 9 weeks after the booster.
24 December
Vaccines
Madelon N, Heikkila N, Sabater Royo I, et al. Omicron-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses are boosted following a third dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in anti-CD20-treated multiple sclerosis patients. medRxiv 2021, posted 21 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.20.21268128
A small study of 20 adults with multiple sclerosis on anti-CD20 treatment (ocrelizumab) who received a third dose of a mRNA COVID-19 vaccine 6 to 7 months after their second vaccination: a third vaccine dose might improve cytotoxic T cell mediated protection against severe disease in those with low humoral response.
Clinical
ICL 2021. Report 50 – Hospitalisation risk for Omicron cases in England. Imperial College London 2021, 22 December. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-global-infectious-disease-analysis/covid-19/report-50-Severity-Omicron
Estimates of the Imperial College London suggest Omicron cases, compared to Delta, could be 20% to 25% less likely to attend hospital, and 40% to 45% less likely to be hospitalized for a night or more.
See also the article published by The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/dec/22/risk-of-hospital-stay-40-lower-with-omicron-than-delta-uk-data-suggests
Immunology beyond COVID
Lee JH, Sutton HJ, Cottrell CA, et al. Long-lasting germinal center responses to a priming immunization with continuous proliferation and somatic mutation. bioRxiv 2021, posted 21 December. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.20.473537
Germinal centers (GC) are the engines of antibody evolution. Here, HIV Env protein immunogen priming was used in rhesus monkeys followed by a long period without further immunization. The authors demonstrate that GC B cells lasted at least 6 months.
Treatment
FDA 2021. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes First Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19. U. S. Food and Drug Administration 2021, published 22 December. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-first-oral-antiviral-treatment-covid-19
FDA emergency use authorization (EUA) for Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir) for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients > 12 years of age who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
Kozlov M. Omicron overpowers key COVID antibody treatments in early tests. Nature 2021, published 21 December. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03829-0
Nearly all anti-COVID monoclonal antibodies are facing an uncertain future with Omicron.
Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE,Paredes R, et al. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients. N Engl J Med 2021, published 22 December. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
A small trial of non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who had symptom onset within the previous 7 days and who had at least one risk factor for disease progression (age ≥ 60 years, obesity, or certain co-existing medical conditions; 279 in the remdesivir group and 283 in the placebo group). COVID-19–related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 2 patients (0.7%) in the remdesivir group and in 15 (5.3%) in the placebo group. After approval of Paxlovid (see https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-first-oral-antiviral-treatment-covid-19), there may be few medical indications for a drug like remdesivir that needs to be administered intravenously.
Graph of the Day
Suliman R. Update of key COVID-19 metrics in Gauteng, South Africa. Twitter 2021, posted 22 December. https://twitter.com/rid1tweets/status/1473733362644885505/photo/1
- Cases and test positivity declining
- Cases trajectory halving time about 5.5 days
- Hospital admissions at or passed its peak
- Deaths rising, but much lower relative to previous wave (~14%)
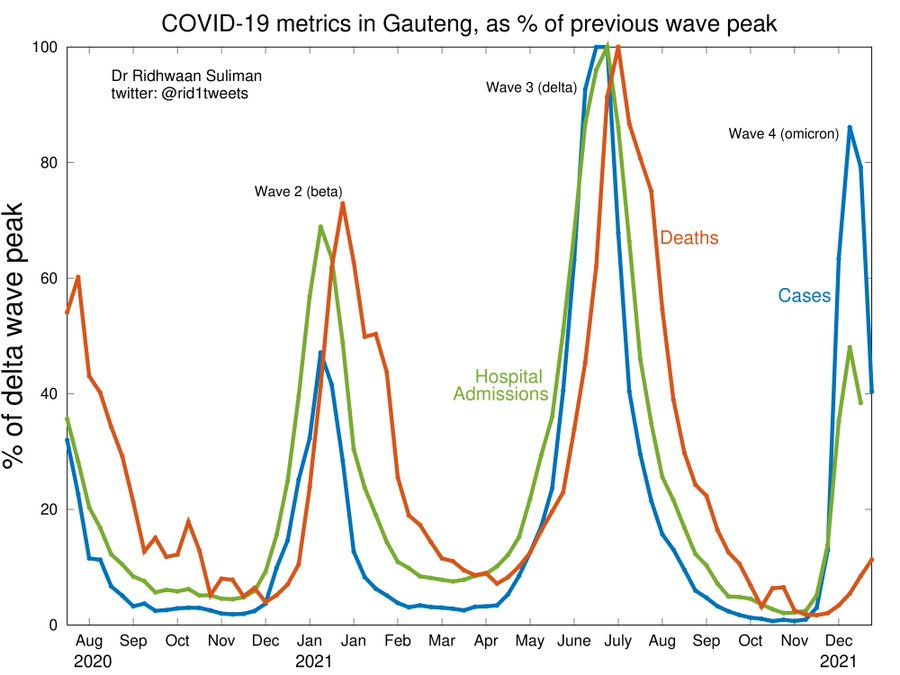
23 December
Transmission
SachdeV DD, Ng RC, Sankaran M, et al. Contact tracing outcomes among household contacts of fully vaccinated COVID-19 patients — San Francisco, California, January 29-July 2, 2021. Clin Inf Dis 20 December 2021, ciab1042, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab1042/6470866
Overall transmission from a symptomatic fully vaccinated patient with breakthrough infection to household contacts was suspected in 14 of 105 (13%) of households. Viral genomic sequencing of samples from 44% of fully vaccinated patients showed that 82% of those sequenced were infected by a variant of concern or interest.
Andrejko KL, Pry J, Myers JF, et al. Predictors of SARS-CoV-2 infection following high-risk exposure. Clin Inf Dis December 21, 2021, ciab1040. https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab1040/6473597?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Adjusted odds of case status were 3.0-fold higher when high-risk exposures occurred with household members (vs. other contacts), 2.1-fold higher when exposures occurred indoors (vs. outdoors only), and 2.15-fold higher when exposures lasted ≥ 3 hours (vs. shorter durations) among unvaccinated and partially-vaccinated individuals.
Vaccine
Lewus NM, Naioto EA, Self WH, et al. Effectiveness of mRNA vaccines in preventing COVID-19 hospitalization by age and burden of chronic medical conditions among immunocompetent US adults, March–August 2021. J Inf Dis December 21, 2021, jiab619, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab619/6472998
Vaccine effectiveness (VE) against COVID-19-associated hospitalization decreases roughly proportionally to the number of chronic medical conditions, both overall and stratified by age. In this case-control study in 1669 hospitalized COVID-19 cases (11% fully vaccinated) and 1950 RT-PCR-negative controls (54% fully vaccinated), VE was higher at 96% among patients with no chronic medical conditions than patients with ≥ 3 chronic conditions (83%).
Chun JY, Park S, Jung J, et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome after vaccination against COVID-19. Lancet Neurology December 17, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00416-6
Two older women in remission from diffuse large B cell lymphoma developed Guillain-Barré syndrome after receiving the BNT162b2 vaccine. However, it remains unclear whether this was coincidental.
Collateral damage
Geric C, Saroufi M, Landsman D, et al. Impact of Covid-19 on Tuberculosis Prevention and Treatment in Canada: a multicentre analysis of 10,833 patients. J Inf Dis December 21, 2021, jiab608, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab608/6469005
Reductions in latent tuberculosis infection treatment initiation rates ranged from 30% to 66%.
Treatment
ACTIV-3/TICO Bamlanivimab Study Group. Responses to a Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 According to Baseline Antibody and Antigen Levels. Annals Int Med 21 December 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-3507
Preliminary results of the ACTIV-3 (aka TICO) trial of bamlanivimab in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 were reported after enrollment was terminated because futility guidelines were met. This sub-analysis suggests that the efficacy and safety of bamlanivimab may differ depending on whether an endogenous nAb response is mounted: the authors found a positive trend for recovery for the bamlanivimab group among the subset of patients (50% of total) without nAbs at study entry and a trend in the opposite direction for those with nAbs.
22 December
Virology
Wang Y, Xu C, Wang Y, et al. Conformational dynamics of the Beta and Kappa SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins and their complexes with ACE2 receptor revealed by cryo-EM. Nat Commun December 2021, 12, 7345. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27350-0
More on immune evasion mechanism of variants. This structural study shows that two variants are enabled to efficiently interact with ACE2 receptor despite their sensitive ACE2 binding surface is modified to escape recognition by some potent neutralizing MAbs.
Vaccine
Katikireddi SV, Cerqueira-Silva T, Vasileiou E et al. Two-dose ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine protection against COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths over time: a retrospective, population-based cohort study in Scotland and Brazil. Lancet December 20, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02754-9/fulltext
Waning vaccine protection of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 against COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths became evident within three months of the second vaccine dose.
Variants
Riou C, Keeton R, Moyo-Gwete T. Escape from recognition of SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant spike epitopes but overall preservation of T cell immunity. Science Translational Medicine December 21, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj6824
This study shows that in spite of loss of recognition of immunogenic CD4 epitopes, CD4 and CD8 T cell responses to Beta are preserved overall. These observations may explain why several vaccines have retained the ability to protect against severe COVID-19 even with substantial loss of neutralizing antibody activity against Beta.
Pediatrics
Ward JL, Harwood R, Smith C, et al. Risk factors for PICU admission and death among children and young people hospitalized with COVID-19 and PIMS-TS in England during the first pandemic year. Nat Med December 21, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01627-9
In the rare instances when children and young people did require hospitalization, risk factors for severe disease were similar to those reported for adults.
Kugelman N, Nahshon C, Shaked-Mishan P, et al. Maternal and Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin G Antibody Levels at Delivery After Receipt of the BNT162b2 Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccine During the Second Trimester of Pregnancy. JAMA Pediatr December 21, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2787270?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 130 pregnant women who received the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine during their second trimester, antibody titers were positive for all women during delivery, and neonatal titers were higher than maternal titers, representing 100% placental antibody transfer.
21 December
Diagnostics
Harris-McCoy K, Lee VC, Munna C, Kim AA. Evaluation of a Test to Stay Strategy in Transitional Kindergarten Through Grade 12 Schools — Los Angeles County, California, August 16–October 31, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 17 December 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm705152e1.htm?s_cid=mm705152e1_w
The Test to Stay (TTS) strategy enables unvaccinated students, exposed in school to a person infected with SARS-CoV-2, to remain in school while under quarantine, if both the infected person and the exposed person wore masks correctly and consistently throughout the exposure. Among LAC schools that implemented TTS, COVID-19 incidence did not increase, and tertiary transmission was not identified in school outbreaks after TTS implementation. Non-TTS districts lost substantial in-person school days.
Nemoto N, Dhillon S, Fink S, et al. Evaluation of Test to Stay Strategy on Secondary and Tertiary Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in K–12 Schools — Lake County, Illinois, August 9–October 29, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 17 December 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm705152e2.htm?s_cid=mm705152e2_w
Same. TTS allows close contacts to remain in the classroom as an alternative to home quarantine. Among 1,035 participants, 16 secondary cases were identified, all of whom were in students. None of the 16 secondary cases appeared to transmit SARS-CoV-2 to other school-based contacts (but nine tertiary cases in five households). Let’s hope that this works with Omicron.
Co-morbidities
Reindl-Schwaighofer R, Heinzel A, Mayrdorfer M, et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response 4 Weeks After Homologous vs Heterologous Third Vaccine Dose in Kidney Transplant Recipients A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med, December 20, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2787200?resultClick=1
Among 197 kidney transplant recipients, 39% developed SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after the third vaccine. There was no statistically significant difference between groups, with an antibody response rate of 35% and 42% for the mRNA and the Ad26COVS1 (Janssen) vaccines, respectively.
Treatment
Ramacciotti E, Barile Agati L, Calderano D, et al. Rivaroxaban versus no anticoagulation for post-discharge thromboprophylaxis after hospitalisation for COVID-19 (MICHELLE): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet December 15, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02392-8/fulltext
In this open-label RCT in Brazil, patients hospitalised with COVID-19 „at increased risk for venous thromboembolism (IMPROVE score of ≥4 or 2-3 with a D-dimer >500 ng/mL)“ were randomly assigned to receive, at hospital discharge, rivaroxaban 10 mg/day or no anticoagulation for 35 days. Thromboembolism occurred in five (3%) of 159 patients assigned to rivaroxaban and 15 (9%) of 159 patients assigned to no anticoagulation (relative risk 0.33, p=0.03).
Pediatrics
Levy M, Recher M, Hubert H, et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children by COVID-19 Vaccination Status of Adolescents in France. JAMA December 20, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2787495?resultClick=1
Most adolescents (26/33) with MIS-C for whom vaccination was indicated in France had not been vaccinated. Among the 7 cases who had received a vaccine, none was fully vaccinated.
20 December
Vaccine
Joyce MG, King HA, Elakhal-Naouar I, et al. SARS-CoV-2 ferritin nanoparticle vaccine elicits protective immune responses in nonhuman primates. Science Translational Medicine, December 16, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abi5735
Ferritin is a naturally occurring, iron-carrying protein. Its polymers are conducive to conjugation and antigen display of trimeric glycoproteins, such as SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The authors developed an adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 spike ferritin nanoparticle vaccine that elicited potent humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in non-human primates.
Pérez-García F, Martin-Vicente M, Rojas-García RL, et al. High SARS-CoV-2 viral load and low CCL5 expression levels in the upper respiratory tract are associated with COVID-19 severity. Journal of Infectious Diseases, December 15, 2021, jiab604, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab604/6463312
The authors analyzed the SARS-CoV-2 RNA load and the expression of selected immune genes in the nasopharynx of 255 SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. High SARS-CoV-2 viral load and low CCL5 expression levels were associated with severe disease. CCL5 was the best predictor of COVID-19 severity.
Variants
Lyngse FP, Mølbak K, Skov RL, et al. Increased transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 by age and viral load. Nat Commun December 13, 2021, 12, 7251. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27202-x
Primary cases infected with B.1.1.7 (Alpha) had an increased transmissibility of 1.5–1.7 times that of primary cases infected with other lineages. The increased transmissibility of B.1.1.7 is multiplicative across age and viral load.
Treatment
Fisher BA, Veenith T, Slade D, et al. Namilumab or infliximab compared with standard of care in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (CATALYST): a randomised, multicentre, multi-arm, multistage, open-label, adaptive, phase 2, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet Resp Med December 16, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00460-4/fulltext
Dysregulated inflammation is associated with poor outcomes in COVID-19. In this Phase II RCT, 146 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 were randomly assigned to usual care, namilumab (a granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor inhibitor) and infliximab (a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor). The addition of namilumab, but not infliximab, to usual care reduced inflammation as measured by CRP concentration.
Pediatrics
Bundle N, Dave N, Pharris A, et al. COVID-19 trends and severity among symptomatic children aged 0–17 years in 10 European Union countries, 3 August 2020 to 3 October 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(50):pii=2101098. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.50.2101098
Among a total of 820,404 symptomatic pediatric cases (12.4% of all ages), hospitalization was reported for 9611 (1.2%) cases, ICU admission for 640 (0.08% of all cases, 6.7% of hospitalized cases) and death for 84 (0.01%). The adjusted odds of hospitalization, ICU admission and death were seven, nine and 27 times higher, respectively, among cases with at least one co-morbidity compared with those with none.
Hoste L, Roels L, Naesens L, et al. IFNγ characterizes immunodysregulation in MIS-C. J Exp Med December 16, 2021. https://rupress.org/jem/article/219/2/e20211381/212918/TIM3-TRBV11-2-T-cells-and-IFN-signature-in?searchresult=1
In rare instances, pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection results in a novel immunodysregulation syndrome termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). This comprehensive study on 14 MIS-C cases employs a multi-omics approach to explore its immunopathogenesis, showing that IFNγ-mediated interactions between T cells, monocytes, and NK cells reside at the heart of the disease.
19 December
Immunology
Chen JS, Chow RD, Song E, et al. High-affinity, neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 can be made without T follicular helper cells. Science Immunology, December 16, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl5652
While protective antibodies are generally thought to originate from pathways depending on T follicular helper/germinal center cells, it is unclear what happens to the antibody response when these structures are disrupted, as observed in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. The authors found that certain class-switched antibodies were reduced but still present in Tfh-deficient mice following SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination.
Afzali B, Noris M, Lambrecht BN, et al. The state of complement in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol December 15, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41577-021-00665-1
Uncontrolled activity of the complement system may be a central player in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. This brilliant review summarizes current knowledge on the contributions of complement following SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as its crosstalk with the coagulation system.
Variants
Pan T, Chen R, He X, et al. Infection of wild-type mice by SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 variant indicates a possible novel cross-species transmission route. Sig Transduct Target Ther, December 14, 2021, 6, 420. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00848-1
This work suggests that B.1.351 (Beta) expands the host range to wild type mice and therefore increases its transmission route without adapted mutation. As the wild house mice live with human populations quite closely, this possible transmission route may be potentially risky.
Dorp CH v, Goldberg EE, Hengartner N, et al. Estimating the strength of selection for new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Commun December 14, 2021, 12, 7239. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27369-3
The authors present two models for quantifying the strength of selection for new and emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2 relative to the background of contemporaneous variants.
Clinical
He X, Liu C, Peng J, et al. COVID-19 induces new-onset insulin resistance and lipid metabolic dysregulation via regulation of secreted metabolic factors. Sig Transduct Target Ther 6, 427 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00822-x
New-onset insulin resistance, elevated blood glucose, as well as reduced HDL-C in COVID-19 patients, which persists even after virus elimination. It is shown that SARS-CoV-2 infection increases the expression of RE1-silencing transcription factor (REST), which modulates the expression of secreted metabolic factors including myeloperoxidase, apelin, and myostatin at the transcriptional level, resulting in the perturbation of glucose and lipid metabolism.
Co-morbidities
Anand S, Montez-Rath ME, Jan J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Antibody Response and Breakthrough Infection in Patients Receiving Dialysis. Ann Int Med December 14, 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-4176
The antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination wanes rapidly in persons receiving dialysis. Among 2563 vaccinated patients, the estimated proportion with an undetectable RBD response increased from 6.6% 14 to 30 days after vaccination to 20.2% 5 to 6 months after vaccination. Low values were associated with higher odds for breakthrough infection.
Collateral damages
Pawelczyk A, Kowalska M, Tylicka M, et al. Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic on the course and treatment of appendicitis in the pediatric population. Sci Rep December 14, 2021, 11, 23999. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03409-2
Data from Poland, suggesting that proper diagnosis of appendicitis was delayed during the pandemic.
18 December
Treatment
Bernal AJ, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al. Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. NEJM December 16, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Paper of the day: The first tablet for outpatients? This large Phase III RCT evaluating the safety and efficacy of treatment with molnupiravir started within 5 days of the onset of signs or symptoms in 1433 non-hospitalized adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. All were unvaccinated and had at least one risk factor for severe disease. The percentage of participants who were hospitalized or died through day 29 was lower with 5 days of molnupiravir treatment (6.8% vs. 9.7%). One death occurred in the treatment group, and nine among placebo recipients.
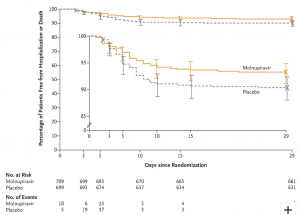
Whitley R. Molnupiravir — A Step toward Orally Bioavailable Therapies for COVID-19. NEJM December 16, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMe2117814
In his comment, Richard Whitley addresses several key questions on this new option, including potential mutagenicity and genotoxicity. However, “This clinical trial potentially provides a tool in the management of COVID-19”.
Immunology
Ubah OC, Lake EW, Gunaratne GS, et al. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by shark variable new antigen receptors elucidated through X-ray crystallography. Nat Commun 12, December 16, 2021, 7325. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27611-y
Learning from sharks. Single-domain Variable New Antigen Receptors (VNARs) from the immune system of sharks are the smallest naturally occurring binding domains found in nature. Their flexible paratopes can recognize protein motifs inaccessible to classical antibodies. This study shows that VNARs recognize separate epitopes on the RBD and have unique mechanisms of virus neutralization, suggesting that VNARs would be effective therapeutic agents.
Bates TA, McBride SK, Winders B, et al. Antibody Response and Variant Cross-Neutralization After SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infection. JAMA December 16, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2787447?resultClick=1
This study on 26 fully vaccinated health care workers subsequently diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 showed substantial boosting of humoral immunity after breakthrough infection, despite predominantly mild disease. Not surprisingly, boosting was most notable for IgA, possibly due to the differences in route of exposure between vaccination and natural infection.
Omicron
Lu L, Mok BW, Chen LL, et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by sera from BNT162b2 or Coronavac vaccine recipients. Clin Inf Dis, December 16, 2021, ciab1041. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab1041
Less than 25% of BNT162b2 recipients and no Coronavac recipients had detectable neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variant (all individuals had received two doses of COVID-19 vaccines, specimens were collected 56 days after the first dose).
Vaccine
Patone M, Mei XW, Handunnetthi L, et al. Risks of myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmias associated with COVID-19 vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med December 14, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01630-0
Using the English National Immunisation (NIMS) database of COVID-19, the authors estimate an extra two, one and six myocarditis events per 1 million people vaccinated with ChAdOx1, BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, respectively, in the 28 days following a first dose and an extra ten events per 1 million vaccinated in the 28 days after a second dose of mRNA-1273. This compares with an extra 40 myocarditis events per 1 million patients in the 28 days following a SARS-CoV-2 positive test. Subgroup analyses by age showed the increased risk of myocarditis associated with the two mRNA vaccines was present only in those younger than 40.
Husby A, Hansen JV, Fosbøl E, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and myocarditis or myopericarditis: population based cohort study. BMJ December 16, 2021; 375. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj-2021-068665
Same issue, Denmark. The absolute number of events were low. Even in the youngest age group (12-39 years), the absolute rates of myocarditis or myopericarditis were 1.6 (95% confidence interval: 1.0 – 2.6) and 5.7 (3.3 – 9.3) per 100,000 individuals within 28 days of BNT162b2 vaccination and mRNA-1273 vaccination, respectively. Clinical outcomes were predominantly mild.
17 December
Vaccine
Dunkle LM, Kotloff KL, Gay CL, et al. Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico. NEJM December 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116185?query=featured_home
A large Phase III RCT on NVX-CoV2373, the recombinant spike protein vaccine from Novavax. Over a period of 3 months, 14 cases were observed among vaccine recipients, versus 63 among placebo recipients (vaccine efficacy, 90.4%; 95% CI: 82.9 to 94.6). Ten moderate and 4 severe cases occurred, all in placebo recipients. Reactogenicity was mostly mild to moderate.
Young-Xu Y, Zwain GN, Powell EI, et al. Estimated Effectiveness of COVID-19 Messenger RNA Vaccination Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Older Male Veterans Health Administration Enrollees, January to September 2021. JAMA Netw Open December 15, 2021. 2021;4(12):e2138975. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2787183
The estimated pre-Delta mRNA vaccine effectiveness (VE) against any SARS-CoV-2 infection was 94.5% in the first month after complete vaccination and decreased to 87.9% by month 3. During the high-Delta period, the estimated VE was 62.0% in the first month and decreased to 57.8% by month 3.
Variants
Espenhain L, Funk T, Overvad M, et al. Epidemiological characterisation of the first 785 SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant cases in Denmark, December 2021. Eurosurveillance – Volume 26, Issue 50, 16 December 2021. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/eurosurveillance/26/50
A total of 599 (76%) cases were fully vaccinated and an additional 56 (7.1%) had received full vaccination plus a booster dose. A high attack rate was reported at one of the events, a seasonal gathering with 150 participants, where 71 (47%) participants got infected.
Brandal LT, MacDonaald E, Veneti L, et al. Outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in Norway, November to December 2021. Eurosurveillance Volume 26, Issue 50, 16/Dec/2021 https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.50.2101147
A Christmas party in a restaurant in Oslo, 26 November. Most of the cases (98%) and non-cases (93%) were fully vaccinated with a median time since having received the last vaccine dose of 79 days for cases and 87 days for non-cases. None reported having received a booster dose. Among the 81 cases, the most common symptoms were cough (83%), followed by runny/stuffy nose (78%), fatigue/lethargy (74%), sore throat (72%), headache (68%) and fever (54%), more than half of grades 3 or 4 (out of 5). By 13 December, the authors had detected nearly 70 other guests who were likely infected at the venue.
Chemaitelly H, Bertollini R, Abu-Raddad LJ, et al. Efficacy of Natural Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection with the Beta Variant. NEJM December 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2110300?query=featured_home
In this large national cohort from Qatar, protection by previous SARS-CoV-2 infection against reinfection with the Beta variant was slightly lower (92% versus 98%) than that against the Alpha variant and the wild-type virus.
Treatment
Ortigoza MB, Yoon H, Goldfeld KS, et al. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma in Hospitalized Patients A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med December 13, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2787090?resultClick=1
The primary outcome in this large RCT did not meet the prespecified definition for efficacy. However, exploratory subgroup analyses revealed a possible benefit in the early months of this trial (April-June 2020), when most received high-titer CCP, and most did not receive remdesivir and/or corticosteroids. “This supports the concept that convalescent plasma may be a feasible treatment option at the beginning of a pandemic or when other therapies are not in use or available” (hopefully, this has changed).
16 December
Coyer L, Boyd A, Schinkel J, et al. Differences in SARS-CoV-2 infections during the first and second wave of SARS-CoV-2 between six ethnic groups in Amsterdam, the Netherlands: A population-based longitudinal serological study. Lancet Regional Health December 13, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanepe/article/PIIS2666-7762(21)00270-2/fulltext
SARS-CoV-2 incidence was higher in the largest ethnic minority groups of Amsterdam, particularly during the second wave. Compared to participants of Dutch origin, cumulative SARS-CoV-2 incidence was higher in participants of South Asian Surinamese (adjusted hazard ratio = 1.66), African Surinamese (1.97), Turkish (2.67), Moroccan (3.13) and Ghanaian (6.00) origin.
Vaccine
Van Gils MJ, van Willigen HD, Wynberg E, et al. A Single mRNA vaccine dose in COVID-19 patients boosts neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Cell Rep December 13, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00358-X
See title. One week after the first vaccine dose, spike protein antibody levels are 27-fold higher and neutralizing antibody titers 12-fold higher, exceeding titers of fully vaccinated SARS-CoV-2-naive controls, with minimal additional boosting after the second dose. (Note: this study was done prior to Omicron).
Ruhl L, Pink I, Kühne JF, et al. Endothelial dysfunction contributes to severe COVID-19 in combination with dysregulated lymphocyte responses and cytokine networks. Sig Transduct Target Ther December 10, 2021, 6, 418. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00819-6
The first study showing that endothelial damage is another major driver of COVID-19 severity together with substantial immune dysregulation. Severe COVID-19 is not only characterized by a highly activated immune phenotype and pro-inflammatory cascades but also by substantial endothelial injuries, which may explain multiorgan involvement in these cases.
Clinical
Weckbach LT, Schweizer L, Kraechan A, et al. Association of Complement and MAPK Activation With SARS-CoV-2–Associated Myocardial Inflammation. Lancet Cardiology December 15, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2786891?resultClick=1
This case series of 19 patients undergoing endomyocardial biopsies found that the cardiac immune signature varied in inflammatory conditions with different etiologic characteristics. Inflammation was characterized by a cellular immune infiltrate that was dominated by macrophages expressing C1q and CD163. Deep phenotyping revealed substantial upregulation of MAPK-associated pathways as well as upregulation of the complement system.
Ma Q, Liu J, Liu Q, et al. Global Percentage of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among the Tested Population and Individuals With Confirmed COVID-19 Diagnosis. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open December 14, 2021;4(12):e2137257. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2787098?resultClick=1
40.5%. (among confirmed cases)
Long COVID
van der Togt V, Mcfarland S, Esperti M. et al. Promotion of non-evidence-based therapeutics within patient-led Long COVID support groups. Nat Med December 10, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01589-y
Important statement. “Long COVID patient support groups need to be aware that the promotion of non-evidence-based treatments is occurring within their groups and ensure the proper vetting and integrity of their membership”.
Co-morbidities
Konishi Y, Sklavenitis-Pistofidis R, Yue L, et al. Attenuated response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with asymptomatic precursor stages of multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Cancer Cell December 08, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(21)00615-2
The humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination is suboptimal, not only in patients with MM and other cancer patients receiving therapy but also in precursor asymptomatic patients, including low-risk smoldering MM. A third vaccine dose improved this attenuated response.
15 December
Another Omicron Special, a week later: the picture becomes clearer. And darker. But some glimmers of hope: three jabs may work and protect against symptomatic disease (75%), some trust in T cells, and sotrovimab as a treatment option. All papers today are only pre-prints, have not been peer-reviewed and were selected from a total of > 100 articles published through three pre-print servers medRxiv, BioRxiv and Arxiv. We have include the UKHSA report, including the first real-life data from the UK, as well as some early clinical data from Denmark.
Virology
Miller NL, Clark T, Raman R, et al. Insights on the mutational landscape of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. BioRxiv posted December 10, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.06.471499v2
The authors analyze and describe the receptor binding domain mutational landscape of the Omicron VOC using amino acid interaction networks.
Immunology
Redd AD, Nardin A, Kared H, et al. Minimal cross-over between mutations associated with Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 and CD8+ T cell epitopes identified in COVID-19 convalescent individuals. BioRxiv posted December 10, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.06.471446v1
T cells as our glimmer of hope. The authors investigated whether the parts of the virus, or epitopes, targeted by the CD8+ T cell response in thirty individuals who recovered from COVID-19 in 2020 were mutated in the Omicron variant. Only one of 52 epitopes identified in this population contained an amino acid that was mutated in Omicron. Conclusion: virtually all individuals with existing anti-SARS-CoV-2 CD8+ T cell responses should recognize Omicron, and SARS-CoV-2 has not evolved extensive T cell escape mutations at this time.
Immune escape (lab data)
Cao Y, Wang J, Jian F, et al. B.1.1.529 escapes the majority of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies of diverse epitopes. BioRxiv posted December 10, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.07.470392v1
Forget most antibodies. Omicron escapes over 85% of NAbs tested. Regarding NAb drugs, Omicron is able to escape the NAb cocktails from Lilly, Regeneron, AstraZeneca, as well as BRII-196, while sotrovimab (VIR7831) and DXP-604 still function (at a reduced efficacy).
Cathcart AL, Havenar-Daughton C, Lempp FA, et al. The dual function monoclonal antibodies VIR-7831 and VIR-7832 demonstrate potent in vitro and in vivo activity against SARS-CoV-2. BioRxiv posted December 7, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.03.09.434607v9
VIR-7831 (sotrovimab) and VIR-7832 are dual action monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2. Both potently neutralize variant pseudotyped viruses including Omicron.
Wilhelm A, Widera M, Grikscheit K, et al. Reduced Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant by Vaccine Sera and Monoclonal Antibodies. MedRxive, posted December 11, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.07.21267432
Data from Sandra Ciesek’s lab. Neutralization of Omicron was 32.8-fold reduced using sera from double BNT162b2-vaccinated and previously SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. Omicron was resistant to casirivimab and imdevimab.
Roessler A, Riepler L, Bante D, et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 variant (Omicron) evades neutralization by sera from vaccinated and convalescent individuals. MedRxive, December 11, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.08.21267491
Same direction: in this study from Austria, sera from vaccinated individuals neutralized Omicron to a much lesser extent than any other variant analyzed. Neutralization capacity was maintained best against sera from super immune individuals (infected and vaccinated or vaccinated and infected).
Dejnirattisai W, Shaw RH, Supasa P, et al. Reduced neutralisation of SARS-COV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 variant by post-immunisation serum. MedRxive, posted on December 11, 2021. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.10.21267534v1
Same again: in this study from Oxford, a substantial fall in neutralization titers was seen in recipients of both AZD1222 and BNT162b2 primary courses, with evidence of some recipients failing to neutralize at all.
Cele S, Jackson L, Khan K, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron has extensive but incomplete escape of Pfizer BNT162b2 elicited neutralization and requires ACE2 for infection. MedRxive, posted on December 11, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.08.21267417
Is protection against severe disease maintained? Possibly: in 5 out of 6 of previously-infected, Pfizer-vaccinated individuals, all of them with high neutralization of D614G virus, showed residual neutralization at levels expected to confer protection from infection and severe disease.
Real-life data
UK Health Security Agency. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England. Technical briefing 31, December 10, 2021. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1040076/Technical_Briefing_31.pdf
The main findings: the household secondary attack rate using routine contact tracing data is 21.6% (95% CI: 16.7%-27.4%) for Omicron, versus 10.7% (95% CI: 10.5%-10.8%) for Delta. Vaccine effectiveness was estimated by period after dose 2 and dose 3. The final analysis included 56,439 Delta and 581 Omicron cases. In all periods, effectiveness was lower for Omicron compared to Delta. From 2 weeks after a Pfizer booster dose, vaccine effectiveness was 71% among those who received AstraZeneca as the primary course and around 76% among those who received Pfizer as the primary course.
Statens Serum Institut. Rapport om omikronvarianten. December 13, 2021. https://www.ssi.dk/-/media/cdn/files/covid19/omikron/statusrapport/rapport-omikronvarianten-13122021-i30w.pdf?la=da
Is it milder?
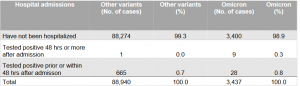
Number and proportion of omicron-related hospitalizations compared to other variants, from 22 November 2021 to 12 December 2021
Check your country
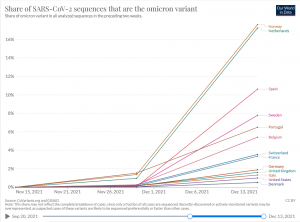
(Only a fraction of all cases are sequenced. Omicron may be overpresented)
14 December
Immunology
Girona-Alarcon M, Argüello G, Esteve-Sole A, et al. Low levels of CIITA and high levels of SOCS1 predict COVID-19 disease severity in children and adults. iScience December 08, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01565-0
In this prospective observational study in 84 patients, those with severe disease had an elevated cytokine pattern, which correlated with the IFN response, with low CIITA (part of the IFN-stimulated immune response) and high SOCS1 values.
Nesterenko PA, McLaughlin J, Tsai BL, et al. HLA-A∗02:01 restricted T cell receptors against the highly conserved SARS-CoV-2 polymerase cross-react with human coronaviruses. Cell Rep December 09, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01667-3
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp/NSP12) is highly conserved likely due to its critical role in the virus life cycle. The authors perform single-cell sequencing in RdRp-specific T cells from SARS-CoV-2 unexposed individuals and found that these CD8+ T cells can recognize evolutionarily diverse coronaviruses.
Virology
Zickler N, Stabelle-Bertram S, Ehret S, et al. Replication of SARS-CoV-2 in adipose tissue determines organ and systemic lipid metabolism in hamsters and humans. Cell Metabolism December 10, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(21)00621-5
SARS-CoV-2 was found in at least one adipose tissue depot in 10 of 18 male individuals who died from COVID-19. Although the study was not sufficiently powered, it is of note that the virus was found only in adipose tissue in those who were overweight or obese.
Variants
SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant — United States, December 1–8, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 10 December 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7050e1
During December 1–8, 2021, 22 US states reported at least one COVID-19 case attributed to the Omicron variant. Among 43 cases with follow-up, one hospitalization and no deaths were reported.
Diagnostics
Bruneau R, Wack, Poulet G, et al. Circulating ubiquitous RNA, a highly predictive and prognostic biomarker in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Clinical Infectious Diseases 11 December 2021, ciab997, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab997
This study quantified SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia and the plasmatic release of an ubiquitous human intracellular marker, the ribonuclease P (RNase P) in 139 COVID-19 hospitalized patients on admission. Both blood biomarkers correlated with disease severity.
13 December
Virology
Zimmer MM, Kibe A, Rand U, et al. The short isoform of the host antiviral protein ZAP acts as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 programmed ribosomal frameshifting. Nat Commun December 10, 2021, 12, 7193 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27431-0
Programmed ribosomal frameshifting (–1PRF) is essential for coronavirus replication. This study explored whether trans-acting host or viral factors can modulate SARS-CoV-2 –1PRF. The short isoform of the interferon-induced zinc-finger antiviral protein ZAP-S can strongly impair SARS-CoV-2 frameshifting and decrease viral replication. ZAP-S was also one of the prominent common hits in genome-wide screens for proteins that interacted with SARS-CoV-2 RNA.
Immunology
Nishikawa M, Kanno H, Zhou Y. et al. Massive image-based single-cell profiling reveals high levels of circulating platelet aggregates in patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun 12, 7135 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27378-2
This study from Japan reports the landscape of circulating platelet aggregates in COVID-19 obtained by massive single-cell image-based profiling and temporal monitoring of the blood of 110 COVID-19 patients. Surprisingly, an anomalous presence of excessive platelet aggregates was found in nearly 90% of all COVID-19 patients.
Clinical
Choksi T, Agrawal A, Date P, et al. Cumulative Mortality and Factors Associated With Outcomes of Mucormycosis After COVID-19 at a Multispecialty Tertiary Care Center in India. JAMA Ophthalmol December 9, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/fullarticle/2787145?resultClick=1
In this case-control study of 73 patients, 26 (36%) died within 10 days of admission. The cumulative probability of death was 53% at day 21.
Co-morbidities
Ampuero J, Lucena A, Hernández-Guerra M, et al. Primary biliary cholangitis and SARS-CoV-2 infection: incidence, susceptibility and outcomes. Gut. 2021 Dec 7:gutjnl-2021-325700. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34876479. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325700
In this large registry, the cumulative incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was 7.3% (85 of 1151) in the PBC population vs 7% in the overall Spanish population. Cumulative incidence of hospitalization and mortality were somewhat more in patients with PBC than in the general Spanish population, although the lack of adjustment for other co-morbidities could be a limitation.
Pediatrics
Diorio C, Shraim R, Vella LA, et al. Proteomic profiling of MIS-C patients indicates heterogeneity relating to interferon gamma dysregulation and vascular endothelial dysfunction. Nat Commun December 10, 2021, 12, 7222. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27544-6
Multi-system Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) is a major complication of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric patients. Using proteomic analysis, the authors “began to unravel” the complex and heterogeneous pathophysiology associated with MIS-C. They noted PLA2G2A (involved in host inflammatory responses) as a candidate biomarker for MIS-C and showed that it is associated with clinical features of thrombotic microangiopathy.
12 December
Virology
Halfmann P, Nakajima N, Sato Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Interference of Influenza Virus Replication in Syrian Hamsters. J Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 7:jiab587. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab587
In a hamster model, SARS-CoV-2 infection at the same time as or prior to H3N2 influenza virus infection resulted in significantly reduced influenza virus titers in the lungs and nasal turbinates of infected animals. This interference may correlate with SARS-CoV-2-induced expression of the antiviral gene MX1.
Vaccine
Zeng G, Wu Q, Pan H, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a third dose of CoronaVac, and immune persistence of a two-dose schedule, in healthy adults: interim results from two single-centre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trials. Lancet Inf Dis December 07, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00681-2/fulltext
Neutralizing antibody titers induced by two doses of an inactivated vaccine (CoronaVac, developed by SinoVac) declined to near or below the lower limit of seropositivity after 6 months. However, a third dose given 8 months after the second dose led to a strong boost in immune response (a three-fold to five-fold increase in neutralizing antibody titers 28 days after the second dose).
Liu X, Luongo C, Matsuoka Y, et al. A single intranasal dose of a live-attenuated parainfluenza virus-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is protective in hamsters. PNAS December 7, 2021. DOI: https://www.pnas.org/content/118/50/e2109744118?cct=2302
In this study on a bovine/human parainfluenza virus 3 (B/HPIV3) vector expressing a prefusion-stabilized version of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (S-2P), a single intranasal dose was highly immunogenic and protective in the hamster model. Based on these results, B/HPIV3/S-2P represents a promising vaccine candidate for clinical evaluation.
Immunology
Waterlow NR, van Leeuwen E, Davies NG, et al. How immunity from and interaction with seasonal coronaviruses can shape SARS-CoV-2 epidemiology. PNAS December 7, 2021 118 (49) e2108395118; https://www.pnas.org/content/118/49/e2108395118?cct=2302
The authors estimated a duration of immunity to seasonal HCoVs of 7.8 years and show that, while cross-protection between HCoV and SARS-CoV-2 may contribute to the age distribution, it is insufficient to explain the age pattern of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the first wave of the pandemic in England and Wales.
Hatton CF, Botting RA, Dueñas ME, et al. Delayed induction of type I and III interferons mediates nasal epithelial cell permissiveness to SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun December 7, 2021, 12, 7092. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27318-0
SARS-CoV-2 demonstrates widespread tropism for nasal epithelial cell types. The host response is dominated by type I and type III IFNs and interferon-stimulated gene products. When provided prior to infection, recombinant IFN-β or IFN-λ1 induces an efficient antiviral state that preserves epithelial barrier integrity. These data suggest nasal delivery of recombinant IFNs to be a potential chemoprophylactic strategy.
11 December
Epidemiology
Suetens C, Kinross P, Berciano PG, et al. Increasing risk of breakthrough COVID-19 in outbreaks with high attack rates in European long-term care facilities, July to October 2021. Euro Surveill, December 9, 2021;26(49):pii=2101070. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.49.2101070
This study shows that there is a risk for outbreaks of COVID-19 in LTCFs in European countries despite the very high uptake of the COVID-19 vaccine by residents and staff. In some cases, the outbreaks can result in high morbidity and high mortality among residents. The risk for COVID-19-related hospitalization and death was higher in large LTCFs than in small LTCFs, which may reflect a higher proportion of frail elderly people in large LTCFs or a higher number of contacts with staff and visitors.
Vaccines
Amirthalingam G, Bernal JL, Andrews NJ, et al. Serological responses and vaccine effectiveness for extended COVID-19 vaccine schedules in England. Nat Commun, December 10, 2021, 12, 7217. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27410-5
The next study suggesting higher effectiveness against infection using an extended vaccine schedule. Serologic responses were evaluated in 750 adults aged 50–89 years with two doses of BNT162b2 (BioNTech) or AZD1222 (AstraZeneca) at different intervals. Antibody levels 14–35 days after the second dose were higher in BNT162b2 recipients with an extended vaccine interval (65–84 days) compared with those vaccinated with a standard (19–29 days) interval.
Virology
Ke R, Zitzmann C, Ho DD, et al. In vivo kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its relationship with a person’s infectiousness. PNAS December 7, 2021, 118 (49) e2111477118; https://www.pnas.org/content/118/49/e2111477118?cct=2302
This interesting modeling study on viral dynamics shows that a person’s infectiousness increases sublinearly with VL and that the logarithm of the VL in the upper respiratory tract is a better surrogate of infectiousness than the VL itself. Simulations also show that more frequent antigen testing (e.g., every day or every 3 d) is comparable to less frequent RT-PCR tests, at the expense of many more false-negative tests.
Immunology
Adamo S, Michler J, Zurbuchen Y, et al. Signature of long-lived memory CD8+ T cells in acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature December 7, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04280-x
This group from Switzerland longitudinally characterized individual SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cells of 20 COVID-19 patients from acute infection to one year post-recovery. They found a distinct signature identifying long-lived memory CD8+ T cells, enriching those cells resembling CD45RA+ effector-memory T (TEMRA) cells.
Diagnostics
Fernández-González M, Agulló V, Padilla S, et al. Clinical performance of a standardized SARS-CoV-2 interferon-γ release assay for simple detection of T-cell responses after infection or vaccination. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2021; ciab1021, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab1021/6459152
The authors used a standardized interferon-γ (IFN-γ) release assay (IGRA) for detection of T cell immune responses in 152 convalescent, 54 vaccinated and 33 uninfected unvaccinated persons. Overall sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values (95% CI) of the IGRA were 81.1% (74.9%‐86%), 90.9% (74.5%‐97.6%), 98.2% (94.5%‐99.5%), and 43.5% (31.8%‐55.9%), respectively.
10 December
Epidemiology
McMahan CS, Self S, Rennert L, et al. COVID-19 wastewater epidemiology: a model to estimate infected populations. Lancet Planetary Health, December, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanplh/article/PIIS2542-5196(21)00230-8/fulltext
Hundreds of communities worldwide are now using wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2. However, the usefulness of wastewater-based epidemiology has been limited by the difficulty of relating the prevalence of the virus in wastewater to the number of infected individuals. According to the authors, their model allows for robust predictions.
Vaccine
Arbel R, Hammerman A, Sergienko R. BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster and Mortality Due to COVID-19. NEJM December 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2115624?query=featured_home
90%. The authors obtained data for all members of Clalit Health Services (843,208 participants) who were 50 years of age or older at the start of the study and had received two doses of BNT162b2 at least 5 months earlier. The adjusted hazard ratio for death due to COVID-19 in the booster group, as compared with the non-booster group, was 0.10 (95% CI: 0.07 to 0.14; P < 0.001).
Cumulative Hazard Ratio for Death Due to Covid-19. The shaded area indicates the 95% confidence interval.
Bar-On YM, Goldberg Y, Mandel M, et al. Protection against Covid-19 by BNT162b2 Booster across Age Groups. NEJM December 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2115926?query=featured_home
Same direction. These authors extracted data from the Israel Ministry of Health database regarding 4,696,865 persons 16 years of age or older who had received two doses of BNT162b2 at least 5 months earlier. Among those 60 years of age or older, mortality was lower by a factor of 14.7 (95% CI: 10.0 to 21.4) in the primary analysis and 4.9 (95% CI: 3.1 to 7.9) in the secondary analysis. The booster dose had a similar effect across different age groups (although in the youngest age group, a larger reduction factor vs confirmed infections was observed).
Severe COVID-19
Ospina-Tascón GA, Calderón-Tapia LE, García AF, et al. Effect of High-Flow Oxygen Therapy vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Invasive Mechanical Ventilation and Clinical Recovery in Patients With Severe COVID-19A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA December 7, 2021, 326(21):2161-2171. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2786830?resultClick=1
In this RCT that included 220 patients with severe COVID-19, the rate of intubation and mechanical ventilation for those treated with high-flow oxygen therapy through a nasal cannula vs with conventional oxygen therapy was 34.3% vs 51.0%, respectively; the median time to clinical recovery was 11 days vs 14 days.
Collateral Damage
Agostino H, Burstein B, Moubayed D, et al. Trends in the Incidence of New-Onset Anorexia Nervosa and Atypical Anorexia Nervosa Among Youth During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Canada. JAMA Netw Open December 7, 2021;4(12):e2137395. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786919?resultClick=1
In a broad national sample of youth during the first wave of the pandemic, monthly cases of new-onset anorexia nervosa or atypical anorexia nervosa increased by more than 60% (24.5 to 40.6), and monthly hospitalizations nearly tripled (7.5 to 20.0) compared with prepandemic rates.
9 December
Today we have a pre-print special on the Omicron variant. All papers are only pre-prints, have not been peer-reviewed and were selected from a total of > 50 articles published through three pre-print servers medRxiv, BioRxiv and Arxiv. We have also included some Twitter messages and preliminary results from Sandra Ciesek’s lab on protection.
Virology
Sarkar R, Lo M, Saha R. S glycoprotein diversity of the Omicron variant. medRxiv, December 6, 2021- doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.04.21267284
A comprehensive analysis of S glycoprotein mutations of the Omicron variant. The authors classified them into different groups based on different combinations of co-existing S glycoprotein mutations.
Bansal K, Kumar S. Mutational cascade of SARS-CoV-2 leading to evolution and emergence of omicron variant. BioRxiv December 7, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.06.471389
Phylogenetic analysis on the evolution and origin of Omicron. Delta and Omicron have evolutionarily diverged into distinct phylogroups and do not share a common ancestry. However, Omicron shares common ancestry with VOI Lambda and its evolution is mainly derived by the non-synonymous mutations.
Transmission
Golcuk M, Yildiz A, Gur N, et al. The Omicron Variant Increases the Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein with ACE2. BioRxiv December 7, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.06.471377v1
Some early experiments, showing why Omicron has a better binding affinity to ACE.
Woo G, Shah M. Omicron: A heavily mutated SARS-CoV-2 variant exhibits stronger binding to ACE2 and potently escape approved COVID-19 therapeutic antibodies. BioRxiv December 7, 2021. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.04.471200v1
Same direction: Omicron binds to ACE2 with greater affinity, enhancing its infectivity and transmissibility. Mutations in the Spike are prudently devised by the virus that enhances the receptor binding and weakens the mAbs binding in order to escape the immune response.
Immune escape
Pulliam JR, van Schalkwyk C, Govender N, et al. Increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection associated with emergence of the Omicron variant in South Africa. MedRxiv December 02, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.11.21266068
Data from South Africa suggesting that the Omicron variant is associated with a substantial ability to evade immunity from prior infection. The estimated hazard ratio for reinfection versus primary infection for the period from 1 November 2021 to 27 November 2021 versus wave 1 was 2.39 (CI95: 1.88–3.11).
Chen J, Wang R, Gilby NB, et al. Omicron (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, vaccine breakthrough, and antibody resistance. ArXiv. Preprint. 2021 Dec 1: arXiv:2112.01318v1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8647651/
The authors used an artificial intelligence (AI) model, trained via tens of thousands of experimental data points and extensively validated by experimental data on SARS-CoV-2. They predict that Omicron is about ten times more infectious than the original virus or about twice as infectious as the Delta variant. Using the structures of 132 known antibody-RBD complexes, they also reveal that Omicron’s vaccine-escape capability is about twice as high as that of the Delta variant and that Omicron may significantly reduce the efficacy of several antibody cocktails. Let’s hope they are wrong.
On Twitter
Three groups from Germany, South Africa and Sweden, see a marked loss of serum neutralization activity in fully immunized people, using slightly different viruses and setups. Very low antibody-mediated neutralization efficacy against Omicron, after various vaccination strategies. Bottom line: Two shots are not enough.
https://twitter.com/CiesekSandra/status/1468465347519041539/photo/1
https://mobile.twitter.com/DrEricDing/status/1468344299184087045/photo/1
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1CuxmNYj5cpIuxWXhjjVmuDqntxXwlfXQ/view
Press release
Pfizer and BioNTech Provide Update on Omicron Variant. Wednesday, December 08, 2021 – 06:54am. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-and-biontech-provide-update-omicron-variant
Preliminary laboratory studies demonstrate that three doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine neutralize the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529 lineage) while two doses show significantly reduced neutralization titers. The only data presented here: “The geometric mean titer of neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variant measured in the samples was 154 (after three doses), compared to 398 against the Delta variant (after three doses) and 155 against the ancestral strain (after two doses).”
8 December
Epidemiology
Indenbaum V, Lustig Y, Mendelson E, et al. Under-diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infections among children aged 0–15 years, a nationwide seroprevalence study, Israel, January 2020 to March 2021. Euro Surveill December 2, 2021;26(48):pii=2101040. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.48.2101040
More than 20% of children aged 0–15 years in Israel were infected with SARS-CoV-2 by March 2021. At least 50% of SARS-CoV-2 infections in this age group were undiagnosed between September 2020 and March 2021 based on the difference observed between cumulative incidence and seropositivity.
Vaccine
Stuart AS, Shaw RH, Liu X, et al. Immunogenicity, safety, and reactogenicity of heterologous COVID-19 primary vaccination incorporating mRNA, viral-vector, and protein-adjuvant vaccines in the UK (Com-COV2): a single-blind, randomised, phase 2, non-inferiority trial. Lancet December 06, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02718-5/fulltext
Paper of the day. This large RCT shows that heterologous (mix and match) COVID-19 vaccination is safe, tolerated, and immunogenic. In particular, mRNA-1273 as a heterologous boost after ChAd or BNT prime induced a higher binding and neutralising antibody response than either homologous schedule.
Richardson CD. Mixing mRNA, adenoviral, and spike-adjuvant vaccines for protection against COVID-19. Lancet December 06, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02757-4/fulltext
In his comment, Christopher D Richardson discusses the implications of this important trial, concluding: “It also remains to be seen how effective the heterologous vaccines are in preventing disease or reinfection against newer variants, such as the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529).”
Variants
Gu H, Krishnan P, Ng DYM, Chang LDJ, Liu GYZ, Cheng SSM, et al. Probable transmission of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in quarantine hotel, Hong Kong, China, November 2021. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Feb [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2802.212422
Bad news: Detection of the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in an asymptomatic, fully vaccinated traveler in a quarantine hotel in Hong Kong, China. Worse news: Omicron was also detected in a fully vaccinated traveler staying in a room across the corridor from the index patient, suggesting transmission despite strict quarantine precautions.
Clinical
Wang SY, Juthani PV, Borfges KA, et al. Severe breakthrough COVID-19 cases in the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant era. Lancet Microbe December 03, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00306-2/fulltext
Though patients with severe breakthrough infections were markedly older and more co-morbid, hospitalisation was shorter and outcome was better than among those who were unvaccinated.
Influenza
Delahoy MJ, Mortenson L, Bauman L, et al. Influenza A(H3N2) Outbreak on a University Campus — Michigan, October–November 2021. MMWR December 3, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7049e1.htm?s_cid=mm7049e1_w
The first substantial influenza activity during the COVID-19 pandemic. During October 6–November 19, among 3121 persons tested, 745 (23.9%) received a virus test result that was positive for influenza A, 137 (4.4%) for SARS-CoV-2, and 84 (2.7%) for respiratory syncytial virus. The similar vaccination rates among persons with positive and negative influenza test results in this outbreak suggest that protection against mild infection with the 2a.2 subgroup of H3N2 viruses was low among these mostly younger adults.
7 December
Immunology
Cillo AR, Somasundaram A, Shan F, et al. Critically ill COVID-19 patients exhibit peripheral immune profiles predictive of mortality and reflective of SARS-CoV-2 viral burden in the lung. Cell Rep Med December 01, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00348-7
This large and comprehensive study evaluated cellular and molecular features associated with the immunopathogenesis of severe COVID-19 illness that were predictive of mortality. In particular, the authors describe distinctive monocyte gene modules as part of a multivariate peripheral immune state to be predictive.
Gerling E, Pinski AN, Stone TE, et al. Roles of antiviral sensing and type I interferon signaling in the restriction of SARS-CoV-2 replication. iScience December 02, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01523-6
This study found different viral growth kinetics and release among the cell lines despite comparable ACE2 expression. Interestingly, gastric cells exhibited robust antiviral gene expression and supported viral replication.
Vaccine
Aikawa NE, Kupa LV, Pasoto SG, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of two doses of the CoronaVac SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in SARS-CoV-2 seropositive and seronegative patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases in Brazil: a subgroup analysis of a phase 4 prospective study. Lancet Rheumatology December 03, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00327-1/fulltext
In patients with autoimmune rheumatic disease, previous exposure to SARS-CoV-2, independent of symptoms, results in better antibody responses to an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac; Sinovac) compared to patients with no previous exposure. The reduced immunogenicity observed in seronegative patients suggest that these patients might benefit from booster doses.
Gagne M, Corbett KS, Flynn BJ, et al. Protection from SARS-CoV-2 Delta one year after mRNA-1273 vaccination in rhesus macaques is coincident with anamnestic antibody response in the lung. Cell December 02, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01405-7
Animal study on mRNA-1273-mediated protection: the three main findings were protection in the lower airway complete by day 4 but delayed compared to prior studies in which viral challenges were done much closer to the time of vaccination; anamnestic antibody responses detected in BAL at day 4 in vaccinated animals; and binding and neutralizing antibody titers in blood and BAL decreased over 48 weeks.
Pannus P, Neven KY, De Craeye S, et al. Poor antibody response to BioNTech/Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination in SARS-CoV-2 naïve residents of nursing homes. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2021;, ciab998, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab998
SARS-CoV-2 naïve residents had lower Ab responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine than naïve staff. These poor responses involved lower levels of IgG to all spike domains, lower avidity of RBD IgG, and lower levels of Ab neutralizing the vaccine strain. None of 78 naïve residents had detectable neutralizing Ab to Delta.
Greinacher A, Selleng K, Palankar R, et al. Insights in ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2021 Dec 2;138(22):2256-2268. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34587242. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021013231
The results of this study support a 2-step mechanism underlying VITT that resembles the pathogenesis of (autoimmune) heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Pediatrics
Gonçalves J, Juliano AM, Charepe N, et al. Secretory IgA and T cells targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are transferred to the breastmilk upon mRNA vaccination. Cell Rep Med December 01, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00340-2
This small study analyzed 23 paired samples of breastmilk, pre-vaccination and after first and second mRNA vaccine administration. Results suggest that breastmilk might convey both immediate, through anti-spike IgA, as well as long-lived, via spike-reactive T cells, immune protection to the infant.
6 December
Epidemiology
Kraay AN, Nelson KN, Zhao CY, et al. Modeling serological testing to inform relaxation of social distancing for COVID-19 control. Nat Commun December 3, 12, 7063 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26774-y
Simulation study revealing that sufficiently frequent testing using high-performance tests combined with serological shielding in the pre-vaccine era would have decreased deaths and allowed relaxed social distancing for a substantial part of the population.
Transmission
Hwang H, Lim JS, Song SA, et al. Transmission dynamics of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 infections in South Korea. Journal of Infectious Diseases, December 2, 2021, jiab586, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab586/6448309
In 23 household contacts, the secondary attack rate was 63%. The authors estimated the mean serial interval as 3.26 days (95% credible interval: 2.92–3.60). 15% of cases seeded 80% of all local transmission.
Vaccine
Grunau B, Goldfarb DM, Asamoah-Boaheng M, et al. Immunogenicity of Extended mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Dosing Intervals. JAMA December 3, 2021. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34860253. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.21921
Small uncontrolled study suggesting that longer mRNA vaccine dosing intervals demonstrated improved immunogenicity, which was consistent when responses were measured based on timing of the first or second dose. These data suggest that extending dosing intervals may be particularly advantageous against the Delta variant.
Tauzuin A, Gong AY, Beaudoin-Bussières G, et al. Strong humoral immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination with a 16-week interval between doses. Cell Host Microbe December 02, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(21)00569-2
Same direction: an extended interval between doses led to stronger humoral responses than in those persons vaccinated with a short interval.
Kim P, Gordon SM, Sheehan MM, et al. Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Natural Immunity and Protection against the Delta Variant: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Clinical Infectious Diseases December 3, 2021, ciab999, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab999.
Among 325,157 patients tested before 31 December 2020, 50,327 (15.5%) tested positive. Protection of prior infection against reinfection with Delta was 85% (95% CI: 80-89). Protection lasted up to 13 months. However, patients over age 65 had slightly lower protection.
Co-morbidities
Herishanu Y, Rahav G, Levi S, et al. Efficacy of a Third BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Dose in Patients with CLL who Failed Standard Two-dose Vaccination. Blood December 3, 2021PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34861036. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021014085
In 172 patients with CLL the antibody response rate was 23.8%. Patients who failed to achieve a humoral response after the standard two-dose BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination regimen, close to a quarter responded to the third dose. The antibody response rates were lower during active treatment and in patients with a recent exposure (< 12 months prior to vaccination) to anti-CD20 therapy.
Latest News on Omicron
Dyer O. Covid-19: South Africa’s surge in cases deepens alarm over omicron variant. BMJ December 3, 2021;375:n3013. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj.n3013
Owen Dyer summarizes the latest findings on Omicron.
Callaway E, Ledford H. How bad is Omicron? What scientists know so far. Nature NEWS, December 2, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03614-z
The same issue: COVID researchers are working at breakneck speed to learn about the variant’s transmissibility, severity and ability to evade vaccines.
Erdbrink T, Libell HP, Frost N, Yoon J. A Christmas party in Norway becomes a possible Omicron-spreading event. New York Times December 3, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/03/world/omicron-norway-christmas-party.html
By now the largest outbreak outside South Africa. At least half of 120 people who attended an office Christmas party in Oslo, where only vaccinated employees were admitted, have tested positive after one guest recently returned from South Africa who was found to carry the Omicron variant.
5 December
Vaccine
Munro AP, Janani L, Cornelius V, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven COVID-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): a blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet December 02, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02717-3/fulltext
Among 2878 participants, this trial demonstrated the potential of all vaccines tested (ChAd, BNT, mRNA1273, NVX-CoV2373, Ad26, CVnCov from CureVac and VLA2001 from Valneva). All vaccines showed acceptable side effect profiles. The immunogenicity of homologous or heterologous third dose boost with all tested vaccines was superior to control regardless of which vaccine had been received in the initial course, apart from VLA2001, which did not achieve predefined criteria for minimum clinically important difference following BNT/BNT.
Variants
Reynolds CJ, Gibbons JM, Pade C, et al. Heterologous infection and vaccination shapes immunity against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science, December 2, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abm0811
Populations infected during waves of different variants carry distinct immune memory, with implications for differential protection against future variants of concern (VOC). The authors found a differential hierarchy of cross-neutralization to VOC after natural infection, one or two vaccine doses, depending on the infecting strain.
Co-morbidities
McKay KA, Piehl F, Englund S, et al. Rituximab Infusion Timing, Cumulative Dose, and Hospitalization for COVID-19 in Persons With Multiple Sclerosis in Sweden. JAMA Netw Open December 1, 2021; 4(12):e2136697. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786701?resultClick=1
Among 172 Swedish persons with multiple sclerosis who received rituximab before contracting COVID-19, the authors found no statistically significant association between the timing of rituximab infusion or cumulative lifetime rituximab dose and the odds of hospitalization for COVID-19, although the study power was limited.
Hoertel N, Sánchez-Rico M, Herrera-Morueco JJ. et al. Comorbid medical conditions are a key factor to understand the relationship between psychiatric disorders and COVID-19-related mortality: Results from 49,089 COVID-19 inpatients. Mol Psychiatry, November 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01393-7
Among patients hospitalized for COVID-19, those with psychiatric disorders have increased risk of death, which could be explained by their greater number of medical conditions.
Treatment
Sourimantr J, Lieber CM, Aggarwal M, et al. 4′-Fluorouridine is an oral antiviral that blocks respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Science, December 2, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj5508
This ribonucleoside analog inhibits RSV, related RNA viruses, and SARS-CoV-2 with a high selectivity index in cells and human airway epithelia organoids. Once-daily oral treatment was highly efficacious in RSV-infected mice or ferrets infected with different SARS-CoV-2 variants-of-concern.
4 December
Vaccines
Dickerman BA, Gerlovin H, Madenci AL, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines in U.S. Veterans. NEJM December 1, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2115463?query=featured_home
The authors used the electronic health records of U.S. veterans who received a first dose of the BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccine in early 2021, during a period marked by predominance of the Alpha variant. The risks of outcomes were low, regardless of the vaccine received. However, recipients of the BNT162b2 vaccine had a 27% higher risk of documented SARS-CoV-2 infection and a 70% higher risk of hospitalization for COVID-19 than recipients of the mRNA-1273 vaccine over 24 weeks of follow-up in a period.
Rosenberg ERS, Dorabawila V, Easton D, et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in New York State. NEJM December 1, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116063?query=featured_home
By analyzing large cohorts of New York State residents, the authors observed declines in vaccine effectiveness from May through August 2021. Trends were inversely correlated with increasing Delta prevalence and plateaued among persons 18 to 64 years of age during the period in which the prevalence of Delta exceeded 85%. These changes occurred simultaneously across age, product, and time cohorts, with the largest declines seen among BNT162b2 recipients.
Variants
Kissler SM, Fauver JR, Mack C, et al. Viral Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Persons. NEJM December 1, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2102507?query=featured_home
Among 173 participants as part of the occupational health program of the National Basketball Association (NBA), the authors found no meaningful difference in the mean peak viral load or proliferation duration between vaccinated and unvaccinated participants. In addition, there were no meaningful differences in the mean peak viral load, proliferation duration, clearance duration, or duration of acute infection of either the Alpha or the Delta variant as compared with other variants.
Diagnostics
Chmielewska AM, Czarnota A, Bieńkowska-Szewczyk K, et al. Immune response against SARS-CoV-2 variants: the role of neutralization assays. npj Vaccines November 29, 2021, 6, 142. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-021-00404-6
Nice review. The authors describe common neutralization assays based on infectious and pseudotyped viruses and evaluate their role in testing neutralizing responses against new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Additionally, they briefly review the recent findings on the immune response elicited by available vaccines against major SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta.
Clinical
Rodríguez-Grande C, Alcalá L, Estévez A, et al. Systematic genomic and clinical analysis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reinfections and recurrences involving the same strain. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022 Jan [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2801.211952
Among 41,195 cases diagnosed March 2020–March 2021, 93 (0.23%) had 2 positive RT-PCR tests (55–346 days apart). Of 22 cases with valid data, 4 cases were recurrences involving the same strain. Eighteen cases were reinfections; patients were 19–84 years of age, and most had no relevant clinical history. Of note, the second episode was more severe in 8 cases.
Treatment
Temesgen Z, Burger CD, Baler J, et al. Lenzilumab in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (LIVE-AIR): a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Resp Med December 01, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00494-X/fulltext
LIVE-AIR was a phase 3 RCT in hospitalised adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia not requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Among 479 participants randomly assigned to receive three intravenous doses of lenzilumab (a GM-CSF neutralising monoclonal antibody) or placebo, the likelihood of survival was slightly greater with lenzilumab (hazard ratio 1.54; 95% CI 1.02–2.32; p=0.04). However, according to the authors, “the added value of lenzilumab beyond other immunomodulators used to treat COVID-19 alongside steroids remains to be confirmed”.
3 December
Transmission
Griffin BD, Warner BM, Chan M, et al. Host parameters and mode of infection influence outcome in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters. iScience November 27, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01501-7
In hamsters, delivery of SARS-CoV-2 by a low versus high volume intranasal or intragastric route resulted in comparable viral titers in the lung and viral shedding but in milder weight loss.
Vaccine
Lapuente D, Fuchs J, Willar J, et al. Protective mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 after heterologous systemic prime-mucosal boost immunization. Nat Commun November 26, 2021, 12, 6871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27063-4
Intranasal vaccinations with adenovirus 5 and 19a vectored vaccines following a systemic plasmid DNA or mRNA priming resulted in systemic and mucosal immunity in mice. In contrast to two intramuscular applications of an mRNA vaccine, intranasal boosts with adenoviral vectors induced high levels of mucosal IgA and lung-resident memory T cells. Mucosal neutralization of viral variants of concern was also enhanced.
Ying B, Whitener B, VanBlargan LA, et al. Protective activity of mRNA vaccines against ancestral and variant SARS-CoV-2 strains. Science Translational Medicine, November 30, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abm3302
In mice, immunization with formulations at different doses induced neutralizing antibodies in serum against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 WA1/2020 and several viral variants, although serum titers were lower against Delta. Protection against weight loss and lung pathology was observed with all high dose vaccines against all viruses. However, low dose formulations of the vaccines, which produced lower magnitude antibody and T cell responses, showed severe breakthrough lung infections with Delta.
Pediatrics
Shi T, Pan J, Katikireddi SV, et al. Risk of COVID-19 hospital admission among children aged 5–17 years with asthma in Scotland: a national incident cohort study. Lancet Resp Med November 30, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00491-4/fulltext
Of 4339 school-aged children with confirmed infection, 67 (1.5%) were admitted to hospital with COVID-19. When using oral corticosteroid prescriptions as the marker of uncontrolled asthma, the adjusted HR was 3.38 (1.84–6.21) for those with three or more prescribed courses of corticosteroids. The authors conclude that school-aged children with asthma with previous recent hospital admission or two or more courses of oral corticosteroids are at markedly increased risk of COVID-19 hospital admission and should be considered a priority for vaccinations.
Zavala M, Ireland G, Amin-Chowdhury Z, et al. Acute and persistent symptoms in children with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to test-negative children in England: active, prospective, national surveillance. Clinical Infectious Diseases November 29, ciab991, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab991
Children with symptomatic COVID-19 had a slightly higher prevalence of ongoing symptoms than symptomatic controls, not as high as previously reported. Using national testing data to identify children aged 2-16 years with a SARS-CoV-2 PCR test, the authors randomly selected PCR-positive cases and matched PCR-negative controls. After one month, 21/320 (6.7%) of symptomatic cases and 6/154 (4.2%) of symptomatic controls (p = 0.24) experienced ongoing symptoms.
2 December
Transmission
Tran Kiem C, Bosetti P, Paireau J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 transmission across age groups in France and implications for control. Nat Commun November 25, 2021, 12, 6895. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27163-1
This great paper is for all who still argue that it is sufficient to protect only the elderly. Pandemic control requires an effort in all age groups: analyzing the French epidemic in summer 2020, the authors found that while the rebound started in young adults, it reached individuals aged ≥ 80 years after 4 weeks, despite substantial contact reductions, indicating substantial transmission flows across ages. While shielding older individuals reduces mortality, it is insufficient to allow any significant relaxation of social distancing. When the epidemic remains manageable (R close to 1), targeting those most contributing to transmission is better than shielding at-risk individuals.
Vaccine
Grunau B, Asamoah-Boaheng M, Lavoie PM, et al. A Higher Antibody Response Is Generated With a 6- to 7-Week (vs Standard) Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Vaccine Dosing Interval. Clinical Infectious Diseases November 30, ciab938, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab938
This study included 186 participants, of whom 70% were vaccinated with the BNT162b2 vaccine and 55 (30%) with the mRNA-1273 vaccine. Compared to the recommended (≤ 4 week) dosing interval, a 6- to 7-week interval for mRNA vaccines resulted in higher spike-related antibody concentrations. Increased development of germinal center B cells associated with vaccine dosing intervals may explain this.
Vaccine
Meslé M, Brown J, Mook P, et al. Estimated number of deaths directly averted in people 60 years and older as a result of COVID-19 vaccination in the WHO European Region, December 2020 to November 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(47):pii=2101021. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.47.2101021
The authors estimate that the widespread implementation of COVID-19 vaccination programs for older people has averted a median of 469,186 deaths (sensitivity range: 129,851–733,744) in people 60 years and older in 33 countries (51% of 911,302 expected deaths; sensitivity range: 23–62%).
Patallon T, Gazit S, Pitzer VE, et al. Odds of Testing Positive for SARS-CoV-2 Following Receipt of 3 vs 2 Doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. JAMA Intern Med November 30, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2786890
The study population included 306,710 members of Maccabi Healthcare Services in Israel. Comparing those who received a booster and those who received 2 doses, there was an estimated odds ratio of 0.14 (95% CI: 0.13-0.15) 28 to 65 days following receipt of the booster (86% reduction in the odds of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2).
Variants
Liu C, Zhou D, Nutalai R, et al. The antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 Beta underscores the antigenic distance to other variants. Cell Rep Microbe November 26, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(21)00519-9
Please repeat these experiments with Omicron. This important, in-depth structure function analysis of potent mAbs from Beta-infected volunteers looked at potent neutralizing mAbs. The anti-Beta response was substantially repositioned towards the three mutated residues found in the Beta RBD. Differential targeting of these residues creates the large antigenic distance between Beta and early pandemic strains used in current vaccines. The majority of Beta-specific mAbs fail to neutralize Delta, which is consistent with the large falls in the ability of Beta- and Gamma-infected sera to neutralize Delta.
Koehler M, Ray A, Moreira RA, et al. Molecular insights into receptor binding energetics and neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Commun November 26, 2021, 12, 6977. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27325-1
Brilliant work, providing unprecedented atomistic detail on the binding of SARS-CoV-2 variants as well as insight into the impact of viral mutations on infection-induced immunity. The authors observed a significant increase in the RBD—ACE2 complex stability for several variants of concern. While the N501Y and E484Q mutations are particularly important for greater stability, the N501Y mutation is unlikely to significantly affect antibody neutralization. Again, please repeat this with Omicron.
1 December
Transmission
Delaugerre C Foissac F, Abdoul H, et al. Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 transmission during a large, live, indoor gathering (SPRING): a non-inferiority, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet November 26, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00673-3/fulltext
This large randomized trial from Paris with 6678 participants shows that infection rates among attendees at a large, indoor gathering event are similar to those in non-attendees, given implementation of a comprehensive prevention strategy including antigen-screening within the 3 days prior, medical mask wearing, and optimised ventilation. Important caveat: the study was conducted in the context of low circulation of SARS-CoV-2 in France (end of May 2021).
Immunology
Wendisch D, Dietrich O, Mari T, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers profibrotic macrophage responses and lung fibrosis. Cell November 26, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01383-0
See title. Gene set enrichment and computational data integration revealed a significant similarity between COVID-19-associated macrophages and profibrotic macrophage populations identified in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Vaccine
Farkash I, Feferman T, Cohen-Saban N, et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies elicited by COVID-19mRNA vaccine exhibit a unique glycosylation pattern. Cell Report November 23, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/pdf/S2211-1247(21)01608-9.pdf
This study shows that vaccine-induced anti-spike IgG is characterized by distinct Fab- and Fc-mediated functions between different age groups and in comparison to antibodies generated during natural viral infection.
Jiang W, Shi L, Cai L, et al. Two-adjuvant multiantigen candidate vaccine induces superior protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Cell Report November 23, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01606-5
Here, the N protein and prefusion-full S protein (SFLmut) were combined with flagellin (KF) and cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) to generate a candidate vaccine, and this vaccine elicited stronger systemic and mucosal humoral immunity than vaccines containing other forms of the S protein.
Treatment
Menichetti F, Popoli P, Puopolo M, et al. Effect of High-Titer Convalescent Plasma on Progression to Severe Respiratory Failure or Death in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia – A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open November 29, 2021;4(11):e2136246. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786680?resultClick=1
In patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia, high-titer anti–SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma (CP) did not reduce the progression to severe respiratory failure or death within 30 days. The primary end point occurred in 59 of 231 patients (25.5%) treated with CP and standard therapy and in 67 of 239 patients (28.0%) who received standard therapy alone.
30 November
Vaccine
Cattaneo D, Bucelli C, Cavallaro F, et al. Impact of diagnosis and treatment on response to COVID-19 vaccine in patients with BCR-ABL1-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. A single-center experience. Blood Cancer J, November 26, 2021. 11, 185. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41408-021-00579-0
Two jabs. The rate of seroconversion to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in MPN patients (77.4%) was lower as compared to healthy adults.
Kumar D, Ferreira VH, Hall VG, et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Transplant Recipients After Two and Three Doses of mRNA-1273 Vaccine. Annals Int Med, November 23, 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-3480
Three jabs. Secondary analysis of a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of a third dose of mRNA-1273 vaccine versus placebo in transplant recipients: based on the pseudovirus neutralization assay against the Delta variant, 33 of 60 (55%) patients were positive in the mRNA-1273 group versus 10 of 57 (18%) in the placebo group.
Kamar N, Abravanel F, Marion O, et al. Assessment of 4 Doses of SARS-CoV-2 Messenger RNA–Based Vaccine in Recipients of a Solid Organ Transplant. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(11):e2136030. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786552
And even four jabs! Among the 31 patients who were seronegative before dose 4, 13 (41.9%) became seropositive. Neutralizing antibody titers and cellular response were low. Conclusion: “Other strategies should be tested for solid organ transplant recipients”.
Chua GT, Wah Kwan MY, Chui CS, et al. Epidemiology of Acute Myocarditis/Pericarditis in Hong Kong Adolescents Following Comirnaty Vaccination. Clin Inf Dis, November 29, 2021. https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab989/6445179?redirectedFrom=fulltext
In this population cohort study in Hong Kong that monitored adverse events following immunization through a pharmacovigilance system for COVID-19 vaccines, among male adolescents, the incidence after the first and second doses were 5.57 (95% CI: 2.38-12.53) and 37.32 (95% CI: 26.98-51.25) per 100,000 persons vaccinated.
Severe COVID-19
Gangneux JP, Dannaoui E, Fekkar A, et al. Fungal infections in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 during the first wave: the French multicentre MYCOVID study. Lancet Resp Medicine, November 26, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00442-2/fulltext
This large retrospective study on 565 patients found a high prevalence of invasive fungal infections (25%) as well as high mortality associated with proven or probable COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19.
Coronapod
Baker N, Van Noorden R. Coronapod: everything we know about the new COVID variant. Nature 26 November 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03562-8
B.1.1.529 (Omicron) has more than 30 changes to the spike protein – and the concern is that these mutations may result in increased transmissibility, severity of disease or even antibody evasion. Noah Baker and Richard van Noorden discuss what is known.
28 November
Immunology
Fumagalli V, Ravà M, Marotta D, et al. Administration of aerosolized SARS-CoV-2 to K18-hACE2 mice uncouples respiratory infection from fatal neuroinvasion. Science Immunology November 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9929
Interesting observation. Mice infected via aerosols developed robust respiratory infection, anosmia, and signs of airway obstruction but, in contrast to mice infected intranasally, did not experience fatal neuroinvasion. Moreover, aerosol exposure resulted in a more severe lung pathology, inflammation, and fibrin deposition. These data support the hypothesis that anosmia stems from infection of sustentacular cells and/or Bowman’s glands rather than of olfactory sensory neurons.
Variants
Callaway E. Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert. Nature NEWS 27 November 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-03552-w
Ewan Callaway summarizes what is known on Omicron and whether this variant poses a threat to COVID vaccines’ effectiveness.
Transmission
Dancer SJ, Bluyssen PM, Li Y, et al. Why don’t we just open the windows? BMJ 26 November 2021, 375. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj.n2895
It is time to accept the fact that most people acquire SARS-CoV-2 by breathing in contaminated air. In their editorial, Philomena M Bluyssen, professor of indoor environment (!), and colleagues argue that “we cannot ignore airborne transmission any longer, however difficult or costly it may be to control”.
Vaccine
Israel A, Merzon E, Schäffer AA, et al. Elapsed time since BNT162b2 vaccine and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection: test negative design study. BMJ November 24, 2021;375:e067873. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34819275. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2021-067873
More evidence for waning protection. In this large population of adults tested for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR after two doses of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine, a gradual increase in the risk of infection was seen for individuals who received their second vaccine dose after at least 90 days.
Treatment
Herman JD, Wang C, Loos C, et al. Functional convalescent plasma antibodies and pre-infusion titers shape the early severe COVID-19 immune response. Nature Commun November 25, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27201-y
Important study, providing new insights into immunomodulatory functions of CP that may help explain its apparent benefit in some patients with severe disease, and its ability to clear virus and reduce inflammatory markers even when it does not affect overall clinical outcome. CP was highly enriched with Fc-functional antibodies that appeared to influence the evolution of CP recipient antibody responses, by limiting the emergence of inflammatory antibody signatures in both recipients with high and low pre-CP-S-specific IgG titers, albeit through different mechanisms.
Pediatrics
Ochoa V, Díaz FE, Ramirez E, et al. Infants younger than 6 months old infected by SARS-CoV-2 show the highest respiratory viral loads. J Inf Dis, November 24, jiab577, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab577
New questions regarding the role of infants in this pandemic: This analysis of the viral loads of 45,318 SARS-CoV-2-positive nasopharyngeal swab samples obtained in Argentina found that infants younger than 6 months old presented higher viral loads than any other age group.
27 November
Today we have a Virology/Variants Special. Several important studies that provide pieces to the big puzzle of which mutations are responsible for which properties of the virus. Let’s take a look at some amino acid substitutions in the spike protein that have an impact on epidemiology, transmission properties and pathogenicity – in other words, that bring us all the crap.
Epidemiology
Lu L, Sikkema RS, Velkers FC, et al. Adaptation, spread and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in farmed minks and associated humans in the Netherlands. Nat Commun November 23, 12, 6802. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27096-9
SARS-CoV-2 infections in minks are concerning as evolution of the virus in an animal reservoir could lead to establishment of additional zoonotic reservoirs with the potential for repeated spill-over events. This study explored the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 between mink farms, and between minks and humans. Viruses belonging to the largest cluster acquired an amino acid substitution in the receptor binding domain of the spike protein (position 486), evolved faster and spread longer and more widely.
Virology
Zech F, Schiertshauser D, Jung C, et al. Spike residue 403 affects binding of coronavirus spikes to human ACE2. Nature Commun Novembver 25, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27180-0
Which specific features help bat CoVs to successfully cross the species barrier to humans? This brilliant study demonstrates a probable single amino acid change of T403R that allows the S protein of RaTG13, one of the closest known bat relatives of SARS-CoV-2, to utilize human ACE2 for viral entry.
Variants
Saito A, Irie T, Suzuki R. et al. Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation. Nature November 25, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04266-9
Sounds bad. Delta is highly fusogenic and notably more pathogenic than prototypic SARS-CoV-2 in infected hamsters. The P681R mutation in the spike protein facilitates spike protein cleavage and enhances viral fusogenicity. Moreover, P681R-bearing virus exhibits higher pathogenicity, suggesting that the P681R mutation is a hallmark of the virological phenotype of Delta. Worryingly, the P681R mutation is not specific for Delta…
Zhang L, Mann M, Syed ZA, et al. Furin cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike is modulated by O-glycosylation. PNAS November 23, 2021 118 (47) e2109905118; https://www.pnas.org/content/118/47/e2109905118
Bad again. SARS-CoV-2 contains a unique insertion of four amino acids within the spike protein. Furin cleavage at this novel insertion site has been shown to increase pseudoviral infectivity and syncytia formation. P681 mutations found in Alpha and Delta variants decrease O glycosylation (a post-translational modification catalyzed by some enzymes), which increases furin cleavage and syncytia formation.
Liu Y, Liu J, Plante KS, et al. The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission. Nature 24 November 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04245-0
Of the 8 individual spike protein substitutions, only N501Y exhibited consistent fitness gains for replication in the upper airway in the hamster model as well as primary human airway epithelial cells.
Torrens-Fontanals M, Peralta-García A, Talarico C, et al. SCoV2-MD: a database for the dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome and variant impact predictions. Nucleic Acids Research November 11, 2021. gkab977, https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkab977/6425545
And here is the database for all this. SCoV2-MD (www.scov2-md.org) is a new online resource that systematically organizes atomistic simulations of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. This ambitious project includes simulations produced by leading groups using molecular dynamics methods to investigate the structure-dynamics-function relationships of viral proteins. SCoV2-MD enables the interactive search by viral protein, isolate, phylogenetic attributes, or specific point mutation.
26 November
Immunology
Murphy WJ, Longo DL. A Possible Role for Anti-idiotype Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination. NEJM November 24, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMcibr2113694?query=featured_home
Some thoughts on the implications of anti-idiotype immune responses, a mechanism by which the antibody responses to an antigen themselves induce downstream antibody responses against the antigen-specific antibody.
Vaccine
Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Bertollini R. Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfections as Compared with Primary Infections. NEJM November 24, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2108120?query=featured_home
Analysing 1304 identified reinfections (32% Delta) in Qatar, the authors conclude reinfections had 90% lower odds of resulting in hospitalization or death than primary infections.
Variants
Bekliz M, Adea K, Essaidi-Laziosi M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid tests for the delta variant. Lancet Microbe November 24, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00302-5/fulltext
SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic tests remain effective to detect variants of concern, including Delta.
Diagnostics
Routsias JG, Mavrouli M, Tsoplou P, et al. Diagnostic performance of rapid antigen tests (RATs) for SARS-CoV-2 and their efficacy in monitoring the infectiousness of COVID-19 patients. Sci Rep 11, November 24, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-02197-z
The authors examined the diagnostic performance of RATs from 14 different manufacturers in 400 clinical samples with known rRT-PCR cycles threshold (cT) and 50 control samples. Substantial variability was observed in the limit of detection (LOD) of different RATs (cT = 26.8–34.7). The use of the most effective RATs leads to true positive rates (sensitivities) of 99.1% and 90.9% for samples with cT ≤ 30 and cT ≤ 33, respectively, percentages that can guarantee a sensitivity high enough to identify contagious patients.
Co-morbidities
OnCovid Study Group. Time-Dependent COVID-19 Mortality in Patients With CancerAn Updated Analysis of the OnCovid Registry. JAMA Oncol November 24, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2786537?resultClick=1
In this registry-based study of 2634 patients in 6 European countries with COVID-19 and cancer, there was significant time-dependent improvement in the risk of death. After adjusting for country, sex, age, comorbidities, tumor stage and status, anti–COVID-19 and anti-cancer therapy, and COVID-19 complications, patients diagnosed in the first outbreak had an increased risk of death at 14 days (hazard ratio 1.85, 95% CI: 1.47-2.32) and 3 months (HR 1.28) compared to those diagnosed in the second outbreak.
25 November
Virology
Luu R, Valdebenito S, Scemes E, et al. Pannexin-1 channel opening is critical for COVID-19 pathogenesis. iScience November 19, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01449-8
Panx-1 channels contain one of the largest mammalian pores enabling the release of small ions, nucleotides, lipids, and small RNA into the extracellular space. Under healthy conditions, Panx-1 channels are generally “closed”. This study shows that Panx-1 channels open in response to SARS-CoV-2 or hCoV-229E. SARS-CoV-2 S protein opened Panx-1 channels aggressively and for a prolonged time compared to hCoV-229E.
Vaccines
Kremsner PG, Guerrero RA, Arana-Arri E, et al. Efficacy and safety of the CVnCoV SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine candidate in ten countries in Europe and Latin America (HERALD): a randomised, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet November 23, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00677-0/fulltext
Not good enough. In this large RCT, efficacy of CureVacs mRNA vaccine against symptomatic disease was 52.5%. CVnCoV contains 12 μg of mRNA, considerably less than BNT162b2 (30 μg) and mRNA-1273 (100 μg) contain. The authors “cannot dismiss the possibility that this dose was insufficient to elicit a protective immune response”. It was decided to cease activities on this vaccine candidate, and to focus efforts on next generation vaccine candidates.
Clinical
Faust JS; Chen AJ, Tiako MJ, et al. Leading Causes of Death Among Adults Aged 25 to 44 Years by Race and Ethnicity in Texas During the COVID-19 Pandemic, March to December 2020. JAMA Intern Med November 22, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2786015?resultClick=1
From March through December 2020, COVID-19 was the second leading cause of death among Black, Hispanic, and White residents of Texas aged 25 to 44 years, and the most common cause during the third quarter of 2020, with a markedly disproportionate increase in mortality among Hispanic residents.
Long COVID
Aranda J, Oriol I, Martín M, et al. Long-term impact of COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Infection, Volume 83, Issue 5, 2021, Pages 581-588, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163445321003960
In this prospective and comprehensive follow-up study of patients who developed ARDS during admission for COVID-19, 80% had at least one persistent symptom 8 months after diagnosis. The most common of these were difficulty breathing and joint pain. Of note, 93% had developed a mental health disorder by the same time, 8 months (PTSD, depression, and anxiety).
Co-morbidities
Teixeira AL, Krause TM, Ghosh L, et al. Analysis of COVID-19 Infection and Mortality Among Patients With Psychiatric Disorders, 2020. JAMA Netw Open Novemb 23, 2021;4(11):e2134969. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786468?resultClick=1
This cross-sectional study used an electronic health record data set aggregated from many national sources in the United States. After fully adjusting for demographic factors and co-morbid conditions, patients with schizophrenia were nearly 4 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than the reference group (OR, 3.74; 95% CI: 2.66-5.24). Patients with mood disorders had a 2.76 times greater odds of mortality than the reference group (anxiety disorders 2.39). “Although the explanations for this finding remain elusive, it is tempting to speculate that… chronic low grade inflammation could be one of the mechanisms”.
24 November
Immunology
Pan L, Chiu Y, Huang E, et al. Mass spectrometric identification of immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 epitopes and cognate TCRs. PNAS November 16, 2021. 118 (46) e2111815118; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2111815118
In this elegant work, the authors used major histocompatibility complex immune precipitation, acid elution, and tandem mass spectrometry to define the SARS-CoV-2 immunopeptidome for membrane glycoprotein (MGP) and the nonstructural protein. They verified the immunogenicity of these MS-defined peptides by in vitro generation peptide-specific T cells and confirmed T cell recognition.
Vaccine
Jabagi MJ, Botton J, Bertrand M, et al. Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and Pulmonary Embolism After BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in People Aged 75 Years or Older. JAMA November 22, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2786667?resultClick=1
In a nationwide study involving persons aged 75 years or older in France, no increase in the incidence of acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or pulmonary embolism was detected in the 14 days following each BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine dose.
Variants
Bushman M, Kahn R, Taylor BP, et al. Population impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants with enhanced transmissibility and/or partial immune escape. Cell November 18, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01374-X
Mathematical modeling study, showing that variants with enhanced transmissibility frequently increase epidemic severity, whereas those with partial immune escape either fail to spread widely, or primarily cause breakthrough infections. However, when these phenotypes are combined, a variant can continue spreading even as immunity builds up in the population, limiting the impact of vaccination and exacerbating the epidemic. The findings are consistent with the global sweeps by the highly transmissible variants such as Alpha and Delta, as well as the failure of Beta to reach high frequency in most areas.
Long COVID-19
Li P, Zhao W, Kaatz S, et al. Factors Associated With Risk of Postdischarge Thrombosis in Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open November 22, 2021;4(11):e2135397. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786413?resultClick=1
Among 2,832 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 36 (1.3%) had postdischarge venous thromboembolic events. These events occurred 3-4 times more often in those with a history of venous thromboembolism, peak D-dimer level greater than 3 μg/mL, and predischarge CRP level greater than 10 mg/dL.
Treatment
Clemency BM, Varughese R, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, et al. Efficacy of Inhaled Ciclesonide for Outpatient Treatment of Adolescents and Adults With Symptomatic COVID-19 – A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med November 22, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2786012?resultClick=1
According to this placebo-controlled RCT of 400 patients with symptomatic COVID-19, inhaled corticosteroids (ciclesonide) do not reduce the time to alleviation of all COVID-19–related symptoms. However, the ciclesonide treatment arm had fewer subsequent emergency department visits or hospital admissions for reasons related to COVID-19 (odds ratio, 0.18; 95% CI: 0.04-0.85). No participants died during the study.
23 November
Vaccination
Giddings R, Krutikov M, Palmer T, et al. Changes in COVID-19 outbreak severity and duration in long-term care facilities following vaccine introduction, England, November 2020 to June 2021 separator commenting unavailable. Eurosurveillance November 18, 2021. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.46.2100995
Outbreak severity decreased as LTCF (long-term care facilities) vaccination coverage increased, with an 81% reduction in the number of infected cases per outbreak and a 46% reduction in outbreak duration when comparing outbreaks between November and December 2020 with outbreaks between May and June 2021. However, the last month of the study (June 2021) saw a slight increase in outbreak numbers relative to previous months.
Vaccines
Canaday DH, Oyebanji OA, Keresztesy D, et al. Significant reduction in vaccine-induced antibody levels and neutralization activity among healthcare workers and nursing home residents 6 months following COVID-19 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021;, ciab963, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab963
A marked antibody decline at 6 months post-BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination in 130 nursing home (NH) residents and 95 healthcare workers: anti-spike, receptor-binding domain and neutralization levels dropped > 81% irrespective of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. Notably, 69% of infection-naive NH residents had neutralizing antibodies at or below the limit of detection of the assay.
Diagnostics
Molero-Salinas A, Rico-Luna C, Losada C, et al. High SARS-CoV-2 viral load in travellers arriving in Spain with a negative COVID-19 test prior to departure. Journal of Travel Medicine 16 November 2021, taab180, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab180
Pre-departure testing is not enough. Among a total of 45,211 travelers tested, 196 with negative-COVID-19-tests prior to departure tested positive on arrival at Madrid (April/June 2021). Of note, viral loads (Ct 20.3) were higher compared to the general population (Ct 27.09).
Pediatrics/Pregnancy
DeSisto CL, Wallace B, Simeone RM, et al. Risk for Stillbirth Among Women With and Without COVID-19 at Delivery Hospitalization — United States, March 2020–September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly RepNovember 19, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7047e1.htm?s_cid=mm7047e1_w#suggestedcitation
Although stillbirth was a rare outcome overall, a COVID-19 diagnosis documented during hospitalization delivery was associated with an increased risk for stillbirth in the United States (adjusted relative risk 1.90; 95% CI: 1.69–2.15) with a strong association during the period of Delta variant predominance.
Treatment
Chuah CH, Chow TS, Hor CP, et al. Efficacy of Early Treatment with Favipiravir on Disease Progression among High Risk COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label Clinical Trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 19 November 2021, ciab962, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab962
In an open label study conducted at 14 public hospitals across Malaysia from February to June 2021 among 500 symptomatic COVID-19 patients, aged ≥ 50 years with ≥ 1 co-morbidity, and hospitalized within the first 7 days of illness, there was no effect seen with favipiravir.
22 November
Epidemiology
Worobey M. Dissecting the early COVID-19 cases in Wuhan. Science November 18, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abm4454
Interesting perspective, providing insights on what happened on Huanan Market in December 2019. A new patient zero? More questions than answers.
Gharpure R, Sami S, Vostok J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infections, including COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections, associated with large public gatherings, United States. Emerg Infect Dis November 18, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2801.212220
A large outbreak, occurring in Provincetown, Massachusetts. During July 3–17, thousands of visitors traveled to Provincetown and participated in large, densely packed indoor and outdoor gatherings “marketed to adult male participants” (or “carnival”, see picture below). Multiple continuous events were held at venues such as restaurants, bars, and guest houses. Not the best idea: Among the 1128 cluster-associated primary and secondary cases, the authors identified 918 (81%) vaccine breakthrough cases. This investigation highlights that Delta can spread quickly through a highly vaccinated population and can be transmitted to others regardless of vaccination status. Probably the worst news during these dark days.
Talic S, Shah S, Wild H, et al. Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of covid-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and covid-19 mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ November 18, 2021; 375. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj-2021-068302
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, several personal protective and social measures, including handwashing (relative risk 0.47), mask wearing (0.47), and physical distancing (0.75) were associated with reductions in the incidence of COVID-19. However, owing to the heterogeneity of the studies, meta-analysis was not possible for the outcomes of quarantine and isolation, universal lockdowns, and closures of borders, schools, and workplaces.
Diagnostics
Leuzinger K, Osthoff M, Dräger S, et al. Comparing Immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection in Patients with and without Laboratory-Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin Microbiology November 18, 2021. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JCM.01381-21
No surprise: By cross-comparing eight immunoassays detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) or spike (S) antigens in three cohorts of 859 samples, the authors found marked differences between the assays. However, the discordance among the different antibody assays was most pronounced (30-60%) in the first week after diagnosis and then almost disappeared (less than 10%), independent of the respective assay or platform used.
Collateral damage
Paccou J, Lenne X, Ficheur G, et al. Analysis of Hip Fractures in France During the First COVID-19 Lockdown in Spring 2020. JAMA Netw Open November 17, 2021;4(11):e2134972. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786201?resultClick=1
Hospitalizations for hip fractures in France decreased by 11% during the first nationwide lockdown.
21 November
Today is an immunology special. Two important papers on the impact of HLA genetics and of previous human coronavirus infections on COVID-19 severity. One paper on mitochondrial dysfunction. The other three papers focus on how vaccines work in patients with certain co-morbidities who are at high risk of poor vaccine response: mixed results in patients treated with CAR-T cells, TNF alpha blockers, rituximab, ocrelizumab etc.
Immunology
Francis JM, Leistritz-Edwards D, Dunn A, et al. Allelic variation in class I HLA determines CD8+ T cell repertoire shape and cross-reactive memory responses to SARS-CoV-2. Science Immunology, November 18, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abk3070
Impressive work on CD8+ T cell response to SARS-CoV-2, highlighting the importance of HLA genetics, TCR repertoire diversity, and epitope-specific navigation. The authors not only describe how only some HLA haplotypes are associated with the existence of a pre-existing CD8+ T cell memory pool in unexposed individuals. They also show how HLA variation plays an important role in shaping the diversity of CD8+ T cell repertoires upon exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Abela IA, Pasin C, Schwarzmüller M, et al. Multifactorial seroprofiling dissects the contribution of pre-existing human coronaviruses responses to SARS-CoV-2 immunity. Nat Commun November 18, 2021, 12, 6703. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-27040-x
Previously infected with human coronaviruses? Then you may be lucky. Recording reactivity against all four HCoVs in a huge number of SARS-CoV-2 uninfected and infected individuals, the authors observed intriguing associations: 1. Higher HCoV antibody levels in SARS-CoV-2-negative donors suggest that pre-existing HCoV immunity may provide protection against SARS-CoV-2 acquisition. 2. In those infected, higher HCoV activity was associated with elevated SARS-CoV-2 responses, indicating cross-stimulation. 3. Most importantly, patients with high HCoV reactivity were less likely to require hospitalization.
Medini H, Zirman A, Mishmar D, et al. Immune system cells from COVID-19 patients display compromised mitochondrial-nuclear expression co-regulation and rewiring towards glycolysis. iScience November 17, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01442-5
Significantly reduced mtDNA gene expression in blood, but not in respiratory tract samples from COVID-19 patients, underlines the importance of mitochondrial dysfunction in COVID-19.
Co-morbidities, vaccines
Parvathaneni K, Torres-Rodriguez K, Meng W, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Specific T-Cell Responses in Patients With B-Cell Depletion Who Received Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Treatments. JAMA Oncol November 18, 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2786409?resultClick=1
Small study (n = 12), showing that immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines are induced in most patients who have been treated with CAR-T cell therapies targeting B cell lineage antigens.
Collier AR, Yu J, Mcmahan K, et al. COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Immunogenicity in Immunosuppressed Individuals. J Inf Dis November 18 2021, jiab569, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab569/6430790
This study analyzed 69 participants who were receiving immunosuppressive therapy (IS) for solid organ transplant, bone marrow transplant, and/or chronic inflammatory disease. IS reduced neutralizing, binding, and non-neutralizing antibody functions in addition to CD4 and CD8 T cell IFN-γ responses following mRNA vaccination compared to immunocompetent individuals. Moreover, IS therapy reduced cross-reactivity against SARS-CoV-2 variants. According to the authors, these populations will “likely not be protected by the current two dose regimens of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines”.
Madelon N, Lauper K, Breville G, et al. Robust T cell responses in anti-CD20 treated patients following COVID-19 vaccination: a prospective cohort study, Clinical Infectious Diseases, November 16 2021;, ciab954, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab954
See title. In this small study from Switzerland, response rates of S-specific CD8+ T cells were higher in 26 ocrelizumab-treated (96%) and 11 rituximab-treated patients (82%) as compared to 22 controls (67%). S-specific T cells were polyfunctional but expressed more activation markers in patients than in controls. The authors conclude that this elicited T cell memory response “could reduce complications of SARS-CoV-2 infection in this vulnerable population”.
Chen RE, Gorman MJ, Zhu DY, et al. Reduced antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta virus in serum of mRNA-vaccinated patients receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor-α inhibitors. Med November 17, 2021. https://www.cell.com/med/fulltext/S2666-6340(21)00378-0
In 77 patients with chronic inflammatory diseases treated with immunosuppressive drugs, longitudinal analysis showed the greatest reductions in neutralizing antibodies and Fc effector functions capacity in individuals treated with TNF-α inhibitors (TNFi), and this pattern appeared worse against Delta. Within five months of vaccination, serum neutralizing titers of all TNFi-treated patients tested fell below the presumed threshold correlate for protection. However, TNFi-treated patients receiving a third mRNA vaccine dose boosted their neutralizing antibody titers by more than 16-fold.
20 November
Today is a treatment special. Four huge, high-quality trials with small (aspirin, lopinavir) or no (sarilumab, colchicine) benefits. One study explaining how dexamethasone works and one paper proposing fluvastatin.
Treatment
RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet November 17, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01825-0/fulltext
In this randomised, open-label, platform trial, several possible treatments were compared with usual care in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Among 14,892 patients enrolled, aspirin was not associated with reductions in 28 day mortality or in the risk of progressing to invasive mechanical ventilation or death, but was associated with a small increase in the rate of being discharged alive within 28 days (75% vs 74%; rate ratio 1.06, 95% CI: 1.02–1.10; p = 0.0062).
The CORIMUNO-19 Collaborative group. Sarilumab in adults hospitalised with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 pneumonia (CORIMUNO-SARI-1): An open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Rheumatology November 17, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00315-5/fulltext
Treatment with sarilumab, a high-affinity anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, did not improve early outcomes in patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19 pneumonia.
Labhardt ND, Smit M, Petignat I, et al. Post-exposure Lopinavir-Ritonavir Prophylaxis versus Surveillance for Individuals Exposed to SARS-CoV-2: The COPEP Pragmatic Open-Label, Cluster Randomized Trial. EClinical Medicine November 05, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(21)00469-7/fulltext
Too early to forget lopinavir? In this pragmatic open-label, cluster-randomized trial in Switzerland and Brazil, persons with close contact to a SARS-CoV-2 case were randomized to receive lopinavir/ritonavir PEP (400/100 mg) twice daily for 5 days or no PEP. During 21-day follow-up, 35/209 (16.7%) vs 13/109 (11.9%) developed COVID-19. In the primary endpoint analysis, adjusted for baseline imbalance, the hazard ratio was 0.60 (95% CI: 0.29-1.26; p = 0.18). The authors believe that lopinavir for this indication “merits further testing”.
Absalón-Aguilar A, Rull-Gabayet M, Pérez-Fragoso A, et al. Colchicine Is Safe Though Ineffective in the Treatment of Severe COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial (COLCHIVID). J Gen Intern Med November 9, 2021: 1–11.
See title (RCT in 116 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in Mexico).
Siska PJ, Decking SN, Babl N, et al. Metabolic imbalance of T cells in COVID-19 is hallmarked by basigin and mitigated by dexamethasone. J Clin Invest November 15, 2021. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/148225
This study explains how dexamethasone works in COVID-19, suggesting that effects are at least partially due to an immunometabolic modulation. More specifically, dexamethasone was effective in preventing intracellular reactive oxygen species accumulation (“oxidative stress”) and basigin elevation in T cells, two important hallmarks of severe COVID-19.
Zapatero-Belinchón FJ, Moeller R, Lasswitz L, et al. Fluvastatin mitigates SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung cells. iScience November 17, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01440-1
The authors investigated the effect of statins on SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lung cells and found that only fluvastatin (and not the other statins!) inhibited low and high pathogenic coronaviruses in vitro and ex vivo in a dose-dependent manner. Fluvastatin treatment specifically down-regulated proteins that modulate protein translation and viral replication.
19 November
Virology
Wu H, Xing N, Meng K, et al. Nucleocapsid mutations R203K/G204R increase the infectivity, fitness and virulence of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe November 12, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe/fulltext/S1931-3128(21)00511-4
R203K/G204R are co-occurring mutations in the N protein (another structural protein of the virion) that are rapidly increasing. Using the authentic virus, the authors showed that these mutations increase viral replication, that enhances the infectivity, fitness and virulence of SARS-CoV-2. R203K/G204R increase the sensitivity of virus to neutralizing antibodies, which may be complemented by immune resistance mutations, such as N501Y and E484K.
Diagnostics
Delgado MK, Morgan AU, Asch DA, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of an Automated Text Messaging Service for Monitoring COVID-19 at Home. Annals Int Med November 16, https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-2019
The COVID Watch service consists of twice-daily, automated text message check-ins with an option to report worsening symptoms at any time. All escalations were managed 24 hours a day, 7 days a week by dedicated telemedicine clinicians. In this large observational study, enrollment of outpatients with COVID-19 in this service was associated with reduced mortality, potentially explained by more frequent telemedicine encounters and more frequent and earlier presentation to the ED.
Co-morbidities
Shapiro LC, Thakkar A, Campbell ST, et al. Efficacy of booster doses in augmenting waning immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell November 15, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(21)00606-1#relatedArticles
Anti-COVID-19 immunity dynamics were assessed in patients with cancer in a small cohort. Waning of immunity was detected 4-6 months post-vaccination with significant increases in anti-spike IgG titers after booster dosing, and 56% (18/32) of seronegative patients seroconverted post-booster vaccination. Prior anti-CD20/BTK inhibitor therapy was associated with reduced vaccine efficacy.
Collateral damage
Harris TG, Jaszi E, Lamb MR, et al. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on HIV Services: Findings from 11 Sub-Saharan African Countries. Clinical Infectious Diseases November 15, 2021, ciab951, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab951
Far less damage than expected. While initial declines were observed, rebound was brisk as the pandemic progressed, with increases noted in the number tested, whether newly-initiated HIV or currently on ART, VL testing, and VLS throughout the period, demonstrating substantial HIV program resilience in the face of the COVID-19 crisis.
Treatment
Bierle DM, Ganesh R, Tulledge-Scheitel S, et al. Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of Breakthrough COVID-19 in Fully Vaccinated Individuals with High-Risk Comorbidities. The Journal of Infectious Diseases November 16, 2021, jiab570, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab570
In this large retrospective cohort of fully vaccinated persons, anti-spike monoclonal antibody treatment was significantly associated with a lower risk of hospitalization (Odds Ratio: 0.23; 95% CI: 0.13 – 0.4; p < 0.001). The number needed to treat to prevent one hospitalization was 225 among the lowest-risk patient group compared to NNT of 4 among those with the highest numbers of medical co-morbidities.
18 November
Virology
Giobbe GG, Bonfante F, Jones BC, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication in human gastric organoids. Nat Commun November 16, 12, 6610 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26762-2
This study shows that the virus can efficiently infect the gastric epithelium, suggesting that the stomach might have an active role in fecal-oral SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Immunology
Yoo JS, Sasaki M, Cho SX, et al. SARS-CoV-2 inhibits induction of the MHC class I pathway by targeting the STAT1-IRF1-NLRC5 axis. Nat Commun November 15, 2021, 12, 6602 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26910-8
Important study, providing insights into SARS-CoV-2 immune evasion. SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs the induction of MHC class I gene expression. This impaired upregulation in the airway and intestinal epithelial cells during SARS-CoV-2 infection interferes with the CD8 T cell-dependent cellular immunity, thus causing a higher risk of exacerbation of viral loads and prolonged infection.
Vaccine
Nanisji E, Borriello D, O’Meara TR, et al. An aluminum hydroxide:CpG adjuvant enhances protection elicited by a SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain vaccine in aged mice. Science Translational Medicine November 16, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj5305
The RBD is an attractive candidate for a SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccine and is relatively easy to produce at scale; however, it is poorly immunogenic on its own. complementary approach to increase the immunogenicity of vaccine antigens is the use of adjuvants. Here, the authors evaluated several combinations and found that formulating the TLR9 agonists CpG oligodeoxynucleotides with aluminum hydroxide and RBD dramatically enhanced immune responses toward RBD in young mice in a prime-boost immunization schedule.
Diagnostics
Cromer, D, Steain M, Reynaldi A, et al. Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact of boosting: a meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe November 15, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00267-6/fulltext
The authors integrated data from in-vitro neutralisation assays and efficacy studies incorporating several vaccines in widespread use and used a previously derived model to predict vaccine efficacy from in-vitro neutralisation titre against SARS-CoV-2 variants. „Normalised“ neutralisation titres remain strongly correlated with protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the observed protection was consistent with the predictions of the previous model. The model can predict the efficacy of all existing vaccines against a new variant once the mean decrease in neutralisation titre for the variant compared with ancestral virus has been determined.
Collateral damage
Asch DA, Buresh J, Allison KC, et al. Trends in US Patients Receiving Care for Eating Disorders and Other Common Behavioral Health Conditions Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open November 16, 2021;4(11):e2134913. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786185?resultClick=1
Inpatient stays for eating disorders on the rise. This increase was around two-fold and was seen across anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and other and unspecified eating disorders.
17 November
Epidemiology
Boon SS, Wong MC, Ng RW, et al. Seroprevalence of Unidentified SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Hong Kong During 3 Pandemic Waves. JAMA Netw Open November 15, 2021;4(11):e2132923. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786137
Until April 2021, more than 99.5% of the general population of Hong Kong remained naive to SARS-CoV-2.
Virology
Van Cleemput J, van Snippenberg W, Lambrechts L, et al. Organ-specific genome diversity of replication-competent SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun November 16, 2021, 12, 6612. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26884-7
A detailed virological analysis of 13 post-mortem cases providing proof of viremia and presence of replication-competent SARS-CoV-2 in extrapulmonary organs of immunocompromised patients, including heart, kidney, liver, and spleen. In parallel, the authors found organ-specific SARS-CoV-2 genome diversity and mutations of concern in multiple organs.
Clinical
Akinbami LJ, Biggerstaff BJ, Chan PA, et al. Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 among previously infected healthcare personnel and first responders. Clinical Infectious Diseases November 2021, ciab952, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab952/6428613
Among 1,572 previously infected persons, only 40 (2.5%) were reinfected. Reinfection differed by serostatus: 8.4% among seronegative versus 1.9% among seropositive participants (p < 0.0001).
Co-morbidities
Andersen K, Bates BA, Rashidi ES, et al. Long-term use of immunosuppressive medicines and in-hospital COVID-19 outcomes: a retrospective cohort study using data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative. The Lancet Rheumatology November 15, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00325-8/fulltext
Good news for all who are treated with immunosuppressive drugs. In this propensity score matched cohort (including 12,841 immunosuppressed patients and 29,386 non-immunosuppressed patients), immunosuppression was associated with a reduced risk of invasive ventilation (HR 0.89, 95% CI: 0.83–0.96). With the exception of rituximab (HR 1.72, 1.10–2.69), there was no increased risk of mechanical ventilation or in-hospital death for the rheumatological, antineoplastic, or antimetabolite therapies examined.
Oskotsky T, Marić I, Tang A, et al. Mortality Risk Among Patients With COVID-19 Prescribed Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. JAMA Netw Open November 15, 2021; 4(11):e2133090. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786136?resultClick=1
Interesting finding: In this multicenter cohort study analyzing electronic health records of 83,584 patients diagnosed with COVID-19, including 3,401 patients who were prescribed SSRIs, a reduced relative risk of mortality of 8% was found to be associated with the use of SSRIs—specifically fluoxetine (28%)—compared with patients who were not prescribed SSRIs.
16 November
Transmission
Daniell H, Naur SK, Esmaeili N, et al. Debulking SARS-COV-2 in saliva using angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in the chewing gum to decrease oral virus transmission and infection. Mol Therapy November 10, 2021. https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/molecular-therapy/fulltext/S1525-0016(21)00579-7
Nice idea. Chewing gum with virus trapping proteins offers a general affordable strategy to protect patients from most oral virus reinfections through debulking or minimizing transmission to others.
Clinical
Kaspersen KA, Hindhede L, Boldsen JK, et al. Estimation of SARS-CoV-2 infection fatality rate by age and comorbidity status using antibody screening of blood donors during the COVID-19 epidemic in Denmark. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 12 November 2021, jiab566, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab566
The IFR was low for people younger than 51 years with no co-morbidity during the two waves (combined IFR = 3.36 per 100,000 infections). The IFR was below 3‰ for people aged 61 to 69 years with no co-morbidity. IFR increased with age and co-morbidity but declined from the first to the second wave.
Nayar M, Varghese C, Kanwar A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increased risk of idiopathic acute pancreatitis but not pancreatic exocrine insufficiency or diabetes: long-term results of the COVIDPAN study. Gut. 2021 Nov 11:gutjnl-2021-326218. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34764192. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326218
Patients who were SARS-CoV-2 positive were more likely to have idiopathic acute pancreatitis (34.7% vs 13.9%, p < 0.001) with over five times increased risk after adjusting for age, smoking status, body mass index and ethnicity (OR: 5.34, p < 0.001)
Co-morbidities
Mansoor E, Alikhan MM, Perez JA, et al. Clinical characteristics, hospitalisation and mortality rates of COVID-19 among patients with coeliac disease in the USA: a multicentre network study. Gut. 2021 Nov 11:gutjnl-2021-325930. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34764191. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325930
No elevated risk.
Treatment
Sinha S, Rosin NL, Arora R, et al. Dexamethasone modulates immature neutrophils and interferon programming in severe COVID-19. Nat Med November 15, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01576-3
In severe COVID-19 cases, dexamethasone affected circulating neutrophils, altered the IFNactive state, downregulated interferon-responsive genes and activated IL-1R2+ neutrophils. Dexamethasone also induced the emergence of immature neutrophils expressing ARG1 and ANXA1, genes encoding immunosuppressive molecules, which were absent in healthy controls.
Pediatrics
Chappell H, Patel R, Driessens C, et al. Immunocompromised children and young people are at no increased risk of severe COVID-19. J Infection November 12, 2021. https://www.journalofinfection.com/article/S0163-4453(21)00548-X/fulltext
Only 4/38 PCR detected infections were admitted to hospital. None had acute severe COVID-19 or died.
15 November
Epidemiology
Stafford N. Covid-19: Germany’s doctors call for clear rules to “break chains of infection” as cases soar. BMJ 2021 November 12;375:n2783. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj.n2783
You could call it “urgent”.
Vaccine
Klok FA, Menaka M, Huisman MV, et al. Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Lancet Hamatology, November 11, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanhae/article/PIIS2352-3026(21)00306-9/fulltext
In this Viewpoint, the authors discuss the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and optimal diagnostic and therapeutic management of VITT. The most urgent questions that remain about VITT include the exact pathophysiological mechanism and the long-term management of those who survive VITT. It is uncertain what vaccine components trigger VITT, for example the adenovirus itself or the added ingredients (adjuvant, aluminum, preservatives, etc).
Pavord S, Scully M, Lester W, et al. Just how common is TTS after a second dose of the ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine? The Lancet, November 13, 2021. Volume 398, ISSUE 10313, P1801. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02285-6
The authors feel it is necessary to distinguish TTS, which can have a number of causes, from vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT), which has a very specific immune pathophysiology. They believe that VITT is extremely rare after the second dose of ChAdOx1 nCov-19.
Variants
Zuckerman N, Nemet I, Kliker L, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant and its neutralisation efficiency following vaccination with Comirnaty, Israel, April to June 2021. Euro Surveill November 11, 2021; 26(45):pii=2100974. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.45.2100974
The Lambda variant of interest (VOI) was first detected in Lima, Peru in August 2020. By April 2021, the proportion reached nearly 100% of sequenced genomic isolates detected in Peru. Its spread in South America occurred despite the presence of additional lineages, including Alpha and Gamma. In this study, neutralization assays of the Lambda VOI with sera from 36 individuals vaccinated with two doses of the Comirnaty vaccine demonstrated a subtle yet statistically significant 1.6-fold decrease in neutralization capacity of the Lambda variant compared with the WT SARS-CoV-2 strain. Thus, the vaccine efficacy against the Lambda VOI was similarly compromised as compared with the Delta VOI.
Diagnostics
Van Walle I, Leitmeyer K, Broberg EK, the European COVID-19 microbiological laboratories group. Meta-analysis of the clinical performance of commercial SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid and antibody tests up to 22 August 2020. Euro Surveill November 11, 2021;26(45):pii=2001675. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.45.2001675
This review presents a comprehensive independent overview of clinical performance of commercially available nucleic acid and antibody tests 5 months into the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis was based on more than 110,000 test results reported in 151 publications. Varying levels of performance in terms of sensitivity and specificity were evident. Not surprisingly, reports of performance by manufacturers tended to significantly overestimate actual performance.
Long COVID-19
Petek BJ, Moulson N, Baggish AL, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of persistent or exertional cardiopulmonary symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection in 3597 collegiate athletes: a study from the Outcomes Registry for Cardiac Conditions in Athletes (ORCCA). Br J Sports Med. 2021 Nov 1:bjsports-2021-104644. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2021-104644
In this large registry, persistent symptoms > 3 weeks were present in 44/3529 (1.2%) athletes with 2/3529 (0.06%) reporting symptoms > 12 weeks. Exertional cardiopulmonary symptoms were present in 137/3393 (4.0%) of athletes.
Co-morbidities
Schmidt AL, Tucker MD, Bakouny Z, et al. Association Between Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Mortality Among Patients With Prostate Cancer and COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open November 12, 2021; 4(11):e2134330. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786026?resultClick=1
No association between androgen deprivation therapy and COVID-19 mortality: in this cohort study of 1106 patients, no statistically significant difference was found in the rates of all-cause 30-day mortality following COVID-19 infection among men with prostate cancer receiving androgen deprivation therapy (15%) vs those not receiving androgen deprivation therapy (14%).
14 November
Transmission
Lebreil AL, Greux V, Glenet M, et al. Surfaces and Air contamination by SARS-CoV-2 using High-flow Nasal Oxygenation or Assisted Mechanical Ventilation System in ICU rooms of COVID-19 Patients. The Journal of Infectious Diseases November 12, 2021, jiab564, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab564
In this study, viral RNA environmental contamination was found in 76% of 100 surfaces samples and in 30% of 40 air samples without any viable virus detection by cell culture assays. No significant differences of viral RNA levels on surfaces and in ambient air were observed between rooms of patients with assisted mechanical ventilation and those of patients with high-flow nasal cannula systems.
Vaccine
Angyal A, Longet S, Moore SC, et al. T-cell and antibody responses to first BNT162b2 vaccine dose in previously infected and SARS-CoV-2-naive UK health-care workers: a multicentre prospective cohort study. Lancet Microbe November 09, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00275-5/fulltext
A single dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine is likely to provide greater protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, than in SARS-CoV-2-naive individuals, including against variants of concern.
Johnson S, Martinez CI, Tedjakusuma SN, et al. Oral vaccination protects against SARS-CoV-2 in a Syrian hamster challenge model. The Journal of Infectious Diseases November 10, jiab561, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab561
An oral, adenovirus-based vaccine candidate, protecting Syrian hamsters.
Clinical
Jafar A, Lasso A, Shorr R, et al. Olfactory recovery following infection with COVID-19: A systematic review. PLOS one, November 9, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259321
According to this review of 44 studies, at 6 months the rate of olfactory recovery was as high as 85.7%. Factors such as age, gender, or medical co-morbidities did not play a major role in recovery.
Collateral damage
Peng Y, Wu P, Schartup AT, et al. Plastic waste release caused by COVID-19 and its fate in the global ocean. PNAS November 23, 2021 118 (47) e2111530118; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2111530118
This work shows that more than eight million tons of pandemic-associated plastic waste have been generated globally, with more than 25,000 tons entering the global ocean. Most of the plastic is from medical waste generated by hospitals that dwarfs the contribution from personal protection equipment and online-shopping package material.
13 November
Epidemiology
Ganslmeier M, Furceri D, Ostry JD. The impact of weather on COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Rep November 11, 2021, 22027. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01189-3
Not new: a negative association between temperature and the spread of the virus. However, the empirical evidence of this work suggests that weather’s containment effects are largest at mealtimes, when weather has a substantial impact on the likelihood of social gatherings held indoors versus outdoors. Data also indicate that temperature has larger effects when containment measures are lifted and mobility is greater.
Vaccine
Lazarus R, Baos S, Cappel-Porter H, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of concomitant administration of COVID-19 vaccines (ChAdOx1 or BNT162b2) with seasonal influenza vaccines in adults in the UK (ComFluCOV): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 4 trial. Lancet November 11, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02329-1/fulltext
Paper of the day. In this trial on 679 participants, concomitant vaccination with ChAdOx1 or BNT162b2 plus an age-appropriate influenza vaccine raised no safety concerns and preserved antibody responses to both vaccines.
Montoya JG, Adams AE, Bonetti V, et al. Differences in IgG Antibody Responses following BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. Microbiol Spectr 2021 November 10;e0116221. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/Spectrum.01162-21
In this cohort of 652 clinicians at a non-profit organization, spike protein antibodies were higher with mRNA-1273 than with BNT162b2. This is biologically plausible, not because this was a non-profit organization (like Covidreference.com), but because mRNA-1273 delivers a larger amount of mRNA (100 μg mRNA) than BNT162b2 (30 μg mRNA), which is translated into spike protein.
Long COVID-19
Xie Y, Bowe B, Al-Aly Z. Burdens of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 by severity of acute infection, demographics and health status. Nat Commun November 11, 2021, 12, 6571. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26513-3
Using the healthcare databases of the US Department of Veterans Affairs to build a cohort of 181,384 people with COVID-19 and 4,397,509 non-infected controls, the authors estimate that post-acute sequelae – defined as at least one sequela in excess of a non-infected control group—was 73 per 1000 persons at 6 months. The burden of PASC increased as a function of the severity of the acute infection at 45, 217, and 360 per 1000 persons at 6 months among non-hospitalized, hospitalized, and those who were admitted to intensive care during the first 30 days of infection, respectively.
Treatment
Mazeraud A, Jamme M, Mancusi RL, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulins in patients with COVID-19-associated moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ICAR): multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respiratory Diseases, November 11, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00440-9/fulltext
No benefit with IVIG in 146 COVID-19 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation for moderate-to-severe ARDS.
Epidemiology (2)
No good prospects these days in Europe.
12 November
Vaccine
Ella R, Reddy S, Blackwelder W, et al. Efficacy, safety, and lot-to-lot immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBV152): interim results of a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet November 11, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02000-6/fulltext
BBV152 is a whole virion inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine formulated with a toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist molecule adsorbed to alum. In this large RCT in Indian adults, 24 (0.3%) cases occurred among 8471 vaccine recipients and 106 (1.2%) among 8502 placebo recipients, giving an overall estimated vaccine efficacy of 77.8% (95% CI 65.2–86.4). Efficacy against severe COVID-19 was 93.4% (57.1–99.8). The authors found no major differences in immune responses across the broad age groups of younger (<60 years) and older (≥60 years) participants. A preliminary analysis showed an efficacy of 65.2% (95% CI 33.1–83.0) against the Delta variant.
Kaplan Meier plot of first occurrence of RT-PCR-confirmed symptomatic cases of COVID-19
Variants
McCallum M, Walls AC, Sprouse KR, et al. Molecular basis of immune evasion by the Delta and Kappa SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science, November 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl8506
In late 2020, B.1.617 variants including B.1.617.1 (Kappa) and B.1.617.2 (Delta) were first detected in India. Mutations in the Kappa and Delta spike glycoproteins abrogate recognition by several monoclonal antibodies via alteration of key antigenic sites, including remodeling of the Delta N-terminal domain.
Co-morbidities
Ooszing SF, van der Veldt AA, van Kessel CH, et al. mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccination in patients receiving chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or chemoimmunotherapy for solid tumours: a prospective, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncology November 09, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(21)00574-X/fulltext
The VOICE trial was the first prospective COVID-19 vaccination trial in patients with solid tumours: the vast majority developed an adequate antibody response to vaccination with mRNA-1273 (MODERNA). However, 9 (7%) of 131 of the patients treated with immunotherapy, 37 (16%) of 229 of the patients treated with chemotherapy, and 16 (11%) of 143 of the patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy were classified as suboptimal responders or non-responders compared with one (<1%) of 240 of the participants without cancer.
Mahil SK, Bechman K, Raharja A, et al. Humoral and cellular immunogenicity to a second dose of COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 in people receiving methotrexate or targeted immunosuppression: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Rheumatology November 09, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00333-7/fulltext
Functional humoral immunity (ie, neutralising antibody responses) at 14 days following a second dose of BNT162b2 was not impaired by methotrexate or targeted biologics. A proportion of patients on immunosuppression did not have detectable T-cell responses following the second dose.
Pediatrics
Smith C, Odd D, Harwood R, et al. Deaths in children and young people in England after SARS-CoV-2 infection during the first pandemic year. Nat Med November 11, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01578-1
Of 12,023,568 children and young people (CYP, <18 years old) living in England, 3,105 died, including 61 who were positive for SARS-CoV-2. Of these deaths, 25 were due to SARS-CoV-2 infection (mortality rate, two per million), including 22 due to COVID-19. Three were due to PIMS. CYP older than 10 years, Asian and Black ethnic backgrounds and comorbidities were over-represented in SARS-CoV-2-related deaths compared with other CYP deaths.
Collateral damage (and benefits)
Grunert KG, Janssen M, Nyland Christensen R, et al. “Corona Cooking”: The interrelation between emotional response to the first lockdown during the COVID-19 pandemic and cooking attitudes and behaviour in Denmark. Food Qual Prefer. 2022 Mar;96:104425. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34629761. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104425
Believe it or not. It appears that the pandemic helped some people rediscover their liking for home cooking and meals at home.
11 November
Vaccine
Walter EB, Talaat KR, Sabharwal C, et al. Evaluation of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children 5 to 11 Years of Age. NEJM November 9, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116298?query=featured_home
Paper of the day. Vaccination regimen consisting of two 10-μg doses of BNT162b2 administered 21 days apart was found to be safe, immunogenic, and efficacious in children 5 to 11 years of age. Among 2268 children, COVID-19 with onset 7 days or more after the second dose was reported in 3 recipients of the BNT162b2 vaccine and in 16 placebo recipients (vaccine efficacy, 90.7%; 95% CI, 67.7 to 98.3).
Variants
de Gier B, Stijn A, Backer JA, et al. Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 transmission to household contacts during dominance of Delta variant (B.1.617.2), the Netherlands, August to September 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(44):pii=2100977. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.44.2100977
Vaccination confers protection against onward transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from vaccinated index cases, albeit somewhat less for the Delta than for the Alpha variant.
Diagnostics
Puyskens A, Krause E, Michel J, et al. Establishment of a specimen panel for the decentralised technical evaluation of the sensitivity of 31 rapid diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2 antigen, Germany, September 2020 to April 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(44):pii=2100442. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.44.2100442
The sensitivity of the 31 rapid tests evaluated here varied extensively and depended largely on the virus load in the respective specimen. While four RDT showed a sensitivity of > 80% over the whole range of virus loads investigated, 26 RDT had a sensitivity of > 80% for potentially infectious specimens, indicating that sensitive RDT can be used to identify contagious individuals in various settings, but not to identify infected individuals with lower virus loads.
Clinical
Vihta KD, Powers KB, Peto T, et al. Symptoms and SARS-CoV-2 positivity in the general population in the UK. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 08 November 2021, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab945
After May-2021 when Delta emerged, headache and fever substantially increased in PCR-positives, but not PCR-negatives. Sensitivity of symptom-based detection increased from 74% using ‘classic’ symptoms, to 81% adding fatigue/weakness, and 90% including all eight additional symptoms.
Co-morbidities
Spanjaart AM, Ljungman P, de La Camara R, et al. Poor outcome of patients with COVID-19 after CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell malignancies: results of a multicenter study on behalf of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Infectious Diseases Working Party and the European Hematology Association (EHA) Lymphoma Group. Leukemia November 8, 2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01466-0
At the time of analysis, 25 of 56 patients had died (45%), the vast majority (23 of 25) due to COVID-19, resulting in a COVID-19 attributable mortality rate of 41%.
10 November
Virology
Syed AM, Taha TY, Tabata T, et al. Rapid assessment of SARS-CoV-2 evolved variants using virus-like particles. Science, November 4, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl6184
The authors present a new strategy for rapidly generating and analyzing SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles that package and deliver exogenous mRNA. This approach allows examination of viral assembly, budding, stability, maturation, entry and genome uncoating involving all of the viral structural proteins without generating replication-competent virus.
Immunology
Kojima N, Klausner JD. Protective immunity after recovery from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Inf Dis November 08, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00676-9/fulltext
Remarkable conclusion. After reviewing studies published in PubMed from inception to Sept 28, 2021, Noah Kojima and Jeffrey Klausner believe that „clinicians should remain optimistic regarding the protective effect of recovery from previous infection“.
Co-morbidities
Felten R, Gallais F, Schleiss C, et al. Cellular and humoral immunity after the third dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients treated with rituximab. Lancet Rheumatology, November 08, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00351-9/fulltext
The authors investigated the course of humoral and cellular immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in 10 patients treated with rituximab after two and three vaccine doses. Median time between last rituximab infusion and first dose of vaccine was 227 days. The 3 seronegative patients and those with B-cell depletion after two doses remained seronegative after the third dose.
Treatment
Pulvirenti F, Milito C, Cinetto F, et al. SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination therapy in patients with COVID-19 and primary antibody deficiency. J Inf Dis, November 8, 2021. https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab554/6423060
In this small prospective study on clinical outcome and antiviral effect of mAbs added to standard of care therapy in 18 patients with Primary Antibody Defects, median time of SARS-CoV-2 qPCR positivity was shorter in eight patients treated with mAbs (22 days) than in ten patients treated with standard of care therapy only (37 days, p=0.026).
9 November
Virology
Weigang S, Fuchs J, Zimmer G, et al. Within-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunosuppressed COVID-19 patient as a source of immune escape variants. Nat Commun November 4, 2021, 12, 6405. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26602-3
Virus genomic changes in an immunosuppressed kidney transplant recipient who acquired SARS-CoV-2 during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. The patient had mild respiratory symptoms and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 for more than 145 days. During this long period, viruses with multiple amino acid substitutions and deletions in the spike protein evolved.
Vaccine
Aguas R, Bharath A, White LJ, et al. Potential global impacts of alternative dosing regimen and rollout options for the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine. Nature Commun November 4, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26449-8
Using data from clinical trials, an individual-based model was constructed to predict its 6-month population-level impact. The main result: in scenarios where the availability of vaccine is insufficient for high-risk groups to receive two doses, administration of a single dose is optimal, even when vaccine efficacy after one dose is just 75% of the two doses.
Mizrahi B, Lotan R, Kalkstein N, et al. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2-breakthrough infections to time-from-vaccine. Nat Commun November 4, 2021, 12, 6379. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26672-3
Leveraging the centralized computer database of Maccabi Healthcare Services, the authors assessed the correlation between time-from-vaccine and incidence of breakthrough infection between June 1 and July 27, 2021. There was a significant correlation between time-from-vaccine and afforded protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. The risk for breakthrough infection was significantly higher for longer time-from-vaccine recipients compared with those who were vaccinated more recently, with an additional trend for higher risk for hospitalization among the longer time-from-vaccine recipients.
Clinical
Islam N, Jdanov DA, Shkolnikov VM, et al. Effects of covid-19 pandemic on life expectancy and premature mortality in 2020: time series analysis in 37 countries. BMJ, 03 November 20212021; 375 https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj-2021-066768
More than 28 million excess years of life were lost in 2020 in 31 countries, with a higher rate in men than women. Excess years of life lost associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 were more than five times higher than those associated with the seasonal influenza epidemic in 2015. The highest reduction in life expectancy was observed in Russia (men: −2.33, women: −2.14), the United States (men: −2.27, women: −1.61), Bulgaria, Lithuania, Chile, and Spain.
Co-morbidities
Ferreira VH, Marinelli T, Ierullo M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces greater T-cell responses compared to vaccination in solid organ transplant recipients. J Inf Diseases 05 November 2021,, jiab542, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab542/6406613
Solid organ transplant recipients generate robust T cell responses following natural infection that correlate with disease severity but generate comparatively lower T cell responses following mRNA vaccination.
8 November
Vaccine
McNamara LA, Wiegand RE, Burke RM, et al. Estimating the early impact of the US COVID-19 vaccination programme on COVID-19 cases, emergency department visits, hospital admissions, and deaths among adults aged 65 years and older: an ecological analysis of national surveillance data. Lancet November 03, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02226-1/fulltext
Vaccines are working at the population level. The initial phases of the US COVID-19 vaccination program were associated with reductions in COVID-19 cases, emergency department visits, and hospital admissions among US adults aged 65 years and older. COVID-19 deaths also declined.
Co-morbidities
Pinato DJ, Tabernero J, Bower M, et al. Prevalence and impact of COVID-19 sequelae on treatment and survival of patients with cancer who recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection: evidence from the OnCovid retrospective, multicentre registry study. Lancet Oncology November 3, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(21)00573-8/fulltext
In this registry, 1557 COVID-19 survivors underwent a formal clinical reassessment after a median of 22 months post cancer diagnosis and 44 days post COVID-19 diagnosis. Sequelae post-COVID-19 affected up to 15% of patients with cancer and adversely affected survival and oncological outcomes after recovery.
Sattui SE, Conway R, Putman MS, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with primary systemic vasculitis or polymyalgia rheumatica from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registry: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatology November 05, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00316-7/fulltext
A total of 374 (31%) patients had polymyalgia rheumatica, 353 (29%) had ANCA-associated vasculitis, 183 (15%) had giant cell arteritis, 112 (9%) had Behçet’s syndrome, and 180 (15%) had other forms of vasculitis. Severe COVID-19 outcomes were associated with variable and largely unmodifiable risk factors, such as age, sex, and number of co-morbidities as well as treatments, including high-dose glucocorticoids.
Treatment
Cox RM, Wolf JD, Lieber CM, et al. Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets. Nat Commun November 5, 2021, 12, 6415. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26760-4
Remdesivir is an antiviral approved for COVID-19 treatment, but its wider use is limited by intravenous delivery. This study has characterized the anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of GS-621763, an oral prodrug of remdesivir parent nucleoside GS-441524. Twice-daily oral reduced SARS-CoV-2 burden to near-undetectable levels in ferrets.
Pediatrics
Conti MG, Terreri S, Mortari EP, et al. Immune Response of Neonates Born to Mothers Infected With SARS-CoV-2. JAMA Netw Open November 3, 2021;4(11):e2132563. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785791?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 21 mothers who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 at delivery and their 22 newborns, there was one case of potential mother-infant vertical virus transmission and one case of horizontal virus transmission. Infants who received breastmilk during the first 2 months of life had significantly higher spike-specific salivary IgA antibody levels compared with formula-fed infants.
7 November
Vaccine
Tenforde M, Self WH, Adams K, et al. Association Between mRNA Vaccination and COVID-19 Hospitalization and Disease Severity. JAMA November 4, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2786039?resultClick=1
In this case-control study that included 4513 hospitalized adults in 18 US states, hospitalization for a COVID-19 diagnosis compared with an alternative diagnosis was associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 0.15 for full vaccination with an authorized or approved mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
Eliakim-Raz N, Leibovici-Weisman Y, Stemmer A, et al. Antibody Titers Before and After a Third Dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 Vaccine in Adults Aged ≥60 Years. JAMA November 5, 2021 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2786096?resultClick=1
This study on 97 adults aged 60 years and older found that a third BNT162b2 dose was associated with significantly increased IgG titers after 10 to 19 days, with no major adverse events.
Rahav G, Lustig Y, Lavee J, et al. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in immunocompromised patients: A prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Nov;41:101158. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101158. Epub 2021 Oct 17. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34693234/
In this large cohort from Israel, antibody response to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was highly variable among different immune deficiencies. RBD-IgG antibodies were detected in 154/156 (98.7%) of patients with HIV, but only in 96/188 (51.0%) of those with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and in 50/110 (45.5%) of patients following kidney transplantation.
Variants
Uriu K, Kimura I, Shirakawa K, et al. Neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Mu Variant by Convalescent and Vaccine Serum. NEJM November 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2114706?query=featured_home
Mu (B.1.621) represents the most recently recognized variant of interest. The epicenter of mu transmission is Colombia, where the variant has outnumbered all other variants, including Gamma. This work shows that mu has a pronounced resistance to antibodies elicited by natural SARS-CoV-2 infection and by the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
Treatment
Li T, Han X, Gu C, et al. Potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies with protective efficacy against newly emerged mutational variants. Nat Commun November 2021, 12, 6304. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26539-7
New potent neutralizing Abs with unique mechanism targeting variants. 58G6 and 13G9 both recognize the steric region S470–495 on the RBD, overlapping the E484K mutation presented in B.1.351. In mice, 58G6 and 510A5 demonstrate prophylactic efficacy against authentic SARS-CoV-2 and B.1.351.
6 November
Immunology
Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, et al. Association of Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection With Risk of Breakthrough Infection Following mRNA Vaccination in Qatar. JAMA Network November 1, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2785918?resultClick=1
A hybrid of natural and vaccine immunity appears to be associated with additional reduction in breakthrough infection. In this cohort study of 1 531 736 mRNA-vaccinated individuals in Qatar, prior SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a statistically significant reduced hazard of breakthrough infection among recipients of both the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech, adjusted hazard ratio, 0.62) and the mRNA-1273 vaccines (Moderna, adjusted hazard ratio, 0.40). However, the observational study design precludes direct comparison of infection risk between the 2 vaccines.
Zhong D, Xiao S, Debes AK, et al. Durability of Antibody Levels After Vaccination With mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Individuals With or Without Prior Infection. JAMA November 1, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2785919?resultClick=1
Same direction. Health care workers with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection followed by 2 doses of mRNA vaccine (3 independent exposures to spike antigen) developed higher spike antibody measurements than individuals with vaccination alone. A longer interval between infection and first vaccine dose may enhance the antibody response.
Vaccine
Woodworth KR, Moulia D, Collins JP, et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ Interim Recommendation for Use of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine in Children Aged 5–11 Years — United States, November 2021. MMWR 5 November 2021. DOI: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7045e1.htm?s_cid=mm7045e1_w#suggestedcitation
Interim recommendation for use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in children aged 5–11 years in the United States for prevention of COVID-19.
Co-morbidities
Sherman AC, Desjardins M, Cheng CA, et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity. Clinical Infectious Diseases November 2, 2021, ciab930, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab930
Small study, showing that not all of 20 HSCT recipients mount a humoral response (Simoa: 75.0% and Roche: 80.0%) one month after completing the mRNA vaccination series.
Treatment
Ezer N, Belga S, Daneman N, et al. Inhaled and intranasal ciclesonide for the treatment of covid-19 in adult outpatients: CONTAIN phase II randomised controlled trial. BMJ 02 November 2021; 375 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2021-068060
No effect with ciclesonide (a corticosteroid used in inhaled form to treat asthma and intranasally to treat allergic rhinitis) in this RCT in 203 healthier young adults with covid-19 presenting with prominent respiratory symptoms.
5 November
Epidemiology
Trauer JM, Lydeamore MJ, Dalton GW, et al. Understanding how Victoria, Australia gained control of its second COVID-19 wave. Nat Commun November 1, 2021, 12, 6266. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26558-4
Face coverings had a considerably greater effect on reversing the epidemic than behavioural changes. Individual-level effect of physical distancing was 37.4% (95%CrI 7.2−56.4%) and 45.9% (95%CrI 32.9−55.6%) of face coverings.
Virology
Khan M, Yoo SJ, Clijsters M, et al. Visualizing in deceased COVID-19 patients how SARS-CoV-2 attacks the respiratory and olfactory mucosae but spares the olfactory bulb. Cell November 02, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.027
SARS-CoV-2 does not appear to be a neurotropic virus. This cohort of 85 cases included COVID-19 patients who died a few days after infection with SARS-CoV-2, enabling the authors to catch the virus while it was still replicating. They found that sustentacular cells are the major target cell type in the olfactory mucosa, but failed to find evidence for infection of olfactory sensory neurons. The parenchyma of the olfactory bulb was spared as well.
Vaccine
Bosch W, Cowart JB, Bhakta S, et al. COVID-19 Vaccine-Breakthrough Infections Requiring Hospitalization in Mayo Clinic Florida through August 2021. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2 November 2021, ciab932, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab932/6415962
Of 1089 breakthrough infections occurring after May 2, 2021, 12% (n=126) required hospitalization. When compared to unvaccinated COVID-19 admissions, vaccine breakthrough admissions were older in age (mean 69.1 vs. 59.6 years, p<0.001), more likely to be immunocompromised (33.3% vs. 14.8%); p<0.001) and had a higher COVID-19 Complication Risk score. In addition, the vaccinated cohort was more likely to have diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease.
Ashrani AA, Crusan DJ, Petterson T, et al. Age- and Sex-Specific Incidence of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Associated With Ad26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccination. JAMA Intern Med November 1, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2785610?resultClick=1
Most CVST events occurred within 15 days after vaccination. The highest risk was among women aged 30 to 49 years, but the absolute CVST risk was still low in this group (up to 29.5 per 100 000 PY among women aged 40-49 years).
Co-morbidities
Embi PJ, Levy ME, Naleway AL, et al. Effectiveness of 2-Dose Vaccination with mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines Against COVID-19–Associated Hospitalizations Among Immunocompromised Adults — Nine States, January–September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 2 November 2021. DOI: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7044e3.htm?s_cid=mm7044e3_w
In this multistate analysis of approximately 89,000 hospitalizations of adults with COVID-19–like illness during January 17–September 5, 2021, effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was lower (77%) among immunocompromised adults than among immunocompetent adults (90%). VE was lower among certain subgroups of immunocompromised adults, such as solid organ or stem cell transplant recipients, than among others.
4 November
Another Delta special today. More arguments for a third jab, interesting data on vaccine effectiveness (VE) from Qatar and from England, the effectiveness of J&J’s vaccine in times of Delta and a paper characterizing breakthrough infections with the variant.
Saciuk Y, Kertes J, Stein NS, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. The J Inf Dis November 1, 2021, jiab556, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab556/6415586
More arguments for a third jab these days. Israel experienced a new wave of largely Delta variant-based infection from mid-June 2021. The Israel Ministry of Health implemented a second national vaccination campaign in August 2021, providing a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine, initially targeting the over-60s, then broadening the target population age bracket on a week-by-week basis. Crude VE was 92.9% (95% CI: 92.6-93.2%) and adjusted VE was 89.1% (95% CI: 87.5-90.5%).
Tang P, Hasan MR, Chemaitelly H. et al. BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in Qatar. Nat Med November 2, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01583-4
BNT162b2 effectiveness against any Delta infection, symptomatic or asymptomatic, was only 51.9% (95% CI: 47.0–56.4%) ≥ 14 d after the second dose. Corresponding mRNA-1273 effectiveness was 73.1% (95% CI: 67.5–77.8%). Notably, effectiveness against Delta-induced severe, critical or fatal disease was 93.4% (95% CI: 85.4–97.0%) for BNT162b2 and 96.1% (95% CI: 71.6–99.5%) for mRNA-1273 ≥ 14 d after the second dose.
Elliott P. Haw D, Wang H, et al. Exponential growth, high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2, and vaccine effectiveness associated with the Delta variant. Science November 2, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl9551
After adjusting for age and other variables, vaccine effectiveness for double-vaccinated people was estimated at between ~50% and ~60% during June/July in England. Important conclusion: “Without additional interventions, increased mixing, including indoors, during the autumn and winter in the presence of the Delta variant may lead to renewed growth, even at high levels of vaccination”. Forget your freedom day.
Corchado-Garcia J, Zemmour D, Hughes T, et al. Analysis of the Effectiveness of the Ad26.COV2.S Adenoviral Vector Vaccine for Preventing COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open November 2, 2021;4(11):e2132540. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785664?resultClick=1
The J&J vaccine is effective at reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection, even with the spread of variants such as Alpha or Delta that were not present in the original studies. In this cohort consisting of 8889 vaccinated and 88,898 unvaccinated matched patients, VE was 73.6%.
Levine-Tiefenbrun M, Yelin I, Alapi H. et al. Viral loads of Delta-variant SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections after vaccination and booster with BNT162b2. Nat Med November 2, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01575-4
Breakthrough infections (BTIs) in recently fully vaccinated individuals have lower viral loads (with a magnitude of ten-fold) than infections in unvaccinated individuals. However, this effect starts to decline 2 months after vaccination and ultimately vanishes 6 months or longer after vaccination. Notably, the authors find that the effect of BNT162b2 on reducing BTI viral loads is restored after a booster dose.
3 November
Today we have a co-morbidity special. Papers on the management of STEMI, of cancer and of urgent surgical cases during the pandemic. Immunogenicity rates after vaccination in people with end-stage kidney disease and with HIV.
Co-morbidities
Saad M, Kennedy KF, Imran H, et al. Association Between COVID-19 Diagnosis and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JAMA October 29, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2785893?resultClick=1
Not so surprising: among patients with STEMI, a concomitant diagnosis of COVID-19 was associated with significantly higher rates of in-hospital mortality.
Gitajn IL, Werth PM, Sprague S, et al. Association of COVID-19 With Achieving Time-to-Surgery Benchmarks in Patients With Musculoskeletal Trauma. JAMA Health Forum October 29, 2021, 2(10):e213460. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/2785581?resultClick=1
This cohort study counters concerns that the unprecedented challenges associated with managing the COVID-19 pandemic would be associated with clinically significant delays in acute management of urgent surgical cases. In the US, there was no association between meeting time-to-surgery benchmarks in either open fracture or closed femur/hip fracture during the COVID-19 pandemic compared with before the pandemic.
Chen JJ, Lee TH, Tian YC, et al. Immunogenicity Rates After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in People With End-stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open, October 28, 2021; 4(10):e2131749. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785567?resultClick=1
This systematic review suggests that the immunogenicity rate among patients receiving dialysis was 41% after the first dose and 89% after the second dose. Diabetes might be a risk factor for non-response in the dialysis population. Patients receiving dialysis had a poorer antibody response rate than did individuals not receiving dialysis.
Chavez-MacGregor M, Lei X, Zhao H, et al. Evaluation of COVID-19 Mortality and Adverse Outcomes in US Patients With or Without Cancer. JAMA Oncol October 28, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2785677?resultClick=1
With regard to COVID-19 severity, patients with cancer represent a heterogenous group. In this large cohort of patients with COVID-19, those with recent cancer treatment had significantly higher rates of adverse outcomes compared with patients without cancer. In the fully adjusted models, however, only patients with recent cancer treatment had a statistically significant increase in the 30-day risk of death, ICU stay, and hospitalization. Patients with no recent cancer treatment had similar or even lower risks.
Noe S, Ochana N, Wiese C, et al. Humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in people living with HIV. Infection October 25, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-021-01721-7
In this cohort study from Munich, Germany, mRNA-containing vaccination schemes, being female, and having a higher CD4 cell count were all associated with a higher concentration of COVID antibodies in people living with HIV.
2 November
Today we’ll have an Immunology special. The largest study by far on antibody kinetics in COVID-19 patients; studies explaining how the virus evades T cell responses; and why some healthy young people develop severe disease. Data on the inflammatory landscape of COVID-19 in pregnancy as well as on antibodies derived from horses.
Wei J, Matthews PC, Stoesser N, et al. Anti-spike antibody response to natural SARS-CoV-2 infection in the general population. Nat Commun 12, 6250 (2021) 29 October 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26479-2
An incredibly huge dataset from a national UK survey to determine predictors of seroconversion following a positive PCR test. Around 1 in 4 people did not develop anti-spike IgG antibodies following a positive PCR test in regular screening. Non-responders were more likely to be older and not report symptoms. Among participants who seroconvert, anti-spike IgG antibodies remained above the positivity threshold for an average of 380–590 days for 20-year-olds, and 471–755 days for 80-year-olds. The rate of antibody decline slowed over time. Overall, at least in the short-term, protection against re-infection appears high.
De Silva IT, Liu G, Lindsey BB, et al. The impact of viral mutations on recognition by SARS-CoV-2 specific T-cells. iScience October 27, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01322-5
How the virus evades the T cell response. This international collaboration identified amino acid variants within dominant SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes by interrogating global sequence data. Several variants within nucleocapsid and ORF3a epitopes have arisen independently in multiple lineages and have resulted in loss of recognition by epitope-specific T cells assessed by IFN-γ and cytotoxic killing assays.
Sheward DJ, Mandolesi M, Urgard E, et al. Beta RBD Boost Broadens Antibody-Mediated Protection Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Animal Models. Cell Reports Medicine October 22, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00318-9
It is not yet clear whether heterotypic boosts would be compromised by original antigenic sin, where pre-existing responses to a prior variant dampen responses to a new one. This work indicates that this may not be the case. In macaques immunized with Wu-Hu-1 spike, a single dose of adjuvanted Beta variant receptor binding domain (RBD) protein broadened neutralizing antibody responses to heterologous VOCs.
Cunha LE, Stolet AA, Strauch MA, et al. Polyclonal F(ab’)2 fragments of equine antibodies raised against the spike protein neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants with high potency. iScience October 23, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01284-0
Trimeric spike glycoprotein induces a high level of horse neutralizing antibodies, supporting the possibility of using equine F(ab’)2 preparation for the clinical treatment of COVID patients.
Foo SS, Cambou MC, Mok T, et al. The systemic inflammatory landscape of COVID19 in pregnancy: Extensive serum proteomic profiling of mother-infant dyads with in-utero SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep Med Oct 26, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00321-9
Comprehensive characterization of the systemic immunity of COVID-19+ pregnancies (93 COVID-19 mothers and 45 of their SARS-CoV-2-exposed infants) revealed distinct alterations of SARS-CoV-2-driven immune landscapes in mother-infant pairs which may explain some of the adverse clinical outcomes associated with severe/critical COVID-19 infection in pregnancy.
Lloréns-Rico V, Gregory AC, Van Weyenbergh J et al. Clinical practices underlie COVID-19 patient respiratory microbiome composition and its interactions with the host. Nat Commun 29 October 2021, 12, 6243 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26500-8
Does the respiratory microbiome play a role in disease progression? Several studies have reported contradictory results. The present study indicates that confounders are driving these contradictory results. Time in the intensive care unit and type of oxygen support, as well as associated treatments such as antibiotic usage, explain the most variation within the upper respiratory tract microbiome, while SARS-CoV-2 viral load has a reduced impact.
Carapito R, Li R, Helms J, et al. Identification of driver genes for critical forms of COVID-19 in a deeply phenotyped young patient cohort. Science Translational Medicine, 26 October 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7521
Why does the course of the disease show such marked differences? It’s the genome. Within a young, otherwise healthy, cohort of individuals with COVID-19, the authors provide the landscape of biological perturbations in vivo where a unique gene signature differentiated critical from non-critical patients. The paper identified ADAM9, a metalloprotease with various functions, as a driver of disease severity and a candidate therapeutic target.
Saker K, Escuret V, Pitiot V, et al. Evaluation of commercial anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody assays and comparison of standardized titers in vaccinated healthcare workers. J Clin Microbiol October 27, 2021. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JCM.01746-21
Antibody titers were measured in 255 sera (from 150 HCW) with 5 quantitative immunoassays (Abbott RBD IgG II quant, bioMérieux RBD IgG, DiaSorin Trimeric spike IgG, Siemens Healthineers RBD IgG, Wantai RBD IgG). Although there was 100% seroconversion with all assays, the titer count differed considerably (up to 60%). The authors conclude that a “true standardization” of the assays would be to include the International Standard in the calibration of each assay to express the results in IU/mL.
1 November

Today we’ll have a special for Joshua Kimmich, the Bayern star who remains unvaccinated due to ‘personal concerns’ he had over vaccines. In particular, he has claimed concerns “about the lack of long-term studies”. We truly respect this differentiated opinion and are happy to learn he is interested in science and in clinical data. Thus, we dedicate today’s top news to him (and have anticipated some of his comments).
Transmission
Dixon BC, Fischer RS, Zhao H, et al. Contact and SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among College Football Athletes in the Southeastern Conference During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open October 29, 2021;4(10):e2135566. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785602?resultClick=1
Good news first: Low risk during the match. In this analysis of US college athletes playing regular season football games during the COVID-19 pandemic, no instances of in-game SARS-CoV-2 transmission was found. Despite 12% of athletes testing positive for SARS-CoV-2, only 18 had competed during the preceding 48 hours, and no downstream infections to members of the opposing team were seen.
Pauser J, Schwarz C, Morgan J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 transmission during an indoor professional sporting event. Sci Rep October 20, 11(1):20723. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8528911/
But please, Joshua, don’t play indoors (at least not basketball). In total, 69 people were present at the 2nd division match of the German professional club basketball (21 players and 48 staff). After the event, one player of team B reported that he developed non-specific symptoms of a respiratory tract infection. Results, despite “standard hygiene concepts”: at least 36 infections (three severe).
Bown JC, Moshe M, Blackwell A, et al. Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 in chlorinated swimming pool water. Water Res October 15, 2021. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34619607/
Swimming is ok. This study found that chlorinated water that adheres to UK swimming pool guidelines is sufficient in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infectious titer by at least 3 orders of magnitude.
Variants
Horiuchi S, Oishi K, Carrau L, et al. Immune memory from SARS-CoV-2 infection in hamsters provides variant-independent protection but still allows virus transmission. Science Immunology October 26, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abm3131
Re-infection of recovered animals with a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern showed that SARS-CoV-2-specific T and B cells could effectively control the infection associated with the rapid induction of neutralizing antibodies but failed to block transmission to both naïve and seroconverted animals. (It is expected that Joshua may conclude that “hamsters are not humans”).
Kant R, Nguyen PT, Blomqvist S, et al. Incidence trends for SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Beta variants, Finland, spring 2021. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 October 27. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/12/21-1631_article
Alpha and Beta variants became dominant in Finland in spring 2021 but diminished by summer. Outbreaks were mostly seeded by a few introductions. (Joshua may point out that this is not of interest because no club from Finland has reached the Champions league).
Bugembe DL, Phan MVT, Abias AG, et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, South Sudan, January–March 2021. Emerg Infect Dis October 27, 2021.
Patterns of SARS-CoV-2 viral genomics in South Sudan in the second wave of infections during February–March 2021, showing circulation of B.1.525 (Eta) as well as the variant A.23.1. The B.1.525 genome encodes a deletion in the N-terminal domain (NTD) at spike positions 69 and 79, as well as being present in B.1.1.7 and many other global variants. A deletion in the spike NTD at positions 141–146 may help in evasion of host immune responses. (Same. South Sudan has presumably never even tried to reach Champions league).
Vaccines
Lanini S, Capone S, Antinori A, et al. GRAd-COV2, a gorilla adenovirus-based candidate vaccine against COVID-19, is safe and immunogenic in younger and older adults. Science Translational Medicine 26 October 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj1996
A COVID-19 vaccine based on a replication-defective gorilla adenovirus expressing the stabilized pre-fusion SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, named GRAd-COV2. The safety and immunogenicity of a single-dose regimen of this vaccine were good in this Phase I, dose-escalation, open-label trial in 90 healthy participants. (Without a doubt, Joshua would refuse a vaccine derived “from a threatened species”).
Collateral damage
Orhant ER, Chapellier JF, Carling C. Injury rates and patterns in French male professional soccer clubs: a comparison between a regular season and a season in the COVID-19 pandemic. Res Sports Med 2021 October 27;1-11. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34706601/
More good news for Joshua. In this national injury database, no differences in the incidence of match injuries affecting the ankle and knee regions were observed during the French 2020/2021 season. However, we urgently need more data to see whether this applies to other leagues.
Ghiani G, Roberto S, Mura R, et al. Body composition changes during the lockdown-restart transition due to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in a group of professional football players. J Sports Med Phys Fitness October 15, 2021. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34651614/
And even more. This groundbreaking study evaluated the body composition of 18 male football players from an Italian Serie A team by bioelectrical impedance. It is encouraging to see that after lockdown, no changes in body mass, body mass index, fat mass, fat-free mass, or total body water were seen.
Long COVID-19
Van Hattum JC, Spies JL, Verwijs SM. Cardiac abnormalities in athletes after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2021, October 12;7(4):e001164. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34691762/
According to this review, rates of pericardial/myocardial abnormalities in athletes are highly variable and dependent on study quality. “Prospective athlete studies, with pre-SARS-CoV-2 imaging (CMR), including structured follow-up and arrhythmia monitoring, are urgently needed”. (Joshua, why not now consider a “pre-SARS-CoV-2 CMR”?)
Epidemiology
Schulz C, Martina B, Mirolo M, et al. SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies in domestic cats during first COVID-19 wave, Europe. Emerg Infect Dis October 25, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2712.211252
Among > 2000 domestic cats from 4 countries during the first coronavirus disease wave in Europe, the authors found 4.4% seroprevalence using a virus neutralization test, demonstrating probable human-to-cat transmission. (Joshua claims he has no cat).

31 October
Vaccines
Barda N, Dagan N, Cohen C. Effectiveness of a third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for preventing severe outcomes in Israel: an observational study. Lancet October 29, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02249-2/fulltext
Older than 40? This is currently the best data for a third jab. In this large study, the third dose and matched control groups each included 728,321 individuals. Participants had a median age of 52 years (IQR 37–68). Evaluated at least 7 days after the third dose, compared with receiving only two doses at least 5 months previously, was estimated to be 93% (231 vs 29 events) for vaccine effectiveness, 92% (157 vs 17 events) for severe disease, and 81% (44 vs 7 events) for COVID-19-related death. Effectiveness was seen in all age groups above 40. Only in those aged 16–39 years, the rate of these severe outcomes was too small for any meaningful estimation of effectiveness of the booster.
Mbaeyi S, Oliver SE, Collins JP, et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ Interim Recommendations for Additional Primary and Booster Doses of COVID-19 Vaccines — United States, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 29 October 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7044e2.htm?s_cid=mm7044e2_w
Detailed recommendations for a third jab in moderately to severely immunocompromised persons and in persons with certain underlying conditions.
Bozio CH, Grannis SJ, Naleway AL, et al. Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19 Among Adults Hospitalized with COVID-19–Like Illness with Infection-Induced or mRNA Vaccine-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Immunity — Nine States, January–September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 29 October 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7044e1.htm?s_cid=mm7044e1_w
Vaccine is better than previous infection. In this US network, laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection was identified among 324 (5.1%) of 6328 fully vaccinated persons and among 89 of 1020 (8.7%) unvaccinated, previously infected persons. The adjusted odds of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 among unvaccinated adults with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection were 5.49-fold higher than the odds among fully vaccinated recipients of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine who had no previous documented infection (95% confidence interval: 2.75–10.99).
Variants
Zhang J, Xiao T, Cai Y, et al. Membrane fusion and immune evasion by the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. Science, October 26, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl9463
Delta spike can fuse membranes more efficiently at low levels of cellular receptor ACE2; also, its pseudotyped viruses infect target cells substantially faster than the other five variants, possibly accounting for its heightened transmissibility.
Severe COVID-19
Declercq J, Van Damme KF, De Leeuw E, et al. Effect of anti-interleukin drugs in patients with COVID-19 and signs of cytokine release syndrome (COV-AID): a factorial, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Resp Med October 29, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00377-5/fulltext
In this open-label RCT from Belgium, drugs targeting IL-1 or IL-6 (anakinra, tocilizumab and siltuximab) did not shorten the time to clinical improvement in patients with COVID-19, hypoxic respiratory failure, low SOFA score (Systematic Organ Failure Assessment), and low baseline mortality risk. Although IL-6 blockade in combination with corticosteroids might be beneficial in the most severely ill patients, it seems less effective when used earlier in the disease course or in populations with low to moderate mortality.
30 October
Epidemiology
Sonabend R, Whittles LK, Imai N, et al. Non-pharmaceutical interventions, vaccination, and the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant in England: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet October 27, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02276-5/fulltext
Main message: with the Delta variant, it might not be possible to fully lift NPIs without a third wave of hospital admissions and deaths, even if vaccination coverage is high.
Variants
Singanayagam A, Hakki S, Dunning J, et al. Community transmission and viral load kinetics of the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in the UK: a prospective, longitudinal, cohort study. Lancet Inf Dis October 29, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00648-4/fulltext
Same. Vaccination is not sufficient to prevent Delta. The authors longitudinally followed index cases and their contacts (regardless of symptoms) in the community early after exposure to the Delta, performing daily quantitative RT-PCR for 14–20 days. Secondary attack rate in fully vaccinated household contacts was high at 25%, but this value was lower than that of unvaccinated contacts (38%). However, fully vaccinated individuals with breakthrough infections had peak viral load similar to unvaccinated cases.
Vaccine
Li L, Robinson LB, Patel R, et al. Association of Self-reported High-Risk Allergy History With Allergy Symptoms After COVID-19 Vaccination. JAMA Netw Open October 26, 2021;4(10):e2131034. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785466?resultClick=1
In this large study on individuals with vs without a history of high-risk allergy more allergic reactions were reported after receiving dose 1 or 2 of the vaccine (11.6% [n = 55] vs 4.7% [n = 2461]). However, reported allergy symptoms did not impede the completion of the 2-dose vaccine protocol.
Woldesmekel BA, Garliss CC, Blankson JN. mRNA Vaccine-Elicited SARS-CoV-2-Specific T cells Persist at 6 Months and Recognize the Delta Variant. Clinical Infectious Diseases October 25, 2021, ciab915, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab915/6409907
This small study found only a modest decline in the frequency of these T cells at 6 months. Moreover, there was a robust expansion in response to antigen and recognition of spike peptides from the Delta variant, indicating that booster shots should successfully increase the frequency of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in circulation.
Treatment
Reis G, dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Medeiros Silva DC, et al. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Global Health October 27, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(21)00448-4/fulltext
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). There are several potential mechanisms in the treatment of COVID-19 illness, including anti-inflammatory and possible antiviral effects. In this large RCT from Brazil, treatment with fluvoxamine (100 mg twice daily for 10 days) among high-risk outpatients with early diagnosed COVID-19 reduced the need for hospitalization. Despite the moderate effects, the authors sound enthusiastic as they “found a clinically important absolute risk reduction of 5.0%, and 32% RR reduction, on the primary outcome“. Let’s wait for more data.
29 October
Treatment
Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al. Early Treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab. NEJM October 27, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2107934?query=featured_home
Paper of the day. Sotrovimab (brand name Xevudy), formerly known as VIR-7831 and developed by Vir Biotechnology and GlaxoSmithKline, is an engineered human monoclonal antibody that neutralizes SARS-CoV-2, including variants of concern and multiple other sarbecoviruses. In this prespecified interim analysis of 583 patients, 3 patients (1%) in the sotrovimab group, as compared with 21 patients (7%) in the placebo group, had disease progression leading to hospitalization or death (relative risk reduction: 85%). Notably, a 500 mg dose may also permit intramuscular administration.
Rubin R. Monoclonal Antibodies for COVID-19 Preexposure Prophylaxis Can’t Come Fast Enough for Some People. JAMA October 27, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2785781?resultClick=1
Some people with compromised immune systems do not mount an effective response to COVID-19 vaccine. These people would qualify for a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PREP). Rita Rubin summarizes the problems and hurdles.
Immunology
Goldberg Y, Mandel Ml, Bar-On YM, et al. Waning Immunity after the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Israel. NEJM October 27, 2021 https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2114228?query=featured_home
Among 5,279,926 fully vaccinated adults, the appearance and rapid predominance of the Delta variant in June 2021 resulted in a dramatic increase in the numbers. This analysis shows that this was seen in all age groups, with and without correction for measured confounding factors. The results provide an epidemiologic basis for the decision by the Israeli Ministry of Health on July 30, 2021, to approve the administration of a booster (third dose) of COVID-19 vaccine to persons who had been vaccinated at least 5 months previously.
Transmission
Amato-Lourenço LF, de Souza Xavier Costa N, Dantas KC, et al. Quantification of airborne SARS-CoV-2 genomic particles in different hospital settings. Sci Rep October 27, 2021, 11, 21284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00761-1
Widespread presence of contaminated aerosols in different hospital units dedicated to or not dedicated to COVID-19 and in the autopsy room, all without negative pressure ventilation systems.
Variants
Hitchings MD, Ranzani OT, Dorion M et al. Effectiveness of ChAdOx1 vaccine in older adults during SARS-CoV-2 Gamma variant circulation in São Paulo. Nat Commun October 27, 12, 6220 (2021). https://www.nature.com/search?q=COVID&order=date_desc
The AstraZeneca vaccine protects well from Gamma. During a period of high prevalence of the Gamma variant, effectiveness of the two-dose schedule was 77.9% (95% CI: 69.2–84.2) against COVID-19, 87.6% (95% CI: 78.2–92.9) against hospitalization, and 93.6% (95% CI: 81.9–97.7) against death.
28 October
Vaccines
Patone M, Handunnetthi L, Saatci D, et al. Neurological complications after first dose of COVID-19 vaccines and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med October 25, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01556-7
Although this study found an increased risk of neurological complications in those who received COVID-19 vaccines, the risk is greater from COVID-19. There was a substantially higher risk of all neurological outcomes in the 28 days after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test including Guillain–Barré syndrome (IRR, 5.25; 95% CI: 3.00–9.18).
Variants
Arora P, Rocha C, Kempf A. et al. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variant A.30 is heavily mutated and evades vaccine-induced antibodies with high efficiency. Cell Mol Immunol October 25, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-021-00779-5
The variant A.30 (also termed A.VOI.V2), which was detected in several patients in Angola and Sweden in Spring 2021 and likely originated in Tanzania, can evade control by vaccine-induced antibodies and might show an increased capacity to enter cells in a cathepsin L-dependent manner, which may aid particularly in an extrapulmonary spread. Close monitoring warranted.
Clinical
Bartley CM, Johns C, Ngo TT, et al. Anti–SARS-CoV-2 and Autoantibody Profiles in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of 3 Teenaged Patients With COVID-19 and Subacute Neuropsychiatric Symptoms. JAMA Neurol October 25, 2021. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34694339/
Of three pediatric patients with subacute neuropsychiatric impairment, two had intrathecal anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies as well as intrathecal antineural antibodies, suggesting central nervous system autoimmunity.
Acosta AM, Garg S, Pham H, et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Rates of COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization, Intensive Care Unit Admission, and In-Hospital Death in the United States From March 2020 to February 2021. JAMA Netw Open October 21, 2021;4(10):e2130479. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785325?resultClick=1
In this large cross-sectional analysis, American Indian or Alaska Native, Latino, Black, and Asian or Pacific Islander persons were more likely than White persons to have a COVID-19–associated hospitalization, ICU admission, or in-hospital death during the first year of the US COVID-19 pandemic.
Satterfield BA, Bhatt DL, Gersh BJ. Cardiac involvement in the long-term implications of COVID-19. Nat Rev Cardiol October 18, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41569-021-00631-3
In this brillliant review, the authors highlight what is known about the cardiovascular sequelae in survivors of COVID-19 and discuss important questions that need to be addressed in future studies.
You may also consider this
Bayern star Joshua Kimmich unvaccinated due to ‘personal concerns’. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-59048800

27 October
Transmission
Lee BU. A high attack rate of 90% of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant infections in crew personnel on a single navy ship. Journal of Travel Medicine October 20, 2021, taab168, 20 October 2021 https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taab168/6404468?searchresult=1
An explosive outbreak on a Navy ship. Within 25 days, 272 sailors out of 301 (unvaccinated) sailors (90.4%) were infected with the Delta variant. 209 (77%) were symptomatic. All recovered. Join the Navy?
Variants
Taylor CA, Patel K, Pham H, et al. Severity of Disease Among Adults Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19 Before and During the Period of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Predominance — COVID-NET, 14 States, January–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 22 October 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7043e1.htm?s_cid=mm7043e1_w
Rates of COVID-19–associated hospitalization in adults increased during July–August 2021 as the Delta variant became predominant in the United States. Although Delta is more transmissible, this study did not find significantly higher proportions of hospitalizations with ICU admission, receipt of IMV, or in-hospital death in non-pregnant hospitalized adults.
Vaccines
Harder T, Külper-Schiek W, Reda S, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25 August 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(41):pii=2100920. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.41.2100920
The main conclusion of this review: COVID-19 vaccines approved in the EU have a moderate to high effectiveness against mild to moderate forms of SARS-CoV-2 infections caused by the Delta variant, while VE against severe disease and hospitalization remains high to very high.
Nordström P, Ballin M, Nordström A, et al. Effectiveness of heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and mRNA prime-boost vaccination against symptomatic Covid-19 infection in Sweden: A nationwide cohort study. Lancet Regional Health October 18, 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666776221002350?via%3Dihub
This study compared >100,000 individuals who received heterologous AZ/BioNTech or Moderna and 430,100 individuals that received homologous AZ/BioNTech prime-boost vaccination. Heterologous vaccination showed 67% to 79% effectiveness against symptomatic COVID-19, higher than the 50% effectiveness from homologous vaccination.
Pediatrics
Pullen KM, Atyeo C, Collier AR. Selective functional antibody transfer into the breastmilk after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep October 21, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109959
A non-pathologic but protective barrier against COVID-19 disease: the authors observed a preferential transfer of antibodies capable of eliciting neutrophil phagocytosis and neutralization compared to other functions, pointing to a selective transfer of certain functional antibodies to breastmilk.
26 October
Epidemiology
Mashe T, Takawira FT, de Oliveira Martins L, et al. Genomic epidemiology and the role of international and regional travel in the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in Zimbabwe: a retrospective study of routinely collected surveillance data. Lancet Global Health October 22, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00434-4
International and regional migration (compared to local migration) was the predominant driver of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Zimbabwe during the early phases of the pandemic.
Vaccine
Xu S, Huang R, Sy LS, et al. COVID-19 Vaccination and Non–COVID-19 Mortality Risk — Seven Integrated Health Care Organizations, United States, December 14, 2020–July 31, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 22 October 2021. DOI: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7043e2.htm?s_cid=mm7043e2_w
There is no increased risk for mortality among COVID-19 vaccine recipients. During December 2020–July 2021, COVID-19 vaccine recipients had lower rates of non–COVID-19 mortality than did unvaccinated persons after adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, and study site.
Hillson K, Clemens SC, Madhi SA, et al. Fertility rates and birth outcomes after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccination. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02282-0
No, there is no fertility issue. Fertility was unaffected among 9755 participants in RCTs. In addition, the rate of miscarriage was not higher in the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 group.
Long COVID
Becker JH, Lin JJ, Doernberg M, et al. Assessment of Cognitive Function in Patients After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw Open October 22, 2021;4(10):e2130645. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785388?resultClick=1
A cohort of 740 patients with COVID-19, indicating a relatively high frequency of cognitive impairment several months later. The most prominent deficits were in processing speed (18%), executive functioning (16%), phonemic (initial letter) fluency (15%) and category fluency (20%), memory encoding (24%), and memory recall (23%).
Wenzel J, Lampe J, Müller-Fielitz H, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 main protease Mpro causes microvascular brain pathology by cleaving NEMO in brain endothelial cells. Nat Neurosci October 21, 2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-021-00926-1
Is this the explanation? Jan Wenzel and colleagues from Germany show microvascular pathology in the brains of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients that likely explains signs and symptoms. They propose a mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 infection compromises brain endothelial function, damages the brain blood barrier and reduces CNS perfusion.
25 October
Variants
Chagla Z, Ma H, Sander B, et al. Assessment of the Burden of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Among Essential Workers in the Greater Toronto Area, Canada. JAMA Netw Open October 19, 2021, 4(10):e2130284. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30284
No surprise: VOC of SARS-CoV-2, similar to wildtype SARS-CoV-2, are disproportionately associated with neighborhoods with lower income and with a higher proportion of essential workers.
Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, et al. Severity, criticality, and fatality of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant Clinical Infectious Diseases, October 17, 2021 ciab909, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab909
The Beta (B.1.351) variant of COVID-19 disease was investigated in Qatar. Compared to the Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant, the odds of progressing to severe disease were 1.24-fold (95% CI: 1.11-1.39) higher for Beta. And the odds of COVID-19 death were 1.57-fold (95% CI: 1.03-2.43) higher for Beta.
Clinical
Couzin-Frankel J. A cancer survivor had the longest documented COVID-19 infection. Science News October 19, 2021. https://www.science.org/content/article/cancer-survivor-had-longest-documented-covid-19-infection-here-s-what-scientists-learned
Jennifer Couzin-Frankel summarizes an interesting preprint case report. A yearlong “chronic” infection in a lymphoma patient (treated with CAR-T cells) spawned a striking mutation beyond SARS-CoV-2’s spike protein.
Nielsen J, Nørgaard SK, Lanzieri G, et al. Sex-differences in COVID-19 associated excess mortality is not exceptional for the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Rep 11 October 20, 2021, 20815 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-00213-w
See title. Sex-differences observed during the COVID-19 pandemic reflects a general sex disparity in excess mortality.
Collateral damage
Abraham JO, Mumma MA. Elevated wildlife-vehicle collision rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Rep October 15 11, 20391 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99233-9
Increased wildlife road use offsets the effects of decreased traffic volume on vehicle-wildlife collisions.
Asare S, Majmundar A, Islami F, et al. Changes in Cigarette Sales in the United States During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann Int Med, October 19, 2021. https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-3350 4
A monthly excess sale of 0.34 packs (95% CI: 0.25 to 0.44 packs) per capita.
Beyond Corona
Baker TB, Piper ME, Smith SS, et al. Effects of Combined Varenicline With Nicotine Patch and of Extended Treatment Duration on Smoking Cessation – A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA October 19 2021;326(15):1485-1493. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2785264?resultClick=1
Talking about smoking (cessation): This huge RCTs shows that combined varenicline plus nicotine patch or doubling the duration of varenicline are not better, compared to standard varenicline monotherapy of 12-weeks.
24 October
Immunology
Andreano E, Paciello I, Piccini G, et al. Hybrid immunity improves B cells and antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature October 20, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04117-7
A detailed look at the B-cell responses. The authors analyzed at single-cell level the memory B cells of five naive and five convalescent people vaccinated with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine to dissect the nature of the B cell and antibody response. People previously exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection, respond to vaccination with more B cells producing antibodies that are not susceptible to escape variants and that have higher neutralization potency.
Lu Z, Laing ED, DaMata JP, et al. Durability of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell responses at 12-months post-infection. The Journal of Infectious Diseases October 21, jiab543, https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab543.
The frequency of SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4, but not CD8, T cells was higher at 12-months in individuals who experienced severe disease.
Vaccine
Mateus J, Dan JM, Zhang Z, et al. Low-dose mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine generates durable memory enhanced by cross-reactive T cells. Science 6566, October 22, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj9853
A smaller jab does the job. Studying 35 vaccinated subjects 7 months out from the initial immunization, the authors found that two-dose 25-mg mRNA-1273 vaccination (Moderna, instead of 100 mg) generated immune memory against spike comparable to that of SARS-CoV-2 infection for antibodies and T-cells.
Treatment
Cho H, Gonzales-Wartz KK, Huang D, et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting distinct regions of the spike protein potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Science Transl Medicine, October 20, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj5413
Monoclonal Abs, when combined as bispecific antibodies, neutralized SARS-CoV-2 better than cocktails of the parental mAbs. These bispecific antibodies bound to distinct regions of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, neutralized variants of concern, including the Delta variant, and conferred protection when administered to hamsters before SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Maisonnasse P, Aldon Y, Marc A, et al. COVA1-18 neutralizing antibody protects against SARS-CoV-2 in three preclinical models. Nat Commun 12, 6097 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26354-0.
COVA1-18, an RBD-specific monoclonal Ab, is one of the most potent NAb in vitro. Using different experimental models as well as mathematical modeling, the authors demonstrate that COVA1-18 may work in vivo.
Severe COVID-19
The COVID STEROID 2 Trial Group. Effect of 12 mg vs 6 mg of Dexamethasone on the Number of Days Alive Without Life Support in Adults With COVID-19 and Severe Hypoxemia. JAMA October 21, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2785529?resultClick=1
Less is more (or at least enough): This RCT in 1000 (!) patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxemia found no difference between both dosages.
23 October
Epidemiology
Lalwani P, Araujo-Castillo RV, Ganoza CA, et al. High anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroconversion rates before the second wave in Manaus, Brazil, and the protective effect of social behaviour measures: results from the prospective DETECTCoV-19 cohort. Lancet Global Health November 1, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(21)00355-7/fulltext
The city of Manaus, Brazil, has seen two collapses of its health system due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on blood donor antibody surveillance, the cumulative proportion of the population infected was estimated to be more than 70%. This study shows that several modifiable behaviors increased the risk of seroconversion, including non-compliance with non-pharmaceutical interventions measures such as not wearing a mask during contact, relaxation of protective measures like distancing, and non-remote working.
Buss LF, Sabino EC. Intense SARS-CoV-2 transmission among affluent Manaus residents preceded the second wave of the epidemic in Brazil. Lancet Global Health, November 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00396-X
Lewis Buss and Ester Sabino conclude that “The results highlight heterogeneities in transmission and hint at a possible asynchronous COVID-19 peak among more affluent Manaus residents who were better able to isolate during the first wave.”
Virology
Han P, Su C, Zhang Y. et al. Molecular insights into receptor binding of recent emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Commun October 20, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26401-w
Important work, characterizing the hACE2-binding affinity and transduction efficiency of SARS-CoV-2 variants. The authors examined six different SARS-CoV-2 RBD variants, including Alpha, Beta and Gamma, and found that these dominant mutations result in enhanced binding affinity to hACE2 and/or enhancement of viral entry to human cells.
Vaccine
Pfizer. Press release, October 21, 2021. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-and-biontech-announce-phase-3-trial-data-showing
Time for a third jab? Unfortunately, this has been published only as a press release. In this phase 3 RCT evaluating the efficacy and safety of a 30-µg booster dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine in more than 10,000 individuals 16 years of age and older, participants who previously completed the primary two-dose series were randomized 1:1 to receive either a 30-µg booster dose (the same dosage strength as those in the primary series) or placebo. The median time between second dose and the booster dose or placebo was 11 months. From day 7, there were 5 cases of COVID-19 in the booster group and 109 cases in the non-boosted group. The observed relative vaccine efficacy was 95.6% (95% CI: 89.3, 98.6).
Co-morbidities
Izadi Z, Brenner EJm Mahil SK, et al. Association Between Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors and the Risk of Hospitalization or Death Among Patients With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Disease and COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open October 18, 2021; 4(10):e2129639. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785080?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 6077 patients with IMIDs and COVID-19, TNF inhibitors in combination with azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine therapy, methotrexate monotherapy, azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine monotherapy, or Janus kinase inhibitor monotherapy were each associated with significantly higher odds of hospitalization or death compared with TNF inhibitor monotherapy.
Treatment
Temple C, Hoang R, Hendrickson RG. Toxic Effects from Ivermectin Use Associated with Prevention and Treatment of Covid-19. NEJM October 20, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2114907?query=featured_home
The Oregon Poison Center recently received an increasing number of calls regarding ivermectin exposure. Six of the 21 cases (from August 2021) were hospitalized for toxic effects, including severe episodes of confusion, ataxia, seizures, and hypotension. Just saying.
Pregnancy
Magnus MC, Gjessing HK, Eide HN. Covid-19 Vaccination during Pregnancy and First-Trimester Miscarriage. NEJM October 20, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2114466?query=featured_home
Large database from Norway, showing no evidence of an increased risk for early pregnancy loss after COVID-19 vaccination.
22 October
Today we’ll have a vaccine special, mainly on the effectiveness against Delta in different populations: adolescents from Israel, from the US, prisoners, and Scottish people.
Vaccine
Reis BY, Barda N, Leshchinsky M. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 Vaccine against Delta Variant in Adolescents. NEJM October 2021, https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2114290?query=featured_home
In 94,354 vaccine recipients from Israel between the ages of 12 and 18 years who were successfully matched with 94,354 unvaccinated controls, effectiveness against documented SARS-CoV-2 infection was 90% (95% CI: 88% – 92%) on days 7 to 21 after the second dose.
Olson SM, Newhams MM, Halasa NB, et al. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA Vaccination Against COVID-19 Hospitalization Among Persons Aged 12–18 Years — United States, June–September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 19 October 2021.
Same findings from the US. Among hospitalized patients aged 12–18 years, vaccine effectiveness of 2 doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine against COVID-19 hospitalization during June–September 2021, was 93% (95% CI: 83%–97%).
Chin ET, Leidner D, Zhang Y, et al. Effectiveness of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine during a SARS-CoV-2 Delta Outbreak in a Prison. NEJM October 20, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2114089?query=featured_home
The Sierra Conservation Center (SCC) in Jamestown, California, is a low-to-medium security prison for men. During an outbreak among residents (468 were fully vaccinated and 359 were unvaccinated), the estimated vaccine effectiveness was 56.6% against infection and 84.2% against symptomatic infection.
Sheikh A, Robertson C, Taylor B. BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against Death from the Delta Variant. NEJM October 20, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2113864?query=featured_home
Overall, vaccine effectiveness against death from the Delta variant 14 or more days after the second vaccine dose was 90% for BNT162b2 and 91% for ChAdOx1 nCoV-19.
Sciascia S, Costanzo P, Radin M, et al. Safety and tolerability of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in people with antiphospholipid antibodies. Lancet Rheumatology, October 20, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00320-9/fulltext
No severe problems with vaccines among 102 patients (52 with a diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome and 50 with antiphospholipid antibodies without clinical features).
Waltz E. COVID vaccine makers brace for a variant worse than Delta. Nature News October 20, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02854-3
Nice article by Emily Waltz, summarizing how companies are updating vaccines and testing them on people to prepare for whatever comes next in the pandemic.
21 October
Variants
Pouwels KB, Pritchard E, Matthews PC, et al. Effect of Delta variant on viral burden and vaccine effectiveness against new SARS-CoV-2 infections in the UK. Nat Med October 14, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01548-7
Vaccination with two doses of BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 substantially reduces the risk of new PCR-positive SARS-CoV-2 infections. However, while the two vaccines provided similar benefits when Alpha was dominant, benefits from two ChAdOx1 doses were reduced more in the presence of Delta than for two BNT162b2 doses, although two ChAdOx1 doses still provide similar protection as that from previous natural infection. With Delta, infections occurring after two vaccinations had similar peak viral burden as those in unvaccinated individuals. Vaccination reduces new infections, but effectiveness and attenuation of peak viral burden are reduced with Delta.
Vaccines
Rovida F, Cassaniti I, Paolucci S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine breakthrough infections with the alpha variant are asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic among health care workers. Nat Commun 12, 6032, October 15, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26154-6
All 33 vaccine breakthrough infections were asymptomatic or symptomatic, mostly with few and mild symptoms like rhinitis.
Dhaval D, Friedson AI, Hansen B, et al. Association Between Statewide COVID-19 Lottery Announcements and Vaccinations. JAMA Health Forum, October 15, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/2785288?resultClick=1
Lottery-style incentives may be less effective than those that definitely pay.
Treatment
Malani AN, LaVasseur B, Fair J, et al. Administration of Monoclonal Antibody for COVID-19 in Patient Homes. JAMA Netw Open October 14, 2021;4(10):e2129388. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784998?resultClick=1
Experience from Michigan, US, showing how home MAb infusion (performed by a team of 3 nurses) provided a critical framework to prevent high-risk patients from seeking ED care and requiring hospitalization.
Kalil AC, Mehta AK, Patterson TF, et al. Efficacy of interferon beta-1a plus remdesivir compared with remdesivir alone in hospitalised adults with COVID-19: a double-bind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Resp Med October 18, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00384-2/fulltext
No efficacy of interferon, administered subcutaneously every other day.
Wilkinson T. Subcutaneous interferon beta-1a in COVID-19: raking the ashes of an intervention trial. Lancet Resp Med October 18, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00412-4/fulltext
Nice comment by Tom Wilkinson. “This observation is a common narrative in recent COVID-19 trials, whereby small, early, uncontrolled studies, which show hopeful signals of benefit, are not subsequently replicated in more definitive, larger scale, and later phase studies”.
Another example?
RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Resp Med October 18, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00435-5/fulltext
Colchicine.
20 October
Pregnancy, Pediatrics
Today we’ll have a pregnancy special. Two landmark studies explain how pregnancy and fetal sex influence the quality of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection and immunization. In addition, some more data on adverse outcomes during pregnancy and on infectiousness during childhood.
Bordt EA, Shook LL, Atyeo C, et al. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection elicits sexually dimorphic placental immune responses. Science Translational Medicine October 19, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abi7428
Mortality and morbidity risk during the perinatal period and infancy is higher in males than females. This may be due to evolutionary differences that occur throughout pregnancy and in the perinatal period. This important paper on the intersection of maternal-fetal antibody transfer, viral-induced placental interferon responses, and fetal sex in pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 demonstrates fetal sex-specific maternal and placental adaptive and innate immune responses.
Atyeo C, DeRiso EA, Davis C, et al. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines drive differential antibody Fc-functional profiles in pregnant, lactating, and non-pregnant women. Science Translational Medicine, October 19, 2019. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abi8631
Although antibody titers are similar, pregnant and lactating women respond to vaccination in qualitatively and kinetically distinct manners compared to non-pregnant women.
Ovies C, Semmes EC, Coyne CB, et al. Pregnancy Influences Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Science Translational Medicine, October 19, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abm2070
This brilliant paper summarizes the two studies and explains how pregnancy and fetal sex influence the quality of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection and immunization.
Sun S, Savitz DA, Wellenius GA, et al. Changes in Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Associated With the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United States. JAMA Netw Open October 15, 2021;4(10):e2129560. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2785014
The largest and most comprehensive study to date on adverse pregnancy outcomes, comparing 152903 deliveries during the COVID-19 pandemic period and 172095 deliveries during the referent period. The pandemic period was not associated with a changing risk of stillbirth and provided only modest evidence of a lower risk of preterm birth.
Yonker LM, Boucau J, Regan J, et al. Virologic features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, October 14, 2021, jiab509, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab509/6396772
Among 110 children with COVID-19 (median age 10 years), age did not impact SARS-CoV-2 viral load. Children were most infectious within the first five days of illness.
Purpura LJ, Alukal J, Chong AM, Liu L, Cantos A, Shah J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 shedding in semen and oligozoospermia of patient with severe coronavirus disease 11 weeks after infection. Emerg Infect Dis October 13, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/28/1/21-1521_article
And let’s not forget men’s issues. This paper describes the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by qRT-PCR in semen and severe oligozoospermia in 1 (one) patient 81 days after onset of severe COVID-19. In addition, 4 other study participants had oligozoospermia. Relieving to hear that sperm count recovery was observed in 2 participants. However, the other 2 did not provide longitudinal samples.
19 October
Epidemiology
Yang B, Sullivan SG, Du Z, Tsang TK, Cowling BJ. Effectiveness of international travel controls for delaying local outbreaks of COVID-19. Emerg Infect Dis October 13, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/28/1/21-1944_article
Analyzing data from 165 countries the authors found that early implementation of international travel controls led to a mean delay of 5 weeks in the first epidemic peak of cases.
Virology
Vöhringer HS, Sanderson T, Sinnott M, et al. Genomic reconstruction of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in England. Nature October 14, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04069-y
How (and when) Alpha and Delta entered England. Even though more than 90% of adults had antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and close to 70% had received two doses of vaccination, England saw rising Delta variant cases in the first weeks of July 2021.
Transmission
Riley J, Huntley JM, Miller JA, Slaichert ALB, Brown GD. Mask effectiveness for preventing secondary cases of COVID-19, Johnson County, Iowa, USA. Emerg Infect Dis 2022, October 12, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/28/1/21-1591_article
In September 2020, the Iowa Department of Public Health released guidance stating that persons exposed to someone with COVID-19 need not quarantine if the case-patient and the contact wore face masks at the time of exposure. Mask use by both parties reduced the secondary attack rate by half, from 25.6% to 12.5%.
Severe COVID-19
Sholzberg M, Tang GH, Rahhal H, et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic heparin versus prophylactic heparin on death, mechanical ventilation, or intensive care unit admission in moderately ill patients with covid-19 admitted to hospital: RAPID randomised clinical trial. BMJ 2021 October 14, 2021, 375. https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj.n2400
At 28 days, no difference was observed in the primary composite outcome that occurred in 37/228 patients (16%) assigned to therapeutic heparin and 52/237 (22%) assigned to prophylactic heparin (p = 0.12). Because death numbers were lower (1.8% vs 7.6%), the authors conclude that therapeutic heparin is beneficial in moderately ill patients with COVID-19 admitted to hospital wards.
Treatment
Boras B, Jones RM, Anson BJ, et al. Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID-19. Nat Commun 12, 6055, October 18, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26239-2
PF-07304814 is a phosphate pro-drug rapidly converted in vivo to PF-00835231, which exhibits high selectivity over human proteases, acts as a broad-spectrum coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor, and demonstrates potent antiviral activity in vivo. The favorable pre-clinical profile presented here supported progression to clinical trials in healthy volunteers and COVID-19 patients.
18 October
Vaccines
Payne RP, Longet S, Austin JA, et al. Immunogenicity of standard and extended dosing intervals of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Cell 2021, published 15 October. Full text: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)01221-6
Antibody levels after two doses of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine are higher after an extended dosing interval in infection-naïve participants compared with the 3-4 week dosing interval used in the licensing studies. The extended regimen also enriches for virus-specific CD4+ T cells expressing IL-2.
Transmission
Sendi P, Baldan R, Thierstein M, et al. A multidimensional cross-sectional analysis of COVID-19 seroprevalence among a police officer cohort: The PoliCOV-19 study. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021, published 17 October. Full text: https://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofab524/6398672
In theory, protests and police fieldwork might provide a high exposure environment for SARS-CoV-2 infections. However, in this study from Bern, Switzerland, the seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies of police officers was comparable to that reported in the general population. In Switzerland, the personal protective equipment of the police seems to have been effective.
Long COVID
Al-Aly Z. The WHO is letting down long Covid patients. The Guardian 2021, published 17 October. Full text: https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/oct/17/who-long-covid-patients
“Failure to recognize the scope of the illness will harm countless people around the globe.”
Severe COVID
Abu-Raddad LJ, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, et al. Severity, criticality, and fatality of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant. Clin Infect Dis 2021, published 17 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab909
In this study from Qatar, the odds of progressing to 1) severe disease, 2) critical disease and 3) death were 1.24-fold, 1.49-fold and 1.57- fold higher, respectively, for people infected with the Beta (B.1.351) variant than with the Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant.
Cartoon of the Day

17 October
Vaccines
Cohn BA Cirillo PM, Murphy CC, et al. Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections in 620,000 U.S. Veterans, February 1, 2021 to August 13, 2021. medRxiv 2021, posted 14 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.13.21264966
Collier AY, Yu J, McMahan K, et al. Differential Kinetics of Immune Responses Elicited by Covid-19 Vaccines. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 15. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34648703. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2115596
Highly interesting data from a small number of individuals who received either the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine (n = 31) or the Moderna (n = 22) or the Johnson & Johnson (n = 8) vaccines. At 8 months of follow-up, the median live virus neutralizing antibody titers, pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titers, and RBD-specific binding antibody titers elicited by the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine were lower than the peak titers by a factor of 34, 4, and 29, respectively. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine never reached titers as high as for the mRNA vaccines; however, at 8 months, the J&J titers were similar to those at week 4. Bigger cohorts needed to confirm these data.
Rubin R. Trying to Block SARS-CoV-2 Transmission With Intranasal Vaccines. JAMA. 2021 Oct 14. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34647956. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.18143
What appears to be promising in animals doesn’t always pan out in humans.
Immunology
Kaplonek P, Wang C, Bartsch Y, et al. Early cross-coronavirus reactive signatures of humoral immunity against COVID-19. Sci Immunol. 2021 Oct 15;6(64):eabj2901. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34652962. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abj2901
Immunity to common seasonal coronaviruses may help to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection. This is the result of an analysis of early antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 and the common cold β-coronavirus OC43 in COVID-19 patients with asymptomatic, moderate, severe, or deadly disease.
Diagnosis
Au WY, Cheung PP. Diagnostic performances of common nucleic acid tests for SARS-CoV-2 in hospitals and clinics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microbe 2021, published 12 October. Full text: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00214-7/fulltext
The authors assessed the performance of three common nucleic acid tests, namely digital PCR (dPCR), quantitative PCR (qPCR), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Overall, dPCR had the highest diagnostic sensitivity but had lower specificity than qPCR and LAMP.
Severe COVID
Trentini F, Marziano V, Guzzetta G, et al. The pressure on healthcare system and intensive care utilization during the COVID-19 outbreak in the Lombardy region: a retrospective observational study on 43,538 hospitalized patients. Am J Epidemiol. 2021 Oct 15:kwab252. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34652416. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwab252
At the height of the first Italian COVID-19 wave in 2020 (March 14-April 25), the extraordinary pressure on the healthcare system forced a shift in intensive care unit (ICU) admission criteria to prioritize patients with higher chances of survival. Here, the authors show that patients above 70 years of age were admitted less often to an ICU.
16 October
Vaccines
Mallapaty S. China’s COVID vaccines have been crucial — now immunity is waning. Nature 2021, published 14 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02796-w
“Billions of shots of China’s CoronaVac and Sinopharm vaccines have been given globally, but studies have questioned the length of protection they offer.”
CDC 202110. Rates of COVID-19 Cases and Deaths by Vaccination Status. Centers for Disease Control 2021. Link: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#rates-by-vaccine-status
The CDC is now posting data on vaccination status for hospitalization and death, and by age.
Immunology
Callaway E. COVID super-immunity: one of the pandemic’s great puzzles. Nature 2021, published 14 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02795-x
“People who have previously recovered from COVID-19 have a stronger immune response after being vaccinated than those who have never been infected. Scientists are trying to find out why.”
Pathogenesis
D’Agnillo F, Walters KA, Xiao Y, et al. Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Oct 14:eabj7790. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34648357. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7790
The authors analyzed lung autopsy samples from 18 patients with fatal COVID-19, with symptom onset-to-death times ranging from 3 to 47 days. The results (among others): progressive diffuse alveolar damage with excessive thrombosis and late onset remodeling; loss of surfactant protein expression and defective tissue repair processes; and impaired clot fibrinolysis with increased concentrations of plasma and lung plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1).
Transmission
de Gier B, Andeweg S, Backer JA, et al. Vaccine effectiveness against SARS‐CoV‐2 transmission to household contacts during dominance of Delta variant (B.1.617.2), August‐September 2021, the Netherlands. medRxiv 2021, posted 14 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.14.21264959
The authors compared secondary attack rates among household members between vaccinated and unvaccinated index cases. They estimated the effectiveness of full vaccination to be 63%.
15 October
Vaccines
Atmar RL, Lyke KE, Deming ME, et al. Heterologous SARS-CoV-2 Booster Vaccinations: Preliminary Report. medRxiv 2021, posted 13 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.10.21264827
The authors evaluated homologous and heterologous booster vaccination in persons who had completed a full COVID-19 vaccine regimen at least 12 weeks earlier. Of 458 individuals, 154 received the BioNTech/Pfizer, 154 received the Moderna, and 150 received the Johnson & Johnson booster vaccine. The authors observed a substantial increase in neutralizing antibody titers in all study participants irrespective of booster and primary vaccine series.
Bergwerk M, Gonen T, Lustig Y, et al. Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 14;385(16):1474-1484. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34320281. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2109072
An analysis of breakthrough infections among 39 fully vaccinated health care workers during the 4-month period after the second vaccine dose. Neutralizing antibody titers in case patients during the peri-infection period were lower than those in matched uninfected controls, and higher peri-infection neutralizing antibody titers were associated with lower infectivity (higher Ct values). Most breakthrough cases were mild or asymptomatic, although 19% had persistent symptoms (> 6 weeks).
Zauche LH, Wallace B, Smoots AN, et al. Receipt of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccines and Risk of Spontaneous Abortion. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 14;385(16):1533-1535. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34496196. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2113891
Is there a risk of spontaneous abortion after receipt of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine either before conception (30 days before the first day of the last menstrual period through 14 days after) or during pregnancy? It doesn’t seem so. Among 2456 participants enrolled in the CDC v-safe COVID-19 pregnancy registry, the cumulative risks of spontaneous abortion were within the expected range.
Long COVID
Groff D, Sun A, Ssentongo AE, et al. Short-term and Long-term Rates of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Oct 1;4(10):e2128568. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34643720. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28568
In this review of 57 studies comprising more than 250,000 survivors of COVID-19, the most common sequelae involved functional mobility impairments, pulmonary abnormalities, and mental health disorders. The authors warn that these long-term effects “occur on a scale that could overwhelm existing health care capacity, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.”
Collateral Effects
Nogrady B. ‘I hope you die’: how the COVID pandemic unleashed attacks on scientists. Nature 2021, published 13 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02741-x
“A survey by Nature of more than 300 scientists who have given media interviews about COVID-19 — many of whom had also commented about the pandemic on social media — has found wide experience of harassment or abuse; 15% said they had received death threats.” See also the Nature editorial: COVID scientists in the public eye need protection from threats. Nature 2021, published 13 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02757-3
14 October
Prevention
House of Commons 20211012. Coronavirus: lessons learned to date. UK Health and Social Care Committee 2021, published 12 October. Full text: https://committees.parliament.uk/work/657/coronavirus-lessons-learnt/news/157991/coronavirus-lessons-learned-to-date-report-published/
Britain’s initial response to the COVID-19 pandemic “ranks as one of its most important public health failures”. The report blames the British government for “many thousands of deaths which could have been avoided.”
Vaccines
Marcotte H, Piralla A, Zuo F, et al. Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 up to 15 months after infection. bioRxiv 2021, posted 11 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.08.463699
More about the longevity of immunity of SARS-CoV-2 immunity. The data “suggest that antiviral specific immunity especially memory B cells in COVID-19 convalescent patients is long-lasting, but some variants of concern, including the fast-spreading Delta variant, may at least partially escape the neutralizing activity of plasma antibodies.”
Virology
Zhang L, Cui Z, Li Q, et al. Ten emerging SARS-CoV-2 spike variants exhibit variable infectivity, animal tropism, and antibody neutralization. Commun Biol 4, 1196 (2021). Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-021-02728-4
Insights into the importance of the E484K mutation. The authors compare the infectivity, host tropism and antigenicity of 10 SARS-CoV-2 variants using a VSV-based pseudovirus system. They suggest that “variants carrying E484K display the most significant reduction in sensitivity to neutralization, and may provide further insight into the development of relevant therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Transmission
Sera F, Armstrong B, Abbott S, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of meteorological factors and SARS-CoV-2 transmission in 409 cities across 26 countries. Nat Commun 12, 5968 (2021). Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25914-8
The authors found little evidence of meteorological conditions having influenced the early stages of local COVID-19 epidemics. Non-pharmaceutical interventions, i.e., population behaviors and government interventions, are far more important drivers of SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Severe COVID
Bos LDJ, Sjoding M, Sinha P, et al. Longitudinal respiratory subphenotypes in patients with COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: results from three observational cohorts. Respir Med 2021, published 12 October. Full text: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00365-9/fulltext
In hundreds of patients with acute respiratory failure due to severe COVID-19, the authors identified two sub-phenotypes that developed during the first 4 days of invasive mechanical ventilation. Trajectories of ventilatory ratio and mechanical power were most discriminatory and modelling these parameters alone provided prognostic value for duration of mechanical ventilation and mortality. See also the comment by Lascarrou JB. COVID-19-related ARDS: one disease, two trajectories, and several unanswered questions. Respir Med 2021, published 12 October. Full text: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00381-7/fulltext
13 October
Vaccines
Lucas C, Vogels CBF, Yildirim I, et al. Impact of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants on mRNA vaccine-induced immunity. Nature. 2021 Oct 11. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34634791. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04085-y
Analysis of plasma neutralization using 16 SARS-CoV-2 variants. The Beta (B.1.351) and Gamma (P.1) strains showed the greatest reduction, followed by the Delta (B.1.617.2) and Alfa (B.1.1.7) strains. Plasma from previously infected vaccinated individuals produced very high neutralizing antibodies against most variants of concern.
Saiag E, Goldshmidt H, Sprecher E, Ben-Ami R, Bomze D. Immunogenicity of a BNT162b2 vaccine booster in health-care workers. Lancet Microbe 2021, published 11 October. Full text: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(21)00272-X/fulltext
The authors report on 346 health care workers (median age: 67 years) of a hospital in Tel Aviv, Israel, who received a third dose of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. “The median (…) SARS-CoV-2 IgG index at baseline was 3.67 (IQR 2.00–7.10), and increased to > 150 (the upper limit of quantification) in 95.7% of vaccine recipients.”
Mahase E. Covid-19: Antibody levels fall after second Pfizer dose, but protection against severe disease remains, studies indicate. BMJ. 2021 Oct 11;375:n2481. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34635474. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n2481
Even falling antibody levels protect against severe COVID-19. A short comment on the two NEJM papers by Levin and Chemaitelly.
Co-morbidities
Melmed GY, Botwin GJ, Sobhani K, et al. Antibody Responses After SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination in Adults With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Oct 12. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34633830. Full text: https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-2483
First, 99% of 582 participants had detectable antibodies after 2 weeks regardless of medication regimen (anti-integrin therapy, anti–interleukin-12/23 therapy, immunomodulator monotherapy, anti–tumor necrosis factor monotherapy, Janus kinase inhibition, anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy combined with an immunomodulator, or systemic corticosteroids).
Wilde B, Korth J, Jahn M, et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients receiving dialysis. Nat Rev Nephrol (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-021-00499-z
“Given the enhanced infection risks associated with dialysis, current vaccines do not replace non-pharmacological measures to prevent infection.”
12 October
Immunology
Loyal L, Braun J, Henze L, et al. Cross-reactive CD4+ T cells enhance SARS-CoV-2 immune responses upon infection and vaccination. Science. 2021 Oct 8;374(6564):eabh1823. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34465633. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abh1823
The authors “identified a universal immunodominant coronavirus peptide found within the fusion peptide domain of coronavirus spike protein. This peptide is recognized by CD4+ T cells in 20% of unexposed individuals, more than 50% of SARS-CoV-2 convalescents, and 97% of subjects treated with the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Although ubiquitous, these coronavirus-reactive T cells decreased with age, which may explain in part the increased susceptibility of elderly people to COVID-19.”
Poon MML, Rybkina K, Kato Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection generates tissue-localized immunological memory in humans. Sci Immunol. 2021 Oct 7:eabl9105. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34618554. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9105
From examination of SARS-CoV-2 seropositive organ donors, the authors report that CD4+ T, CD8+ T, and B cell memory generated in response to infection is present in bone marrow, spleen, lung, and multiple lymph nodes (LNs) for up to 6 months post-infection. They also identified SARS-CoV-2-specific germinal centers in the lung-associated LNs up to 6 months post-infection.
Schepens B, van Schie L, Nerinckx W, et al. An affinity-enhanced, broadly neutralizing heavy chain-only antibody protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection in animal models. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Oct 5:eabi7826. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34609205. Full text: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abi7826
The authors describe camelid-derived single domain antibodies (VHHs) that bind to a highly conserved epitope in the receptor-binding domain of the viral spike protein and neutralize both SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2, including the currently circulating variants. An affinity enhanced VHH-human IgG1 Fc fusion molecule controlled SARS-CoV-2 replication in prophylactic and therapeutic settings in mice and in hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Transmission
Emecen AN, Keskin S, Boncukcu Eren E, et al. Impact of social contacts on SARS-CoV-2 exposure among healthcare workers. Occupational Medicine 2021, published 11 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqab141
Interactions between healthcare workers (HCW) may pose a high risk for SARS-CoV-2 exposure. In this study from Turkey, 260 of 329 exposed clusters (79%) were HCW-to-HCW contact clusters. High-risk exposure was higher in the HCW-to-HCW contacts (44%), when compared to patient-to-HCW contacts (5%).
Prevention
Thompson T. Real-world data show that filters clean COVID-causing virus from air. Nature 2021, published 6 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02669-2
A short discussion of how inexpensive portable filters may help reduce the risk of hospital-acquired SARS-CoV-2. See also the paper by Conway-Morris A, Sharrocks K, Bousfield R, et al. The removal of airborne SARS-CoV-2 and other microbial bioaerosols by air filtration on COVID-19 surge units. medRxiv 2021. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.16.21263684
11 October
Vaccines
Mallapaty S. Heart-inflammation risk from Pfizer COVID vaccine is very low. Nature 2021, published 8 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02740-y
Three days ago, we presented two papers about myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination. Find a short summary in this Nature news feature.
Woo EJ, Mba-Jonas A, Dimova RB, Alimchandani M, Zinderman CE, Nair N. Association of Receipt of the Ad26.COV2.S COVID-19 Vaccine With Presumptive Guillain-Barré Syndrome, February-July 2021. JAMA. 2021 Oct 7. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34617967. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.16496
February 2021 to July 2021, 130 cases of presumptive Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) were reported within the US Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System following vaccination with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The overall estimated observed to expected rate ratio was 4.18, corresponding to an absolute rate increase of 6.36 per 100,000 person-years.
Treatment
Spyropoulos AC, Goldin M, Giannis D, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Therapeutic-Dose Heparin vs Standard Prophylactic or Intermediate-Dose Heparins for Thromboprophylaxis in High-risk Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: The HEP-COVID Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Oct 7. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34617959. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6203
In this randomized clinical trial of 253 adult in-patients with high risk COVID-19, the incidence of major thromboembolism or death was 28.7% with therapeutic-dose vs 41.9% with prophylactic/intermediate-dose heparins. The treatment effect was not seen in ICU patients.
Collateral Effects
Cousien A, Acquaviva E, Kernéis S, Yazdanpanah Y, Delorme R. Temporal Trends in Suicide Attempts Among Children in the Decade Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Paris, France. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Oct 1;4(10):e2128611. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34618041. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28611
The authors describe a dramatic increase in suicide attempts among children in late 2020 and early 2021 after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in France. “This aberrant dynamic of suicide attempts was independent from its annual seasonality and its trend over the 10-year period.”
COVID-19 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, published 8 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7
A systematic review of major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic. Daily SARS-CoV-2 infection rates and reductions in human mobility were associated with increased prevalence of major depressive disorder. Females were more affected than males for major depressive disorder, and younger age groups were more affected than older age groups.
10 October
Vaccines
Clemens SAC, Folegatti PM, Emary KRW, et al. Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 lineages circulating in Brazil. Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 6;12(1):5861. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34615860. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25982-w
The authors report that the AstraZeneca vaccine protects against various SARS-CoV-2 variants in Brazil, even those that have the spike protein mutation E484K: Zeta (P.2), 69%; B.1.1.28, 73%. The AstraZeneca vaccine also provided 95% protection against hospitalization due to COVID-19.
Epidemiology
Arık SÖ, Shor J, Sinha R, et al. A prospective evaluation of AI-augmented epidemiology to forecast COVID-19 in the USA and Japan. npj Digit. Med. 4, 146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-021-00511-7
The authors present an artificial intelligence (AI)-augmented forecast modeling framework that provided daily predictions of the expected number of confirmed COVID-19 deaths, cases, and hospitalizations over the next 4 weeks. Their simulations might also indicate what non-pharmaceutical interventions (alongside vaccinations) might be essential for faster recovery from the pandemic.
Immunology
Gee S, Chandiramani M, Seow J, et al. The legacy of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection on the immunology of the neonate. Nat Immunol. 2021 Oct 6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34616036. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-01049-2
In this study (n = 30), the authors found multiple immunological perturbations within the neonate associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 exposure during pregnancy, many of which were associated with recent or ongoing infections. As the consequences could be far-reaching (i.e., hyper-inflammatory response similar to multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children), long-term follow-up of the newborns in this study could establish if maternal exposure to SARS-CoV-2 has a long-lasting impact on the child.
Treatment
Willyard C. How antiviral pill molnupiravir shot ahead in the COVID drug hunt. Nature 2021, published 8 October. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02783-1
Molnupiravir is a nucleoside analog that gets incorporated into burgeoning RNA strands. The compound can shift its configuration, sometimes mimicking the nucleoside cytidine and sometimes mimicking uridine. The new RNA strands become faulty blueprints for the next round of viral genomes.
Collateral Effects
Das-Munshi J, Change CK, Bakolis I, et al. All-cause and cause-specific mortality in people with mental disorders and intellectual disabilities, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: cohort study. Lancet Regional Health 2021, published 7 October. Full text: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanepe/article/PIIS2666-7762(21)00214-3/fulltext
Data from a prospective analysis of 167,122 people in the UK: “People with mental disorders and intellectual disabilities were at a greater risk of death relative to the general population before, during and after the first peak of COVID-19 deaths, with similar risks by ethnicity.” The authors conclude that the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated pre-existing health inequalities in people living with mental disorders and intellectual disabilities.
9 October
Vaccines
Tartof SY, Slezak JM, Fischer H, et al. Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2021 Oct 4:S0140-6736(21)02183-8. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34619098. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02183-8
Retrospective study, n = 3,436,957. Effectiveness of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections declined from 88% during the first month after full vaccination to 47% after 5 months. The good news: vaccine effectiveness against hospital admissions for infections with the Delta variant for all ages was 93% up to 6 months.
Seror R, Camus M, Salmon JH, et al. Do JAK inhibitors affect immune response to COVID-19 vaccination? Data from the MAJIK-SFR Registry. Rheumatology 2021, published 6 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00314-3
In 113 patients on disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (87% had rheumatoid arthritis and 13% had psoriatic arthritis), such as such as JAK inhibitors, the overall response rate to vaccination was 88%. Non-responders were older than responders. The rate of non-response was higher with upadacitinib (seven [26%] of 27 patients) than with baricitinib (five [9%] of 56) or tofacitinib (one [3%] of 30).
Clinical
Steenblock C, Schwarz PEH, Ludweig B, et al. COVID-19 and metabolic disease: mechanisms and clinical management. Diabetes Endocrinol 2021, published 4 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00244-8
Patients with metabolic dysfunction (i.e., obesity, hypertension, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and diabetes) at an increased risk of developing severe COVID-19, and infection with SARS-CoV-2 might lead to new-onset diabetes or aggravation of pre-existing metabolic disorders. The authors discuss how metabolic and endocrine disorders might predispose patients to develop severe COVID-19.
Severe COVID
Ariya M, Karimi J, Abolghasemi S, et al. Food insecurity arises the likelihood of hospitalization in patients with COVID-19. Sci Rep 11, 20072 (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99610-4
In this study from Iran of 219 COVID-19 patients, people with food insecurity were 3.9 times more likely to be hospitalized than those with food security. (Food insecurity can be defined as “uncertain or limited availability of adequate and healthy food or uncertain or limited ability to acquire acceptable foods in socially acceptable ways”).
Collateral Effects
COVIDSurg Collaborative. Effect of COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns on planned cancer surgery for 15 tumour types in 61 countries: an international, prospective, cohort study. Oncology 2021, published 5 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00493-9
Although surgery, the main modality of cure for solid cancers, was prioritized to continue during COVID-19 outbreaks, 2003 (10%) of 20,006 eligible patients did not receive surgery after a median follow-up of 23 weeks.
8 October
Vaccines
Levin EG, Lustig Y, Cohen C, et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34614326. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2114583
The authors tested 4868 health care workers for the presence of anti-spike IgG and neutralizing antibodies 6 months after vaccination with the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. The level of IgG antibodies decreased at a consistent rate, whereas the neutralizing antibody level decreased rapidly for the first 3 months with a relatively slow decrease thereafter. Neutralizing antibody titers were substantially lower among men than among women, and lower among persons 65 years of age or older than among those 18 to less than 45 years of age.
Chemaitelly H, Tang P, Hasan MR, et al. Waning of BNT162b2 Vaccine Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Qatar. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34614327. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2114114
A study of the resident population of Qatar (n = almost 1,000,000). The effectiveness of vaccine declined to approximately 20% in months 5 through 7 after the second BioNTech/Pfizer dose. The excellent news: effectiveness against any severe, critical, or fatal case of COVID-19 reached 96% or higher in the first 2 months after the second dose and persisted at approximately this level for 6 months.
Rubin EJ, Baden LR, Morrissey S. Audio Interview: Are Covid-19 Vaccine Boosters Necessary? N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 7;385(15):e63. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34614335. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe2115835
Discussion of four new studies that inform two questions: are COVID-19 vaccine boosters needed, and are they safe?
Witberg G, Barda N, Hoss S, et al. Myocarditis after Covid-19 Vaccination in a Large Health Care Organization. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34614329. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2110737
The authors report 142 individuals with symptoms of myocarditis after receiving the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine (136 diagnoses were definitive or probable). The clinical presentation was judged to be mild in 129 recipients (95%); one fulminant case was fatal. The risk was more than twice that among unvaccinated persons. This association was highest in young male recipients within the first week after the second dose: definite or probable cases of myocarditis among persons between the ages of 16 and 19 years within 21 days after the second vaccine dose occurred in approximately 1 of 6637 male recipients and in 1 of 99,853 female recipients.
Mevorach D, Anis E, Cedar N, et al. Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine against Covid-19 in Israel. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34614328. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2109730
Another study of BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine-associated myocarditis from Israel. Among more than 2.5 million vaccinated members of Clalit Health Services who were 16 years of age or older and who had received at least one dose of the vaccine, 54 cases met the criteria for myocarditis. The estimated incidence of myocarditis was 2.13 cases per 100,000 persons; the highest incidence was among male patients between the ages of 16 and 29 years. Most cases of myocarditis were mild or moderate in severity.
7 October
Epidemiology
Giuliani R, Cairone C, Tavoschi L, et al. COVID-19 outbreak investigation and response in a penitentiary setting: the experience of a prison in Italy, February to April 2020. Euro Surveill. 2021 Sep;26(38). PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34558404. Full text: https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.38.2001385
In Italy, the median age of people in prison is between 50 and 55 years. The study describes an outbreak of COVID-19 in a prison situated in the city of Milan at the beginning of the Italian epidemic in late winter 2020. The attack rate (AR) was highest among custodial staff with 17.6% (94/535 including probable cases) followed by the healthcare workers with 8.8% (7/80) and the people in prison with 2.5% (22/865).
Immunology
Swanson PA 2nd, Padilla M, Hoyland W, et al. AZD1222/ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination induces a polyfunctional spike protein-specific Th1 response with a diverse TCR repertoire. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Sep 30:eabj7211. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34591596. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7211
In AstraZeneca vaccine recipients aged 18 to 85 years who enrolled in a Phase II/III study (n = 296), vaccination “induced a polyfunctional Th1-dominated T cell response, with broad CD4+ and CD8+ T cell coverage across the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.”
Pathogenesis
Cheon IS, Li C, Son YM, et al. Immune signatures underlying post-acute COVID-19 lung sequelae. Sci Immunol. 2021 Sep 30:eabk1741. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34591653. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abk1741
Survivors of severe COVID-19 are at high risk of developing chronic pulmonary sequelae that may be accompanied by abnormal chest imaging and impaired lung function testing. The authors suggest that dysregulated respiratory CD8+ T cell responses might be associated with impaired lung function following acute COVID-19.
Clinical
Al-Aly Z, Bowe B, Xie Y, Xu E. One-year Risks and Burdens of Incident Cardiovascular Disease in COVID-19: Cardiovascular Manifestations of Long COVID. Research Square 2021, posted 5 October. Full text: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-940278/v1
In this cohort of more than 150,000 people with COVID-19, the authors document that even beyond the first 30 days of infection, “people with COVID-19 are at increased risk of incident cardiovascular disease spanning several categories including cerebrovascular disorders, dysrhythmias, ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease, pericarditis, myocarditis, heart failure, and thromboembolic disease.”
Shiels MS, Haque AT, Haozous EA, et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Excess Deaths During the COVID-19 Pandemic, March to December 2020. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Oct 5. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34606321. Full text: https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-2134
Age-standardized excess deaths per 100,000 persons among Black, American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN), and Latino males and females were more than double those in White and Asian males and females. To estimate excess deaths in the US, the authors used death certificate data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and US Census Bureau population estimates.
6 October
Vaccines
Bruxvoort KJ, Ackerson B, Sy LS, et al. Recombinant adjuvanted zoster vaccine and reduced risk of COVID-19 diagnosis and hospitalization in older adults. medRxiv 2021, posted 3 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.01.21264400
Could boosting of innate immune responses with other vaccines help protect against COVID-19? The authors evaluate the association between recombinant adjuvanted zoster vaccine (RZV) and COVID-19 outcomes by matching 149,244 RZV recipients to 298,488 unvaccinated individuals. RZV vaccination was associated with a 16% lower risk of COVID-19 diagnosis and 32% lower risk of hospitalization.
Immunology
Anderson EM, Eiloa T, Goodwin E, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infections elicit higher levels of original antigenic sin antibodies compared to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations. medRxiv 2021, posted 1 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.30.21264363
In this small study (10 acutely infected health care workers and 23 individuals who received two doses of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine), “SARS-CoV-2 infections elicited a large proportion of original antigenic sin-like antibodies that bound efficiently to common seasonal human coronaviruses but poorly to SARS-CoV-2. In converse, vaccination only modestly boosted antibodies reactive to common seasonal human coronaviruses and these antibodies bound efficiently to SARS-CoV-2”. The authors conclude that SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations elicit fundamentally different antibody responses compared to SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Epidemiology
Shitrit P, Zuckerman NS, Mor O, Gottesman BS, Chowers M. Nosocomial outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a highly vaccinated population, Israel, July 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021 Sep;26(39). PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34596015. Full text: https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.39.2100822
The authors describe an investigation of a COVID-19 outbreak in Israel that started from one unidentified COVID-19 patient (mid-July 2021), with extensive, rapid nosocomial spread. Of the 42 cases in this outbreak, 38 were fully vaccinated with two doses of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. The attack rate among exposed individuals reached 23.3% in patients and 10.3% in staff. Worryingly, “several transmissions probably occurred between two individuals both wearing surgical masks, and in one instance using full PPE, including N-95 mask, face shield, gown and gloves.”
Pathogenesis
Ferren M, Favède V, Decimo D, et al. Hamster organotypic modeling of SARS-CoV-2 lung and brainstem infection. Nat Commun 12, 5809 (2021). Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26096-z
The authors present organotypic cultures from hamster brainstem and lung tissues that could help to study the early steps of viral infection and screening antivirals.
Diagnosis
Chappleboim A, Joseph-Strauss D, Rahat A, et al. Early sample tagging and pooling enables simultaneous SARS-CoV-2 detection and variant sequencing. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Sep 30:eabj2266. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34591660. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj2266
The authors describe an improved RNA-seq protocol that allowed for pooling of barcoded samples prior to reverse transcription (called Amplicon Pooling by Hybridization And RNA-Seq [ApharSeq]). Due to early pooling, they anticipate a 10-fold to 100-fold reduction in labor, automated liquid handling, and reagent requirements in high throughput settings compared to current testing methods.
Beyond COVID
Ravuri S, Lenc K, Willson M, et al. Skilful precipitation nowcasting using deep generative models of radar. Nature. 2021 Sep;597(7878):672-677. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34588668. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03854-z
The authors present a deep-learning tool called DGMR that produces rainfall predictions over regions up to 1536 km × 1280 km and with lead times from 5-90 min ahead (“nowcasting”).
5 October
Vaccines
Mair MJ, Berger JM, Berghoff AS, et al. Humoral Immune Response in Hematooncological Patients and Health Care Workers Who Received SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinations. JAMA Oncol. 2021 Sep 30:1-8. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34591965. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5437
In this retrospective study of 595 patients with hematooncological diseases and a control group of 58 health care workers (HCWs), antibody levels after full immunization were higher in HCWs (median, 2500 U/mL; range, 485-2500 U/mL) than in patients with cancer (median, 117.0 U/mL; range, 0-2500 U/mL; P < 0.001). Specific subgroups, such as patients who received B cell–targeting therapy, showed impaired seroconversion. The authors suggest dedicated vaccination trials in patients with cancer.
Immunology
McDonald JT, Enguita FJ, Taylor D, et al. Role of miR-2392 in Driving SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell Reports 2021, 29 September. Full text: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01303-6#%20
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation that have a major impact on many diseases. The authors show that miR-2392 is present in the blood and urine of patients positive for COVID-19 and discuss the potential for developing a minimally invasive COVID-19 detection method. They also designed an miRNA-based antiviral therapeutic that reduces SARS-CoV-2 viability in hamsters.
Virology
Mendez AS, Ly M, Gonzáles-Sánchez AM, et al. The N-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 plays key roles in suppression of cellular gene expression and preservation of viral gene expression. Cell Reports 2021, 29 September. Full text: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01305-X
SARS-CoV-2, like other viruses, relies on cellular ribosomes for protein synthesis and thus competes with endogenous mRNA for access to the translation machinery. In this article, find out more about host shut-off and how SARS-CoV-2 mRNA binding functionally alters the association of non-structural protein 1 (nsp1) with the ribosome, which might have implications for drug targeting.
Diagnosis
Krempe F, Schöler L, Katschinski B, et al. A rapid test recognizing mucosal SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies distinguishes prodromal from convalescent COVID-19. iScience 2021, published 29 September. Full text: https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01162-7
In the absence of symptoms, it is difficult to distinguish prodromal from the late phases of SARS-CoV-2 infection just by RT-PCR since both phases are characterized by low viral loads and corresponding high Ct values (> 30). Here, evaluating a new rapid test detecting IgG antibodies recognizing SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, the authors report that one single clinical nasopharyngeal swab specimen was a fast, cost-effective, and reliable way to discriminate prodromal from the later phases of COVID-19.
Beyond COVID
Tandon PS, Zhou C, Johnson AM, Gonzalez ES, Kroshus E. Association of Children’s Physical Activity and Screen Time With Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Oct 1;4(10):e2127892. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34596669. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27892
Everyone knows that screens are bad, but watch this! In this cross-sectional survey that included 1000 school-aged children in the US, those who engaged in more physical activity and less screen time had better mental health outcomes.
4 October
Vaccines
Shroff RT, Chalasani P, Wei R, et al. Immune responses to two and three doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in adults with solid tumors. Nat Med. 2021 Sep 30. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34594036. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01542-z
The authors report data at 1 week after a third immunization with the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine in 20 patients with solid tumors. Sixteen patients demonstrated a median threefold increase in neutralizing antibody responses, but no improvement was observed in T cell responses. Adverse events were mild.
Immunology
Townsend JP, Hassler HB, Wang Z, et al. The durability of immunity against reinfection by SARS-CoV-2: a comparative evolutionary study. Microbes 2021, published 1 October. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00219-6
How long will immunity against COVID-19 last? Here, the authors use data on the durability of immunity among close coronavirus relatives of SARS-CoV-2 (SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV, human coronavirus 229E, OC43, and NL63) to estimate times to reinfection. They conclude that “reinfection by SARS-CoV-2 under endemic conditions would likely occur between 3 months and 5.1 years after peak antibody response, with a median of 16 months.”
Epidemiology
Tonzel JL, Sokol T. COVID-19 Outbreaks at Youth Summer Camps — Louisiana, June–July 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 1 October 2021. Full text: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7040e2
Widespread circulation of the fairly transmissible Delta variant and underutilization of preventive measures such as vaccination, masking, and physical distancing? Not good. The authors report 28 camping outbreaks in Louisiana (US), which included a total of 321 COVID-19 cases among an estimated 2988 campers and staff members. The mean outbreak size was 11.5 cases (range = 2–59 cases). Compared with the June–July period of 2020, when only two outbreaks were identified in Louisiana, this represents a thirty-one-fold increase in confirmed camp-associated cases.
Prevention
Van Naarden Braun K, Drexler M, Rozenfeld RA, et al. Multicomponent Strategies to Prevent SARS-CoV-2 Transmission — Nine Overnight Youth Summer Camps, United States, June–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 1 October 2021. Full text: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7040e1
Get them vaccinated and test them. In 9 overnight summer camps in the US (7173 campers and staff members with high vaccination coverage [> 93% among eligible persons aged ≥ 12 years]), pre-arrival and frequent screening testing (38,059 tests) were sufficient to reduce the number of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases to 9 and prevent secondary infections.
Diagnosis
Hepp C, Shiaelis N, Robb NC, et al. Viral detection and identification in 20 min by rapid single-particle fluorescence in-situ hybridization of viral RNA. Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 1;11(1):19579. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34599242. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98972-z
The authors explore a rapid fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) protocol capable of detecting influenza virus, avian infectious bronchitis virus and SARS-CoV-2 specifically and quantitatively in approximately 20 minutes – quicker than current RT-PCR protocols.
3 October
Vaccines
Eyre DW, Taylor D, Purver M, et al. The impact of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination on Alpha & Delta variant transmission. medRxiv 2021, posted 29 September. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.28.21264260
Vaccines reduce transmission, but the extent may vary with the vaccine and the SARS-CoV-2 strain. Data from a retrospective observational cohort study of 139,164 contacts of 51,798 SARS-CoV-2-infected index cases.
Epidemiology
Dyson L, Hill EM, Moore S, et al. Possible future waves of SARS-CoV-2 infection generated by variants of concern with a range of characteristics. Nat Commun. 2021 Sep 30;12(1):5730. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34593807. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25915-7
How will new variants shape future COVID-19 waves? As expected, the authors’ model demonstrate that a new strain with a substantial transmission advantage over resident variants, or with immune escape properties, can generate a wave of infections and hospitalizations comparable to previous waves. “Moreover, a variant that is less transmissible, but shows partial immune-escape could provoke a wave of infection that would not be revealed until control measures are further relaxed.”
Prevention
Rathnasinghe R, Jangra S, Miorin L, Schotsaert M, Yahnke C, Garcίa-Sastre A. The virucidal effects of 405 nm visible light on SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A virus. Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 30;11(1):19470. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34593848. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97797-0
Wavelengths with less irradiation energy than ultra-violet light such as visible light (405 nm) have thus far been explored in the context of bactericidal and fungicidal applications. What about its virucidal potential? Here, the authors demonstrate increased susceptibility of lipid-enveloped respiratory pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A virus to 405 nm. Visible light for the continuous decontamination in occupied areas within hospitals and/or infectious disease laboratories?
Diagnosis
Natarajan A, Han A, Zlitni S, et al. Standardized preservation, extraction and quantification techniques for detection of fecal SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 1;12(1):5753. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34599164. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25576-6
Monitoring the fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may help to fully understand SARS-CoV-2 and its effect on patient health. Here, the authors find that the Zymo DNA/RNA preservative and the QiaAMP extraction kit yield more detectable RNA than the others, using both ddPCR and RT-qPCR.
Clinical
Nguyen S, Chan R, Cadena J, et al. Budget constrained machine learning for early prediction of adverse outcomes for COVID-19 patients. Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 1;11(1):19543. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34599200. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98071-z
The authors present a method to evaluate risk of deterioration for patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection at the time of clinical evaluation. The study suggests that “the variables that best predicted mortality as the outcome were older age, elevated BUN, elevated serum potassium, elevated diastolic blood pressure, and elevated D-dimer levels.”
2 October
Immunology
Feng S, Phillips DJ, White T, et al. Correlates of protection against symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med September 29, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01540-1
Using data from 171 cases and 1404 controls, this study shows that higher anti-spike IgG, anti-RBD IgG, and neutralizing antibody titers were all associated with lower risk of symptomatic disease. The authors believe that their correlates of vaccine efficacy could be used to extrapolate efficacy to immunogenicity data for novel vaccines. However, data were based on cases of COVID-19 detected in a mainly white population in the UK, mostly due to Alpha variants.
Nakayama T, Lee IT, Jiang S, et al. Determinants of SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication in airway mucosal tissue and susceptibility in smokers. Cell Rep Med September 27, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(21)00283-4
SARS-CoV-2 infection is present in all examined head & neck tissues, with a notable tropism for the nasal cavity and tracheal mucosa. This study also uncovered an association between smoking and higher SARS-CoV-2 viral infection in the human proximal airway, which may explain the increased susceptibility of smokers to developing severe COVID-19. This is at least partially explained by differences in IFN-β1 levels.
Diagnostics
Allen N, Brady M, Carrion Martin AI, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing in health care workers: a comparison of the clinical performance of three commercially available antibody assays. Microbiol Spectr 9:e00391-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00391-21
The Roche anti-nucleocapsid total antibody assay is better suited than the Abbott IgG assay. Of those with previously confirmed infection, 41% (150/367) and 95% (348/367) tested positive on the Abbott IgG and Roche antibody, respectively. At 21 weeks (150 days) after confirmed infection, positivity on Abbott started to decline. Roche positivity was retained for the entire study period (33 weeks).
Variants
Choi A, Koch M, Wu K, et al. Serum Neutralizing Activity of mRNA-1273 Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J Virology 22 September 2021. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JVI.01313-21
Minimal effects on neutralization titers against Alpha. Other VOCs such as Beta, Gamma and Delta, showed significantly decreased neutralization titers ranging from 2.1-fold to 8.4-fold reductions compared with D614G, although all remained susceptible to mRNA-1273–elicited serum neutralization.
Severe COVID-19
Barbaro RP, MacLaren G, Boonstra PS, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: evolving outcomes from the international Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Lancet September 29, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01960-7/fulltext
This study of 4812 patients from 349 sites in 41 countries showed that during 2020, mortality after ECMO support in patients with COVID-19 increased by about 15% and the median duration of ECMO support increased by 6 days. This was not attributable to differences in known risk factors at baseline. However, a higher proportion of patients supported with ECMO after May 1 had treatment-refractory disease than those treated earlier, and thus might represent a different clinical phenotype with a worse overall prognosis.
1 October
Immunology
Luo L, Liang W, Pang J, et al. Dynamics of TCR repertoire and T cell function in COVID-19 convalescent individuals. Cell Discov September 28, 2021, 7, 89. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41421-021-00321-x
More on T cells. While the diversity of the TCR repertoire was increased in discharged patients, it returned to base level one 1 week after becoming virus free. The top expanded T cell clones (~ 10% of total T cells) display the key antiviral features in CD8+ T cells (explaining how a dramatically decreased level of CD8+ T cells can clear the virus in most SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals).
Vaccines
Falsey AR, Sobieszczyk ME, Hirsch I, et al. Phase 3 Safety and Efficacy of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) Covid-19 Vaccine. NEJM September 29, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2105290?query=featured_home
A total of 32,451 participants (in the US, Chile and Peru) received AstraZeneca’s vaccine or placebo. Overall estimated vaccine efficacy was 74.0% (73 vs 130) and was 83.5% (5 vs 14) in participants 65 years of age or older. Severe or critical symptomatic COVID-19 occurred in 0 vs 8 patients.
Agrawal U, Katikireddi SK, McCowan C, et al. COVID-19 hospital admissions and deaths after BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccinations in 2.57 million people in Scotland (EAVE II): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Resp Med September 29, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00380-5/fulltext
This national level analysis found that at 14 days or longer since the first vaccine dose, there were 883 COVID-19 admissions to hospital and 541 deaths in almost 2.57 million individuals in Scotland. Only 39 deaths and hospitalizations were found among individuals who received a second vaccine dose, which translated into an event rate of 0.9 per 1000 person-years. Rates were higher with BNT162b2, but the authors were unable to make robust comparisons between the two vaccines because of differential use of the two deployed vaccines during the study period.
Long COVID-19
Zhang X, Wang F, Shen Y, et al. Symptoms and Health Outcomes Among Survivors of COVID-19 Infection 1 Year After Discharge From Hospitals in Wuhan, China. JAMA Netw Open September 29, 2021; 4(9):e2127403. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784558
Long-term follow up from Wuhan. Of 2433 patients with a 1 year follow-up, 1095 (45%) reported at least one symptom. The most common symptoms included fatigue, sweating, chest tightness, anxiety, and myalgia. Older age, female sex, and severe disease during hospital stay were associated with higher risks of fatigue. Of note, 4.2% of patients reported palpitations, which may point to long-term damage of COVID-19 to the cardiovascular system.
Treatment
Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, et al. REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19. NEJM September 29, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2108163?query=featured_home
A large Phase 3 trial, showing that the early use of the two antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab in outpatients with risk factors for severe COVID-19 can lower the risk of hospitalization or death from any cause. Both doses of intravenous REGEN-COV (1200 mg and 2400 mg) led to a reduction in hospitalization or death over a period of 28 days after treatment, compared to their concurrent placebo groups (1.0 and 1.3 % vs 4.6% and 3.2%, respectively). Both doses reduced viral loads, particularly in patients with higher viral loads, with a faster time to viral clearance than placebo.
30 September
Immunology
Wickenhagen A, Sugrue E, Lytras S, et al. A prenylated dsRNA sensor protects against severe COVID-19. Science September 28, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj3624
An all-in-one paper. OAS1 is an evolutionarily ancient interferon-stimulated gene that has maintained IFN responsivity for hundreds of millions of years. The authors not only found out that this gene potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2. They also describe how and how different gene variants are distributed in different populations and animals. Finally, it is shown that, among 499 hospitalized patients, expression of prenylated OAS1 is associated with protection from severe COVID-19 (34% vs 45%), suggesting this antiviral defense is a major component of a protective antiviral response.
Vaccine
Hause AM, Baggs J, Gee J, et al. Safety Monitoring of an Additional Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine — United States, August 12–September 19, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 28 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7039e4.htm?s_cid=mm7039e4_w
Among 12,591 registrants who completed a health check-in survey after all 3 doses of an mRNA, adverse reactions after dose 3 were similar to those after dose 2.
Glatman-Freedman A, Hershkovitz Y, Kaufman Z, et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 vaccine in adolescents during outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant infection, Israel, 2021. Emerg Infect Dis September 27, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/11/21-1886_article
Nationwide retrospective cohort study, showing a crude vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection of 88% in the fourth week among adolescents.
Co-morbidities
Kumar N, AbdulRahman A, AlAwadhi AI, et al. Is glucose-6-phosphatase dehydrogenase deficiency associated with severe outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients? Sci Rep September 28, 2021, 11, 19213. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-98712-3
No.
Lacedonia D, Scioscia G, Santomasi C, et al. Impact of smoking, COPD and comorbidities on the mortality of COVID-19 patients. Sci Rep September 28, 2021, 11, 19251. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-98749-4
Cohort study from Italy, finding that COPD patients and former smokers were those with the highest all-cause mortality, which seemed to be mainly related to the presence of comorbidities and not to COPD and smoking itself.
29 September
Epidemiology
Vam Loon W, Theuring S, Hommes F, et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among Students, Teachers, and Household Members During Lockdown and Split Classes in Berlin, Germany. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(9):e2127168. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784548?resultClick=1
Only a few isolated SARS-CoV-2 infections, no clusters in early 2021.
Virology
Zhang Y, Huang K, Xie D. et al. In vivo structure and dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome. Nat Commun September 28, 12, 5695. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25999-1
This study provides a global landscape of relationships between SARS-CoV-2 RNA structure and key processes of the viral life cycle, such as replication, discontinuous transcription and translation.
Transmission
Hu X, Liu Z, Liang J, et al. Environmental contamination of a quarantine hotel via SARS-CoV-2 positive travellers. Journal of Travel Medicine September 2021; taab148, https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taab148/6377253?searchresult=1
Report on the extent of environmental contamination of a quarantine hotel via two SARS-CoV-2 VOC-positive travelers. The bathroom had the highest rate for SARS-CoV-2 positive samples. Except for the TV remote control, samples from the two bedrooms were negative.
Benenson S, Ottolenghi M, Cohen MJ, et al. High attack rate of COVID-19 in an organized tour group of vaccinated travelers to Iceland. Journal of Travel Medicine, September 28, 2021, taab157, https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taab157/6377252?searchresult=1
In a group of 25 twice-vaccinated Israeli travelers, 21 became infected (84%), despite negative pre-flight PCR tests, probably due to close and prolonged exposures during long bus drives.
Vaccines
Sánchez van Kammen M, Aguiar de Sousa D, Poli S, et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine–Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. JAMA Neurology September 28, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2784622?resultClick=1
International registry of 116 CVST cases occurring after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, among them 78 cases with CVST-TTS (76 had received ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine from AstraZeneca). These patients had a clinical profile distinct from patients with CVST before the COVID-19 pandemic, with high rates of coma and intracerebral hemorrage and a high mortality rate.
Clinical
Barrett E, Hingle ST, Smith CD, et al. Getting Through COVID-19: Keeping Clinicians in the Workforce. Annals Int Medicine September 28, 2021. https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-3381
The authors are gravely concerned about their colleagues’ exhaustion, burnout and disillusion. They urge employers and medical organizations to take tangible steps to preserve the clinical workforce.
28 September
Epidemiology
Jehn M, McCullough JM, Dale AP, et al. Association Between K–12 School Mask Policies and School-Associated COVID-19 Outbreaks — Maricopa and Pima Counties, Arizona, July–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep September 24, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7039e1.htm?s_cid=mm7039e1_w
Still any doubts? Please forward to all your friends, especially the mask-doubters! After adjusting for potential confounders, the odds of a school-associated COVID-19 outbreak in schools without a mask requirement were 3.5 times higher than those in schools with an early mask requirement (95% CI: 1.8–6.9).
Budzyn SE, Panaggio MJ, Parks SE, et al. Pediatric COVID-19 Cases in Counties With and Without School Mask Requirements — United States, July 1–September 4, 2021. MMWR 24 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7039e3.htm?s_cid=mm7039e3_w
Same idea: after controlling for co-variates, school mask requirements remain associated with lower daily case rates of pediatric COVID-19 (β = −1.31; 95% confidence interval: −1.51 to −1.11) (p < 0.001).
Transmission
Bigouette JP, Ford L, Segaloff HE, Langolf K, Kahrs J, Zochert T, et al. Association of shared living spaces and COVID-19 in university students, Wisconsin, USA, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis September 22, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/11/21-1000_article
Among 2187 students residing on a university campus, 528 (24%) received a COVID-19 diagnosis during the fall semester 2020. Not a big surprise: students sharing a bedroom or suite had approximately twice the odds of contracting COVID-19 as those living alone.
Vaccine
Siegler AJ, Luisi N, Hall EW, et al. Trajectory of COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy Over Time and Association of Initial Vaccine Hesitancy With Subsequent Vaccination. JAMA Netw Open September 24, 2021;4(9):e2126882. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784480
This large cohort study found that COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is not a stable trait. More than one-third (37%) transitioned from vaccine hesitant into vaccine willing within a few months (by normal variables: sex, age, race, age, etc).
Treatment
Qian Y, Lei T, Patel PS, et al. Direct activation of endothelial cells by SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is blocked by Simvastatin. J Virology September 22, 2021. https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JVI.01396-21
It was found that the nucleocapsid protein (NP) of SARS-CoV-2 significantly activated human endothelial cells through several signaling pathways. Simvastatin was identified as a potent inhibitor of NP-induced endothelial activation (in contrast to other statins).
27 September
Transmission
Lesieur E, Torrents J, Fina F, et al. Congenital infection of SARS-CoV-2 with intrauterine foetal death: a clinicopathological study with molecular analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 23, 2021, ciab840, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab840
A case of in utero foetal death at 24+2 weeks of gestation that occurred seven days after the diagnosis of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection in the mother.
Diagnostics
Surasi K, Cummings KJ, Hanson C, et al. Effectiveness of Abbott BinaxNOW rapid antigen test for detection of SARS-CoV-2 infections in outbreak among horse racetrack workers, California, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Nov [date cited]. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/11/21-1449_article
The Abbott BinaxNOW rapid antigen test (RAT) is cheaper and faster than real-time PCR. During an outbreak occurring in a horse racetrack in California, USA, RAT enabled some SARS-CoV-2–positive employees to be identified and isolated faster than if rRT-PCR had been used alone. Among 127 rRT-PCR–positive specimens, the 55 with paired RAT-positive results had a lower mean cycle threshold than the 72 with paired RAT-negative results (17.8 vs. 28.5)
Crowe J, Schnaubelt AT, SchmidtBonne S, et al. Assessment of a Program for SARS-CoV-2 Screening and Environmental Monitoring in an Urban Public School District. JAMA Netw Open September 22, 2021;4(9):e2126447. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784428?resultClick=1
In this study of staff and students in 3 urban public schools in Nebraska, weekly screening of asymptomatic staff and students by saliva PCR testing was associated with increased SARS-CoV-2 case detection. A total of 46 cases of SARS-CoV-2 (22 students and 24 staff members) were detected, representing an increase in cumulative case detection rates from 1.2% to 7.0% among students and from 2.1% to 5.3% among staff compared with conventional reporting mechanisms during the pilot period.
Clinical
Patel P, deCuir J, Abrams J, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Adults A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open September 22, 2021;4(9):e2126456. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784427?resultClick=1
According to this systematic review of 221 patients with MIS-A reported worldwide, the syndrome presents approximately 4 weeks after acute COVID-19. Clinical presentation was heterogeneous, likely owing to a dysregulated immune response, with hyperinflammation and extrapulmonary multiorgan involvement that may be difficult to discern from acute biphasic COVID-19 and postacute sequelae.
Nemani K, Conderino S, Marx J, et al. Association Between Antipsychotic Use and COVID-19 Mortality Among People With Serious Mental Illness. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2784469?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 464 adults with serious mental illness diagnosed with COVID-19 infection in a New York City medical system, antipsychotic treatment was not associated with an increased risk of mortality.
Comorbidities
Disanto G, Sacco R, Bernasconi E, et al. Association of Disease-Modifying Treatment and Anti-CD20 Infusion Timing With Humoral Response to 2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol September 23, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2784448?resultClick=1
Among 120 patients from Switzerland, the humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 at 1 month after vaccination was appropriate under treatment with cladribine and teriflunomide and diminished/absent under treatment with anti-CD20 therapies and S1P modulators. Delaying anti-CD20 infusions by 3 to 6 months before vaccination could, however, increase the probability of developing appropriate humoral responses.
Brill L, Rechtman A, Zveik O, et al. Humoral and T-Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Ocrelizumab. JAMA Neurol September 23, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2784449?resultClick=1
Same issue. In this cohort study of 112 participants from Jerusalem, those treated with ocrelizumab developed lower serology response compared with untreated patients and healthy controls but showed preserved T-cell response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine compared with healthy controls.
Other facts to consider today

26 September
Today we’ll have another Vaccine special. Longer follow up with MODERNA’s mRNA-1273 vaccine, effectiveness in HCWs, and new data from Israel and Portugal. And about the consequences of unequal vaccine allocation.
Vaccine
El Sahly HM, Baden LR, Essink B, et al. Efficacy of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine at Completion of Blinded Phase. NEJM September 22, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2113017?query=featured_home
Longer follow up of this large RCT in 30,415 participants (interim analysis has been published on December 30, 2020 https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2035389). At a median follow-up of 5.3 months in the blinded phase, the efficacy of the MODERNA vaccine in preventing severe disease was 98.2%, with 2 versus 106 cases in the placebo group. Vaccine efficacy was consistent across ethnic and racial groups, age groups, and participants with coexisting conditions.
Pilishvili T, Gierke R, Fleming-Dutra KE, et al. Effectiveness of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine among U.S. Health Care Personnel. NEJM September 22, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2106599?query=featured_home
Among 1482 case and 3449 control participants, vaccine effectiveness for complete vaccination was 88.8% (95% CI, 84.6 to 91.8) with the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer–BioNTech) and 96.3% (95% CI, 91.3 to 98.4) with the mRNA-1273 vaccine (MODERNA).
Haas EJ, McLaughlin JM, Khan F, et al. Infections, hospitalisations, and deaths averted via a nationwide vaccination campaign using the Pfizer–BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in Israel: a retrospective surveillance study. Lancet Inf Dis September 22, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00566-1/fulltext
Without the national vaccination campaign, Israel probably would have had triple the number of hospitalisations and deaths compared with what actually occurred during its largest wave of the pandemic to date, and the health-care system might have become overwhelmed.
Wagner CE, Saad-Roy CM, Morris SE, et al. Vaccine nationalism and the dynamics and control of SARS-CoV-2. Science September 24, 2021, Vol. 373, NO. 656224. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj7364
Complex modeling study showing that unequal vaccine allocation will result in sustained transmission and increased case numbers in regions with low vaccine availability and thus to a higher associated clinical burden compared with a vaccinated population. Moreover, under certain scenarios, sustained local transmission could lead to an increased potential for antigenic evolution.
Nunes B, Rodrigues AP, Kislaya I, et al. mRNA vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19-related hospitalisations and deaths in older adults: a cohort study based on data linkage of national health registries in Portugal, February to August 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(38):pii=2100833. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.38.2100833
High mRNA vaccine effectiveness in older people in Portugal, supporting data from Israel and U.S. Of note, there was no evidence of VE reduction up to 3 months after the second dose and during the period of Delta variant circulation.
Zhu F, Jin P, Zhu T, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine with a homologous prime-boost regimen in healthy participants aged 6 years and above: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 22, 2021, ciab845, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab845/6374123
An Ad5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine (from China) with a single dose was safe and induced robust immune responses in 150 children and adolescents aged 6-17 years.
25 September
Epidemiology
Giuliani R, Cairone C, Tavoschi L, et al. COVID-19 outbreak investigation and response in a penitentiary setting: the experience of a prison in Italy, February to April 2020. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(38):pii=2001385. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.38.2001385
An outbreak of COVID-19 within a prison in Italy. The infection spread not only among cellmates but also among individuals living in contiguous cells and sharing adjacent spaces. Transmission was more common between detained individuals with a shared culture or language, forming micro-clusters.
Immunology
Fröberg J, Gillard J, Philipsen R, et al. SARS-CoV-2 mucosal antibody development and persistence and their relation to viral load and COVID-19 symptoms. Nat Commun September 24, 2021, 12, 5621. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25949-x
This study examined the development and persistence of nasal antibodies following infection with SARS-CoV-2 in a household contact study. Mucosal antibodies against S and RBD increased 7–9 days after symptom onset and remain elevated for at least 9 months. Mucosal antibodies may play a key role in limiting disease as they were found to be correlated with a lower viral load and were related to a faster decline in systemic symptoms.
Collateral damage
Agarwal S, Huang P, Luo C, et al. Assessment of Online Food Ordering and Delivery in Singapore During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open September 23, 2021;4(9):e2126466. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784439?resultClick=1
Less vegetables, more junk food: using a data set of 42,495 real food orders, this study suggests an association with unhealthier eating habits during the COVID-19 lockdown. The probability that the order contained vegetables decreased by 15%, while the probability of an order in the barbecue/fried food or beverage category increased by 11% and 4%, respectively. Of note, changes in eating habits persisted after lockdown measures were removed.
Ray LC, Collins JP, Griffin PM, et al. Decreased Incidence of Infections Caused by Pathogens Transmitted Commonly Through Food During the COVID-19 Pandemic — Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 U.S. Sites, 2017–2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1332–1336. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7038a4.htm?s_cid=mm7038a4_w
More junk food, but less infections: the 26% decrease in incidence of infections caused by pathogens transmitted commonly through food during 2020 was the largest single-year variation in incidence over the last 25 years in the US. Widespread public health interventions implemented to prevent SARS-CoV-2 transmission might have contributed to this decrease.
Treatment
Hastie KM, Li H, Bedinger D, et al. Defining variant-resistant epitopes targeted by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: A global consortium study. Science, September 23, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abh2315
Incredible work, providing a detailed structural and competitive landscape of key antibody binding sites on Spike. The results of this effort can be used to predict and interpret effects of variants of concern, and for strategic selection of durable therapeutics and cocktails against emerging variants.
Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, Díaz Martinez JP, et al. Antibody and cellular therapies for treatment of covid-19: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ September 23, 2021;374:n2231. https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n2231
Review of 47 trials: in patients with non-severe COVID-19, casirivimab-imdevimab probably reduces hospitalization; bamlanivimab-etesevimab, bamlanivimab, and sotrovimab may reduce hospitalization. Convalescent plasma, IVIg, and other antibody and cellular interventions may not confer any meaningful benefit.
Huo J, Mikolajek H, Le Bas A, et al. A potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralising nanobody shows therapeutic efficacy in the Syrian golden hamster model of COVID-19. Nat Commun September 22, 2021, 12, 5469. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25480-z
Neutralizing single domain antibodies (“nanobodies”) are small, stable and thus compatible with respiratory administration. The authors report four nanobodies (C5, H3, C1, F2) engineered as homotrimers with picomolar affinity for the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein. Administration of C5 trimer via the respiratory route showed potent therapeutic efficacy in the Syrian hamster model of COVID-19 along with being an effective prophylaxis.
Christie MJ, Irving AT, Forster SC, et al. Of bats and men: Immunomodulatory treatment options for COVID-19 guided by the immunopathology of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Science Immunology September 17, 2021, Vol 6, Issue 63. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abd0205
Another excellent review, summarizing current knowledge on COVID-19 immunopathogenesis in relation to three clinical disease stages. The article also focusses on immune evasion strategies used by pathogenic coronaviruses such as skewing type I, II, and III interferon responses and inhibiting detection via pattern recognition and antigen presentation.
24 September
Immunology
Abishek C, Liu J, Yu J, et al. Prior infection with SARS-CoV-2 WA1/2020 partially protects rhesus macaques against re-infection with B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants. Science Translational Medicine September 21, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj2641
This was a study on 27 brave Indian-origin adult rhesus macaques, demonstrating that natural immunity induced by the Wuhan strain provides robust short-term protection against re-challenge with the same SARS-CoV-2 strain but reduces protection against re-challenge with certain SARS-CoV-2 variants. A greater reduction of efficacy was observed against B.1.351 as compared with B.1.1.7.
Vaccine
Dooling K, Gargano JW, Moulia D, et al. Use of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine in Persons Aged ≥16 Years: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 21 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7038e2.htm?s_cid=mm7038e2_w
After 8 months of use under an FDA EUA and CDC ACIP interim recommendation, the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, Comirnaty, now has full FDA approval and is recommended by ACIP for use in persons aged ≥ 16 years in the US. A brief discussion.
Paulsen FO, Schaefers C, Langer F, et al. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura after vaccination with COVID-19 vaccine (ChAdOx1 nCov-19). Blood September 16, 2021, 138 (11): 996–999. https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/138/11/996/476455/Immune-thrombocytopenic-purpura-after-vaccination
Four patients with symptomatic thrombocytopenia associated with previous administration of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (but not associated with VITT). Of note, 3 of 4 patients presented with a medical history known to be associated with the occurrence of thrombocytopenia.
Diagnostics
Leutzinger K, Osthoff M, Dräger S, et al. Comparing immunoassays for SARS-Coronavirus-2 antibody detection in patients with and without laboratory-confirmed SARS-Coronavirus-2 infection. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 15 September 2021, https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JCM.01381-21
Cross-comparison of eight immunoassays detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid(N) or spike(S) antigens in three cohorts consisting of 859 samples from 622 patients. Assays showed substantial agreement, but interpretation of qualitative and semi-quantitative results depends on the time elapsed post-diagnosis and the choice of viral antigen (discordance mostly resulted from N-based assays).
Treatment
Fenwick C, Turelli P, Perez L, et al. A highly potent antibody effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Cell Rep September 20, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01278-X
While screening B cells from COVID-19 donors, the authors identified P5C3, a highly potent and broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibody with picomolar neutralizing activity against all SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC). P5C3 shows complete prophylactic protection in a SARS-CoV-2 infected hamster challenge model.
23 September
Epidemiology
Hagan LM, McCormick DW, Lee C, et al. Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant Infections Among Incarcerated Persons in a Federal Prison — Texas, July–August 2021. MMWR 21 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7038e3.htm?s_cid=mm7038e3_w
Bad news from a federal prison in Texas. During an outbreak involving the Delta variant, transmission was incredibly high among vaccinated (70%) and unvaccinated (93%) persons. Although hospitalizations, deaths, and attack rates were higher among unvaccinated than vaccinated persons, the duration of positive serial PCR test results was similar between these two groups, and infectious virus was cultured from both vaccinated and unvaccinated participants. This underscores the importance of implementing and maintaining multiple COVID-19 prevention strategies.
Virology
Patchett S, Ly Z, Rut W, et al. An A molecular sensor determines the ubiquitin substrate specificity of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Cell Rep September 20, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01208-0
The SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) is essential for processing viral polyproteins for replication and functions in host immune evasion by cleaving ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein conjugates. This study gives insight into the ensemble of conformations that the highly conserved active site of PLpro can adopt.
Vaccine
Sokal A, Barba-Spaeth G, Fernández I, et al. mRNA vaccination of naive and COVID-19-recovered individuals elicits potent memory B cells that recognize SARS-CoV-2 variants. Immunity September 20, 2021. https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(21)00396-4
Although naïve individuals had weaker neutralizing serum responses than recovered patients, many of their RBD-specific memory B cells (MBCs) displayed high affinity towards multiple variants of concern (VOCs), including Delta and Beta. These data suggest that an additional challenge in naive vaccinees could recall such affinity-matured MBCs and allow them to respond efficiently to VOCs.
Transmission
Hu M, Wang J, Lin H, et al. Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission among Air Passengers in China. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 21, 2021, ciab836, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab836/6373518
This analysis of 175 index cases among 5797 passengers on 177 airplanes came to the conclusion that the overall risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission during domestic travel on planes is relatively low. However, the attack rates (AR) among travellers varied considerably. The seats immediately adjacent to the index cases had an AR of 9.2%, with a relative risk of 27.8 compared to other seats in the upper limit estimation. The middle seat had the highest AR.
Dhanasekaran V, Edwards KM, Xie R, et al. Air travel-related outbreak of multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. Journal of Travel Medicine, September 21, 2021, taab149, https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taab149/6372544?searchresult=1
And the thing is: sometimes it’s not only one single index case. In this report, a large cluster of 59 (!) cases were linked to a single flight with 146 passengers from New Delhi to Hong Kong in April 2021. Transmission of three VOI/VOC lineages occurred from at least seven index cases. Take your seats (or stay home).
22 September
Virology
Meyer B, Chiaravalli J, Gellenoncourt S, et al. Characterising proteolysis during SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies viral cleavage sites and cellular targets with therapeutic potential. Nat Commun September 21, 2021, 12, 5553. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25796-w
An improved understanding of the exact ways in which proteolytic cleavage is regulated, modulates protein activity, and serves to benefit viral replication will be crucial for targeting cellular substrates of viral proteases as a therapeutic strategy. The authors applied mass spectrometry-based methods for N-terminomics to study proteolysis, enabling the identification of novel cleavage and processing sites within viral proteins. They discover that several of these novel viral cleavage sites show altered cleavage following treatment with the cathepsin/calpain inhibitor calpeptin.
Variants
Tao K, Tzou PL, Nouhin J, et al. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Rev Genet September 19, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41576-021-00408-x
Brilliant review. And the best Figure of the day (Figure 1, your new bedroom poster)!
Clinical
Reif J, Heun-Johnson H, Tysinger B, et al. Measuring the COVID-19 Mortality Burden in the United States. Ann Int Med September 21, 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-2239
In approximately 1 year, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in half the premature mortality caused by all cancer types combined or all cardiovascular diseases combined. This modeling study estimated that the US COVID-19 pandemic resulted in 9.08 million YLL through 13 March 2021. By comparison, Americans lost an estimated 15.4 million YLL from cancer and an estimated 14.7 million from cardiovascular diseases in 2019.
Treatment
Yamin R, Jones AT, Hoffmann HH, et al. Fc-engineered antibody therapeutics with improved anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy. Nature September 21, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04017-w
The antiviral activity of IgG antibodies is the outcome of Fab-mediated virus neutralization coupled with the capacity of the Fc domain to mediate effector functions through interactions with Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) expressed on effector leukocytes. Here, the authors report the development and evaluation of Fc-optimized anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAbs with superior potency to prevent or treat COVID-19 disease.
Dong J, Zost SJ, Greaney AJ, et al. Genetic and structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 variant neutralization by a two-antibody cocktail. Nat Microbiol September 21, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-021-00972-2
Two non-competing antibodies, designated COV2-2196 and COV2-2130 (later engineered to be long-acting IgG molecules designated as AZD8895 and AZD1061, respectively), synergistically neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in animal models. This study provides a comprehensive mapping of the effect of RBD mutations on the binding of these two antibodies (both are currently being investigated in Phase III studies), underscoring their use as a rationally designed cocktail, given that they have different escape mutations.
Karbiener M, Farcet MR, Schwaiger J, et al. Plasma from post-COVID-19 and COVID-19-Vaccinated Donors Results in Highly Potent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization by Intravenous Immunoglobulins. The Journal of Infectious Diseases September 20, 2021, jiab482, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab482/6372887
As of September 2020, some immunoglobulin (IG) lots from US plasma have contained neutralizing antibodies against the newly emerged SARS-CoV-2. Since then, antibody positivity and antibody titers have increased sharply.
21 September
Vaccine
Self WH, Tenforde MW, Rhoads JP, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) Vaccines in Preventing COVID-19 Hospitalizations Among Adults Without Immunocompromising Conditions — United States, March–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 17 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7038e1.htm?s_cid=mm7038e1_w
Vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 hospitalization during March 11–August 15, 2021, was higher for the Moderna vaccine (93%) than the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (88%) and the Janssen vaccine (71%). However, as with all real-world data, residual confounding is possible.
Warren CM, Snow TT, Lee AS, et al. Assessment of Allergic and Anaphylactic Reactions to mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines With Confirmatory Testing in a US Regional Health System. JAMA Netw Open September 17, 2021;4(9):e2125524. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784268?resultClick=1
Immunological testing of 22 patients with suspected vaccine allergy suggests that non–IgE-mediated allergic reactions to polyethylene glycol may be responsible for many cases of allergy to mRNA vaccines.
Clinical
Reiterer M, Rajan M, Gómez-Banoy N, et al. Hyperglycemia in Acute COVID-19 is Characterized by Insulin Resistance and Adipose Tissue Infectivity by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Report September 15, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(21)00428-9
This important study suggests that SARS-CoV-2 may trigger adipose tissue dysfunction to drive insulin resistance and adverse outcomes in acute COVID-19.
Hippisley-Cox J, Coupland CA, Mehta N, et al. Risk prediction of covid-19 related death and hospital admission in adults after covid-19 vaccination: national prospective cohort study. BMJ September 19, 2021. https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n2244
The authors identified a range of important clinical risk factors for severe COVID-19 outcomes in vaccinated people. In this national linked dataset from more than 6.9 million adults, risk ratios were highest for people with Down’s syndrome, kidney transplantation, sickle cell disease, care home residency, chemotherapy, recent bone marrow transplantation or solid organ transplantation ever, HIV/AIDS, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, neurological conditions, and liver cirrhosis.
Moon RC, Mackey RH, Cao Z, et al. Is COVID-19 Less Deadly Now? — Trends of In-Hospital Mortality Among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 17, 2021, ciab830. https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab830/6371824
No. Despite more time and experience in treating COVID-19, there has been no continued decline in mortality among in-patients: after an initial decline from April through June 2020 (from 22.2% to 11.9%), adjusted in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 in-patients peaked twice and was significantly higher than June 2020 for subsequent months except in July and October 2020.
20 September
Vaccine
Falsey AR, Frenck RW, Walsh EE, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization with BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose 3. NEJM September 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2113468?query=featured_home
Preliminary findings from a small pivotal trial, suggesting that a third dose could prolong protection and further increase the breadth of protection.
Clinical
Seedat S, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection hospitalization, severity, criticality, and fatality rates in Qatar. Sci Rep September 14, 2021, 11, 18182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97606-8
With Qatar’s young population, overall SARS-CoV-2 severity and fatality were not high with < 4 infections in every 1000 being severe or critical and < 2 in every 10,000 being fatal. However, the authors argue that these rates would have been much higher if Qatar’s population had the demographic structure of Europe or the United States.
Iroungou BA, Mangouka LG, Bivigou-Mboumba B, et al. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics Associated With Severity, Clinical Outcomes, and Mortality of COVID-19 Infection in Gabon. JAMA Netw Open September 14, 2021; 4(9):e2124190. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784059?resultClick=1
Same findings from Gabon. Young people, only a few severe infections.
Treatment
Ananworanich J, Mogg R, Dunne MW, et al. Randomized study of rivaroxaban vs. placebo on disease progression and symptoms resolution in high-risk adults with mild COVID-19. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 15, 2021, ciab813, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab813/6370549
Large RCT, showing no impact of rivaroxaban on disease progression in high-risk adults with mild COVID-19.
Cho H, Gonzales-Wartz KK, Huang D, et al. Bispecific antibodies targeting distinct regions of the spike protein potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Science Translational Medicine September 14, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj5413
Hyeseon Cho and colleagues from NIH have isolated a panel of monoclonal antibodies from plasmablasts and memory B cells from COVID-19 convalescent individuals that target distinct regions of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. From this antibody panel, the authors have designed bispecific antibodies that potently neutralize a range of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, including Delta.
Pediatrics
Vono M, Huttner A, Lemeille S, et al. Robust innate responses to SARS-CoV-2 in children resolve faster than in adults without compromising adaptive immunity. Cell Rep September 14, 2021. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)01227-4
This study demonstrates that children mount potent antiviral innate responses, similar in amplitude to those of adults with mild COVID-19, yet significantly different in duration: the transience of innate responses in children may explain their limited symptomatology.
Beyond Corona
Pappalardo L, Rossi A, Natilli M, et al. Explaining the difference between men’s and women’s football. PLOS, August 4, 2021. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0255407
We almost overlooked this important contribution. Bottom line: Men’s and women’s football have similar play intensity. Whereas women do fewer fouls, there are some technical gaps between men and women. Nicely said: According to the authors, the “results are open to various interpretations”.
19 September
Variants
Blanquart F, Abad C, Ambroise J, et al. Characterisation of vaccine breakthrough infections of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Alpha variants and within-host viral load dynamics in the community, France, June to July 2021. Euro Surveill September 15, 2021;26(37). https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.37.2100824
A French study, confirming other reports on Delta: higher viral load, longer duration of infection and, probably most important, similar values among fully vaccinated individuals and those who were not.
Luna-Muschi A, Borges IC, de Faria E, et al. Clinical features of COVID-19 by SARS-CoV-2 Gamma variant: a prospective cohort study of vaccinated and unvaccinated healthcare workers. J Infection September 16, 2021. https://www.journalofinfection.com/article/S0163-4453(21)00474-6/fulltext
Some differences in the clinical presentation between Gamma variant (P1 from Brazil) and non-VoC infection with a decreased frequency of hyposmia/anosmia and dysgeusia in Gamma variant cases.
Diagnostics
Cubas-Atienzar AI, Kontogianni K, Edwards T, et al. Limit of detection in different matrices of 19 commercially available rapid antigen tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sci Rep 11, 18313 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97489-9
This comprehensive study evaluated the analytical performance of 19 antigen rapid diagnostic tests that are currently on the market and in use in multiple countries. Check your RDT: the most sensitive tests on dry swabs and direct culture supernatant were Espline, Mologic, Sure-Status and Roche and the least sensitive on all matrices were Biocredit, iChroma, Standard-F and Genedia.
Collateral damage
Peña PA, Jena A. Mass Shootings in the US During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open September 16, 2021;4(9):e2125388. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784187?resultClick=1
Beautifully put. After arguing that “mass shootings are rare events with causes that are not well understood”, the authors analyzed 2985 (!) mass shootings in the US, involving 3185 people killed and 12,547 injured. Bottom line: mass shootings are on the increase, possibly indicating that mass murderers may also be stressed these days (well, has anyone suggested gun laws?)
Pediatrics
Strutner J, Ramchandar N, Dubey S, et al. Comparison of RT-PCR Cycle Threshold Values from Respiratory Specimens in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Children with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 15, 2021, ciab403, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab403/6370557
In this retrospective review of 728 children who tested positive by RT-PCR for SARS CoV-2, the mean Ct was significantly lower in symptomatic children and was lowest in children under 5, indicating that symptomatic children and younger children may have a higher viral load in the nasopharynx.
18 September
Today we’ll have a Vaccines special. A lot of data on the long-term efficacy of the BioNTech vaccine and some arguments for a third jab in older people. Some more data on breakthrough infections, waning immunity, on immune correlates of protection and on how to identify VITT cases.
Vaccines
Bar-On YM, Goldberg Y, Mandel M, et al. Protection of BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster against Covid-19 in Israel. NEJM September 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2114255?query=featured_home
Paper of the day, providing important data from the Israeli Ministry of Health on a third shot (“booster”). Among 1,137,804 persons who were 60 years of age or older and had been fully vaccinated (two doses of BNT162b2) at least 5 months earlier, the rate of confirmed infection was lower in the booster group by a factor of 11.3; the rate of severe illness was lower by a factor of 19.5. Though sources of bias may not have been measured or corrected for adequately, these data strongly argue for a third shot in the elderly.
Thomas SJ, Moreira ED, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. NEJM September 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2110345?query=featured_home
Follow up of the large Phase III RCT (published a few months ago), showing a gradual decline in vaccine efficacy over time. Efficacy peaked at 96.2% during the interval from 7 days to less than 2 months after the second dose and declined gradually to 83.7% from 4 months after the second dose to the data cutoff date — an average decline of approximately 6% every 2 months.
Rosenberg ES, Holtgrave DR, Dorabawila V, et al. New COVID-19 Cases and Hospitalizations Among Adults, by Vaccination Status — New York, May 3–July 25, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep September 15, 2021;70:1306–1311. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037a7.htm?s_cid=mm7037a7_w
Same direction in the “real world”. From May 3–July 25, 2021, the overall age-adjusted vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization in New York was relatively stable. However, the overall age-adjusted vaccine effectiveness against infection for all New York adults declined from 91.8% to 75.0%, coinciding with a period of easing societal public health restrictions and increasing Delta variant circulation.
Salih F, Schönborn L, Kohler S, et al. Vaccine-Induced Thrombocytopenia with Severe Headache. NEJM September 15, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2112974?query=featured_home
Small case series, providing some evidence that vaccine-induced thrombocytopenia (VIT) without associated cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and with severe headache as the heraldic symptom may precede VITT (“pre-VITT syndrome”). The authors argue that patients who present with severe headache 5 to 20 days after adenovirus vector vaccination should undergo immediate testing for thrombocytopenia and d-dimer levels.
Corbett KS, Nason MC, Flach B, et al. Immune correlates of protection by mRNA-1273 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates. Science September 17, 2021. Vol 373, Issue 6561. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj0299
In monkeys, S-specific binding antibody induced by the Moderna vaccine was a surrogate marker of protection. Moreover, protection of the lower respiratory tract required lower serum antibody concentrations, possibly explaining why most current vaccines are highly effective against severe lower airway disease.
Xia L, Zhang YT, Wang YX, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV, in people younger than 18 years: a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Inf Dis September 15, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00462-X/fulltext
The inactivated COVID-19 vaccine BBIBP-CorV was safe and well-tolerated at all tested dosing levels in 288 participants aged 3–17 years. The vaccine also elicited robust humoral responses.
17 September
Today we have an Immunology Special, mainly on T cells but also on new onset auto-antibodies that are observed in COVID-19, as well as on immune responses to vaccines in patients with complex co-morbidities.
Immunology
Autoantibodies
Chang SE, Feng A, Meng W, et al. New-onset IgG autoantibodies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Nat Commun September 14, 2021, 12, 5417. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25509-3
Approximately half of hospitalized COVID-19 patients develop serum autoantibodies against one or more antigens. Moreover, a surprisingly large number of anti-cytokine antibodies (ACA) were identified in this study (80%), far more than just the interferon autoantibodies described recently. Some autoantibodies are newly triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that severe COVID-19 can break tolerance to self.
T cells
Mateus J, Dan JM, Zhang Z, et al. Low-dose mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine generates durable memory enhanced by cross-reactive T cells. Science September 14, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj9853
Studying 35 vaccinated subjects out to 7 months, this research group from La Jolla, US found that a two dose 25 μg mRNA-1273 vaccination (Moderna) generated immune memory against spike comparable to that of SARS-CoV-2 infection for antibodies, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, immune responses were significantly enhanced by the presence of pre-existing cross-reactive CD4+ T cell memory.
Niessl J, Sekine T, Lange J, et al. Identification of resident memory CD8+ T cells with functional specificity for SARS-CoV-2 in unexposed oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue. Science Immunology September 14, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abk0894
This study provides a comprehensive picture of pre-existing SARS-CoV-2-specific mCD4+ and mCD8+ T cell immunity (likely generated via previous encounters with common cold human coronaviruses) in the tonsils, representing key lymphoid organs in the upper respiratory tract and the intravascular circulation. SARS-CoV-2-specific mCD4+ T cells were distributed evenly between these compartments, whereas SARS-CoV-2-specific mCD8+ T cells were almost exclusively present in the tonsils. Earlier studies confined to analyses of peripheral blood samples have therefore likely underestimated the overall prevalence of heterologous mCD8+ T cell responses.
Pathogenesis
Lee S, Yu Y, Trimpert J, et al. Virus-induced senescence is driver and therapeutic target in COVID-19. Nature September 13, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03995-1#author-information
Virus-induced senescence (VIS) is indistinguishable from other forms of cellular senescence and composed of pro-inflammatory cytokines, extracellular matrix-active factors and pro-coagulatory mediators. This study marks VIS as a pathogenic trigger of COVID-19-related cytokine escalation and organ damage, and suggests senolytic targeting of virus-infected cells as a novel treatment option.
Immune responses in co-morbidities
Le Bourgeois A, Coste-Burel M, Guillaume T, et al. Safety and Antibody Response After 1 and 2 Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. JAMA Network September 14, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784061?resultClick=1
A high response rate of 83% was found in this cohort of 117 allogeneic HSCT recipients after 2 doses of BNT162b2 vaccine.
Apostolidis SA, Kakara M, Painter MM, et al. Cellular and humoral immune responses following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with multiple sclerosis on anti-CD20 therapy. Nat Med September 14, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01507-2
Although most patients with MS treated with anti-CD20 therapy do not generate optimal antibody responses, T cell priming, especially of TH1 and CD8 T cells, is largely intact. However, treatment with anti-CD20 therapy as well as having B cell deficiency were associated with altered coordination of the immune response, and circulating TFH responses were compromised.
16 September
Transmission
Adenaiye OO, Lai J, Bueno de Mesquita J, et al. Infectious SARS-CoV-2 in Exhaled Aerosols and Efficacy of Masks During Early Mild Infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 14, 2021, ciab797, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab797/6370149
A heroic study and without a doubt the paper of the day. No one can say anymore that masks have not been studied: Oluwasanmi Adenaiye and colleagues recruited 49 COVID-19 cases to give blood, saliva, mid-turbinate and fomite (phone) swabs, and 30-minute (!) breath samples while vocalizing into a Gesundheit-II, with and without masks at up to two visits two days apart. Masks reduced viral RNA by 48% in fine aerosols and by 77% in coarse aerosols; cloth and surgical masks were not significantly different. The Alpha variant was associated with a 43-fold increase in fine aerosol viral RNA.
Epidemiology
Young BC, Eyre DW, Kendrick S, et al. Daily testing for contacts of individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection and attendance and SARS-CoV-2 transmission in English secondary schools and colleges: an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet September 14, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01908-5/fulltext
In this huge controlled study, supervised daily testing with lateral flow devices was non-inferior to self-isolation for close contacts to control SARS-CoV-2 transmission. However, school absence was not significantly reduced due to daily testing.
Vaccines
Choi A, Koch M, Wu K, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 variant mRNA vaccine boosters in healthy adults: an interim analysis. Nat Med September 15, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01527-y
This very preliminary evaluation described the antibody persistence of mRNA-1273 and the safety and immunogenicity of a booster dose of mRNA-1273 and two updated versions (mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273.211) in 80 participants who had been vaccinated 6 months previously with the authorized schedule of mRNA-1273. The bottom line: tolerability was good (“generally similar to (that) observed after the primary series”). More importantly: booster vaccination with all 3 vaccines (seemingly, no big differences between them) induced strong anamnestic responses, indicative of a robust B cell memory response.
Van Praet JT, Vandecasteele S, De Roo A, et al. Dynamics of the cellular and humoral immune response after BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccination in Covid-19 naive nursing home residents. J Infect Dis September 13, 2021; jiab458, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab458/6369254
Among nursing home residents after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, both humoral and cellular responses significantly decreased over the course of 24 weeks and were substantially lower than those of healthcare workers at all time points. The half-life of the antibody response was only 47 days, indicating a quantitatively lower immune reaction and shorter duration of protection for the residents.
Treatment
Ader F, Bouscambert-Duchamp M, Hites M, et al. Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): a phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Inf Dis September 14, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00485-0/fulltext
The end for remdesivir? This large RCT conducted in 48 sites in Europe found no clinical benefit in patients who were admitted to hospital for COVID-19, were symptomatic for more than 7 days, and required oxygen support. The authors believe that the discrepancy observed between the present results and those from the ACTT-19 (which contributed to obtaining its Emergency Use Authorization) might be explained by the differences in study populations. There was also no effect of remdesivir on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics, indicating a genuine absence of effect or that treatment was administered too late to be effective.
15 September
Epidemiology
Love J, Keegan LT, Angulo FJ, et al. Continued need for non-pharmaceutical interventions after COVID-19 vaccination in long-term-care facilities. Sci Rep 11, 18093 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97612-w
A stochastic model to simulate outbreaks in LTCF populations with differing vaccination coverage and NPI adherence to evaluate their interactive effects. Bottom line: to prevent further illness and deaths, there is a continued need for NPIs in LTCFs during vaccine rollout.
Davis EL, Lucas TCD, Borlase A, et al. Contact tracing is an imperfect tool for controlling COVID-19 transmission and relies on population adherence. Nat Commun 12, 5412 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25531-5
Well-implemented contact tracing could provide up to a 15% reduction in R but is not currently appropriate as the sole measure of control. Reporting and adherence are the most important predictors of programme impact but tracing coverage and speed also play an important role.
Virology
Arbeitman CR, Rojas P, Ojeda-May P, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is vulnerable to moderate electric fields. Nat Commun 12, 5407 (2021). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25478-7
The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 (and especially its RBD) is unusually vulnerable to external electric fields.
Vaccine
Schönborn L, Thiele T, Kaderali L, et al. Decline in Pathogenic Antibodies over Time in VITT. NEJM September 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2112760?query=featured_home
Anti-PF4 antibodies are transient in most patients with VITT. In 14/15 patients with follow-up of more than 12 weeks, the platelet-activation assay became negative.
Variants
Burugorri-Pierre C, Lafuente-Lafuente C, Oasi C, et al. Investigation of an Outbreak of COVID-19 in a French Nursing Home With Most Residents Vaccinated. JAMA Netw Open September 13, 2021; 4:e2125294. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783985?resultClick=1
An outbreak in Biscarrosse, France, due to the B.1.1.7 variant, indicating that SARS-CoV-2 vaccination may not be sufficient as the sole means to prevent COVID-19 in nursing homes. Of 74 residents, 70 were fully and 2 were partially vacccinated. Among the 17 infected residents, one was unvaccinated, two were partially and were 14 fully vaccinated. Eight residents developed severe disease, 2 were hospitalized, and 1 individual (the unvaccinated resident) died.
(No good) Treatment
Dyer O. Covid-19: Hospital may cease giving patient ivermectin, US court rules, as prescriptions soar. BMJ 2021; https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n2228
Read here how crazy people can be (i.e. people who believe vaccines are too “experimental” and then sue a hospital in order to get ivermectin treatment).
14 September
Epidemiology
Sanders JG, Spruijt P, van Dijk M, et al. Understanding a national increase in COVID-19 vaccination intention, the Netherlands, November 2020–March 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(36):pii=2100792. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.36.2100792
In March 2021, approximately one in five people in the Netherlands reported having no intention or being unsure of whether to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
Vaccines
Thompson MG, Stenehjem E, Grannis S, et al. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines in Ambulatory and Inpatient Care Settings. NEJM September 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2110362?query=featured_home
Real-world data from the US. The effectiveness of mRNA-based vaccines was 88% against a SARS-CoV-2 infection leading to hospitalization and 90% against infection leading to ICU admission. This was also seen in those most at risk for severe COVID-19 (advanced age, underlying medical conditions, race or ethnic group). However, it is of note that during this observation period, the Alpha variant was predominant.
Grannis SJ, Rowley EA, Ong TC, et al. Interim Estimates of COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness Against COVID-19–Associated Emergency Department or Urgent Care Clinic Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults During SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant Predominance — Nine States, June–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 10 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e2.htm?s_cid=mm7037e2_w
What about Delta? Here, the same network as above provided data from 187 hospitals and 221 emergency departments (EDs) and urgent care (UC) clinics across nine US states June–August 2021. Vaccine effectiveness (VE) of all three US-authorized COVID-19 vaccines combined remained high against hospitalization (86%) and ED/UC encounters (82%). However, VE among adults aged ≥ 75 years was significantly lower. This decline should be interpreted with caution and might be related to changes in SARS-CoV-2, waning of vaccine-induced immunity, or a combination of factors.
Bajema KL, Dahl RM, Prill MM, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Against COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization — Five Veterans Affairs Medical Centers, United States, February 1–August 6, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 10 September 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7037e3.htm?s_cid=mm7037e3_w
Same direction: mRNA COVID-19 vaccines remain highly effective, even during periods of widespread circulation of the Delta variant. However, VE in preventing COVID-19–related hospitalization was 80% among adults aged ≥ 65 years compared with 95% among adults aged 18–64 years. Growing evidence that the vaccines start to weaken when Delta catches the elderly.
Treatment
Murray J, Hogan RJ, Martin DE, et al. Probenecid inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vivo and in vitro. Sci Rep September 10, 2021, 11, 18085. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97658-w
Probenecid potently blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication in mammalian cells and virus replication in a hamster model. Plasma concentrations were up to 50-fold higher than the protein binding adjusted IC90 value following a single oral dose, supporting “the potential clinical utility” of probenecid.
Beyond Corona
Bulut OC, Oladdokun D, Lippert BM, et al. Can Sex Improve Nasal Function?—An Exploration of the Link Between Sex and Nasal Function. Ear Nose Throat J 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320981441
At the 31st First Annual Ig Nobel Prize ceremony, on Thursday, September 9, this milestone work in 18 couples from Heidelberg/Germany won the Ig Nobel Prize in Medicine – quite rightly, as the conclusion gives us an essential insight: “Sexual intercourse with climax can improve nasal breathing to the same degree as application of nasal decongestant for up to 60 minutes in patients having nasal obstruction”. However, please note the main limitation that “the data were only obtained if both individuals experienced sexual orgasm”.
Blavatslyy P. Obesity of politicians and corruption in post-Soviet countries. Econ Transit Institut Change. 2021;29:343–356. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/ecot.12259
Ig Nobel Prize in Economics. The median ministers’ body-mass index (estimated from frontal face images) was highly correlated with conventional measures of corruption (based on perception surveys among foreign experts).
13 September
Epidemiology
Shen K, Loomer L, Abrams H, et al. Estimates of COVID-19 Cases and Deaths Among Nursing Home Residents Not Reported in Federal Data. JAMA Netw Open September 9, 2021;4(9):e2122885. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2784031
In this cross-sectional study of 15,307 US nursing homes, approximately 44% of COVID-19 cases and 40% of COVID-19 deaths that occurred before the start of reporting were not reported in the first NHSN submission in sample states, suggesting there were more than 68,000 unreported cases and 16,000 unreported deaths nationally.
Vaccine
Sauré D, O’Ryan M, Torres JP, et al. Dynamic IgG seropositivity after rollout of CoronaVac and BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccines in Chile: a sentinel surveillance study. Lancet Inf Dis September 09, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00479-5/fulltext
In this huge study, IgG seropositivity was lower after CoronaVac than after BNT162b2 and declined over time since vaccination for CoronaVac recipients but not BNT162b2 recipients.
Transmission
Rebmann T, Loux TM, Arnold LD, Charney R, Horton D, Gomel A. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission to Masked and Unmasked Close Contacts of University Students with COVID-19 — St. Louis, Missouri, January–May 2021. MMWR 2021;70:1245–1248. DOI: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7036a3.htm?s_cid=mm7036a3_w
An observational study in a university setting indicating that compared with only masked exposure, close contacts with any unmasked exposure had higher adjusted odds of a positive test result. Each additional exposure was associated with a 40% increase in the odds of a positive test.
Co-morbidities
Moor MB, Suter-Riniker F, Horn MP, et al. Humoral and cellular responses to mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with a history of CD20 B-cell-depleting therapy (RituxiVac): an investigator-initiated, single-centre, open-label study. Lancet Rheumatology September 7, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(21)00251-4/fulltext
Further evidence of blunted humoral and cell-mediated immune responses elicited by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with a history of CD20 B-cell-depleting treatment. Only 9/66 (14%) patients were double positive for anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG and cell-mediated responses, compared with 21/28 (75%) healthy controls. Lymphocyte subpopulation counts were associated with vaccine response in this highly vulnerable population.
Pregnancy
Zauche LH, Wallace B, Smoots AN, et al. Receipt of mRNA Covid-19 Vaccines and Risk of Spontaneous Abortion. NEJM September 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2113891?query=featured_home
Using data of 2456 participants who were enrolled in the CDC COVID-19 pregnancy registry, Lauren Zauche and colleagues provide more evidence that the risk of spontaneous abortion after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, either before conception or during pregnancy, “is consistent with the expected risk” of spontaneous abortion.
12 September
Transmission
Shah AS, Gribben C, Bishop J, et al. Effect of Vaccination on Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. NEJM September 8, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2106757?query=featured_home
Incredible huge study on 194,362 household members of 144,525 health care workers from Scotland, among them 113,253 HCWs who had received at least one dose of either Pfizer–BioNTech or the AstraZeneca vaccine. The hazard ratio for a household member to become infected was 0.70 (95% CI, 0.63 to 0.78) for the period beginning 14 days after the first dose and 0.46 (95% CI, 0.30 to 0.70) for the period beginning 14 days after the second dose. As not all cases in the household members were transmitted from the health care worker, the effect of vaccination may be larger.
Vaccine
To KK, Li Y, Lung DC et al. False COVID-19 cases due to contamination by inactivated virus vaccine. Clin Inf Dis September 9, 2021, ciab684, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab684/6367446
Two individuals whose respiratory specimens were contaminated by inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine strain (CoronaVac), likely at vaccination premises.
Variants
Oude Munnink BB, Worp N, Nieuwenhuijse DF, et al. The next phase of SARS-CoV-2 surveillance: real-time molecular epidemiology. Nat Med September 9, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01472-w
This Review summarizes the current knowledge on key viral mutations and variants.
Diagnostics
Michalakis Y, Sofonea MT, Alizon S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels are not “viral load”. Trends in Microbiology September 03, 2021. https://www.cell.com/trends/microbiology/fulltext/S0966-842X(21)00208-0#%20
Yannis Michalakis and colleagues argue that current RT-qPCR target amplification does not distinguish replicative from transcriptional RNA. Although analyses of Ct values remain informative, equating them with viral load may lead to flawed conclusions as it is presently unknown whether (and to what extent) variation in Ct reflects variation in viral load or in gene expression.
Pediatrics
Somekh I, Stein M, Karakis I, et al. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Israeli Children During the Circulation of Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants. JAMA Netw Open September 7, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783851?resultClick=1
In this observational study, transmission rates from children aged 0 to 9 years to other contacts were doubled during the time of B.1.1.7 circulation in Israel. However, hospitalization rates among children decreased.
11 September
Epidemiology
Wilkinson E, Giovanetti M, Tegally H, et al. A year of genomic surveillance reveals how the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic unfolded in Africa. Science Sepember 9, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj4336
Phylogeographic reconstruction of (past) viral dissemination patterns, suggesting a strong epidemiological linkage between Europe and Africa, with 64% of detectable viral imports into Africa originating in Europe and 41% of detectable viral exports from Africa landing in Europe. Strong conclusion: “If the pandemic is not controlled in Africa, we may see the production of vaccine escape variants that may profoundly affect the population in Africa and across the world.”
Immunology
Kaplonek P, Wang C, Bartsch Y, et al. Early cross-coronavirus reactive signatures of humoral immunity against COVID-19. Science Immunology September 9, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abj2901
Convincing evidence on the importance of cross-coronavirus immunity as a correlate of protection against COVID-19. Individuals who survive COVID-19 may have an advantage as they may be able to rapidly redeploy S2-specific antibodies across coronaviruses in order to combat disease. Early development of SARS-CoV-2-specific immunity occurred in tandem with pre-existing common β-coronavirus OC43 humoral immunity in survivors, which was also selectively expanded in individuals that developed a paucisymptomatic infection.
Clinical
Boyapati A, Wipperman MF, Ehmann PJ, et al. Baseline SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load is Associated With COVID-19 Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes: Post-Hoc Analyses of a Phase 2/3 Trial. J Inf Dis September 8, 2021. jiab445, https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab445/6366357
In this large Phase II/III trial of sarilumab in 1362 COVID-19 hospitalized patients, higher baseline viral load was associated with higher mortality, lower likelihood of improvement in clinical status and supplemental oxygenation requirements, and lower rates of hospital discharge. Viral load was not impacted by sarilumab treatment versus placebo over time.
Treatment
Bégin, P., Callum, J., Jamula, E. et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat Med September 8, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01488-2
Huge RCT, providing the last nail in the coffin for convalescent plasma (CP). CP did not reduce the risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Moreover, transfusion of convalescent plasma with unfavorable antibody profiles could be associated with worse clinical outcomes compared to standard care. “The lack of benefit and the potential concern of harm caution against the unrestricted use of convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19”.
Congly SE, Varughese RA, Brown CE, et al. Treatment of moderate to severe respiratory COVID-19: a cost-utility analysis. Sci Rep September 7, 2021, 11, 17787. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97259-7
Dexamethasone for moderate-severe COVID-19 infections was the most cost effective strategy and would have minimal budget impact. Based on current data, remdesivir is unlikely to be a cost effective treatment for COVID-19.
10 September
Variants
Grint DJ, Wing K, Houlihan C, et al. Severity of SARS-CoV-2 alpha variant (B.1.1.7) in England. Clin Infect Dis September 6, 2021, ciab754, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab754
Using data from 185,234 people who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 in the community, in fully adjusted analysis accounting for individual-level demographics and comorbidities as well as regional variation in infection incidence, the authors found alpha associated with 73% higher hazards of all-cause death and 62% higher hazards of hospital admission, compared to wild-type virus.
Tostanoski LH, Yu J, Mercado NB, et al. Immunity elicited by natural infection or Ad26.COV2.S vaccination protects hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Science Translational Medicine September 7, 2021. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj3789
See title. The Ad26.COV2.S vaccine (J&J) induced cross-reactive binding and neutralizing antibodies that were reduced against the B.1.351 strain (Beta) compared with wild type, but nevertheless still provided robust protection against B.1.351 challenge, as measured by weight loss and pathology scoring in the lungs.
Transmission
Dabisch PA, Biryukov J, Beck K. Seroconversion and fever are dose-dependent in a nonhuman primate model of inhalational COVID-19. PLOS Pathogens August 23, 2021. https://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1009865
Small study in which 16 healthy, young adult macaques were exposed to small particle aerosols containing SARS-CoV-2, with calculated deposited doses. The probability of seroconversion and fever were both dose-dependent, but the median dose for seroconversion was significantly lower than that of fever. However, the study used an isolate from early in the pandemic (no variant).
Pregnancy
Kharbanda EO, Haapala J, DeSilva M, et al. Spontaneous Abortion Following COVID-19 Vaccination During Pregnancy. JAMA Network September 8, 2021 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2784193?resultClick=1
In this large surveillance study of 105446 unique pregnancies, 13160 spontaneous abortions and 92286 ongoing pregnancies were identified. Spontaneous abortions did not have an increased odds of exposure to a COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in the prior 28 days compared with ongoing pregnancies (adjusted odds ratio, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.96-1.08).
Dagan N, Barda N, Biron-Shental T, et al. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in pregnancy. Nat Med September 7, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01490-8
Paper of the day. A total of 10,861 vaccinated pregnant women were matched to 10,861 unvaccinated pregnant controls using demographic and clinical characteristics. Study outcomes included documented infection with SARS-CoV-2, symptomatic COVID-19, COVID-19-related hospitalization, severe illness and death. Estimated vaccine effectiveness from 7 through to 56 d after the second dose was 96% (95% confidence interval 89–100%) for any documented infection, 97% (91–100%) for infections with documented symptoms and 89% (43–100%) for COVID-19-related hospitalization.
9 September
Transmission
Mishra A, Kumar N, Bhatia S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant among Asiatic lions, India. Emerg Infect Dis 2021 August 31, 2021 https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/10/21-1500_article
Identical SARS-CoV-2 infections in nine lions in a short period of time, indicating the possibility of lion-to-lion transmission.
Immunology
Bertoletti A, Le Bert N, Qui M, et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in infection and vaccination. Cell Mol Immunol September 2, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-021-00743-3
Great review about the function of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells in patients and in vaccinated individuals.
Diagnostics
Torres JR. Are rapid antigen SARS-Cov-2 tests effective for mass screening of travelers at airports? The Olympic experience. Journal of Travel Medicine 03 September 2021, taab135, https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taab135/6363815?searchresult=1
Jaime Torres argues that a significant number of asymptomatic carriers will fail to be detected via mass screening of travelers at airports by means of rapid antigenic tests, unless additional strategies, such as supervised quarantine, frequent retesting and close follow up of those who test positive are also carefully implemented.
Severe COVID-19
Boscolo A, Pasin L, Sella N, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 patients intubated after failure of non-invasive ventilation: a multicenter observational study. Scientific Reports September 6, 2021, volume 11, Article number: 17730. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-96762-1
Among 280 patients who underwent endotracheal intubation, only the length of NIV application before ICU admission (OR 2.03) and age (OR 1.18) were identified as independent risk factors of in-hospital mortality.
Co-morbidities
Ghione P, Gu JJ, Attwood K, et al. Impaired humoral responses to COVID-19 vaccination in patients with lymphoma receiving B-cell–directed therapies. Blood, September 2, 2021. https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/138/9/811/476275/Impaired-humoral-responses-to-COVID-19-vaccination?searchresult=1
In this cohort of patients with B-cell lymphoma who were actively receiving B-cell-depleting agents or were within 9 months of completing B-cell-directed therapy, only 6/52 developed antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus, regardless of the type of vaccine used.
Treatment
Al Sulaiman K, Aljuhani O, Saleh KB, et al. Ascorbic acid as an adjunctive therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a propensity score matched study. Sci Rep 11 September 3, 2021, 17648. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-96703-y
Retrospective study in which low dose ascorbic acid as an adjunctive therapy in COVID-19 critically ill patients was not associated with mortality benefits, but was associated with a lower incidence of thrombosis. And yes, “further studies are required to confirm these findings.”
8 September
Virology
Shan KJ, Wei C, Wang Y, et al. Host-specific asymmetric accumulation of mutation types reveals that the origin of SARS-CoV-2 is consistent with a natural process. The Innovation. August 30, 2021. https://www.cell.com/the-innovation/fulltext/S2666-6758(21)00084-9
Some data-driven support for the natural origin of SARS-CoV-2.
Transmission
Rosca EC, Heneghan C, Spencer EA, et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 associated with aircraft travel: A systematic review. Journal of Travel Medicine September 3, 2021. taab133, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab133
Current evidence is very limited. Data suggests SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted during aircraft travel, but published data do not permit any conclusive assessment of likelihood and/or extent.
Vaccine
Klein NP, Lewis N, Goddard K, et al. Surveillance for Adverse Events After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. JAMA September 3, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2784015
They. Are. Safe. In this interim analysis of surveillance monitoring of more than 11.8 million doses of 2 mRNA vaccines in diverse populations and weekly analyses from December 14, 2020, to June 26, 2021, no vaccine-outcome association met the prespecified threshold for a signal.
Seppälä E, Veneti L, Starrfelt J, et al. Vaccine effectiveness against infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant, Norway, April to August 2021. Euro Surveill September 2, 2021;26(35):pii=2100793. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.35.2100793
The adjusted VE against infection with the Delta variant was 22% among those partly vaccinated and 65% among those fully vaccinated, compared with 55% and 84%, respectively, against the Alpha variant.
Variants
Mlcochova P, Kemp S, Dhar MS, et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion. Nature September 6, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03944-y
This study combined in vitro experimentation and molecular epidemiology, confirming increased replication fitness and reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) to neutralizing antibodies.
7 September
Treatment
Kyriazopoulou E, Poulakou G, Milionis H, et al. Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: a double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial. Nat Med September 3, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-021-01499-z
Paper of the day, presenting encouraging data on anakinra from the SAVE-MORE study, a double-blind randomized controlled trial in 594 patients with COVID-19 at risk of progressing to respiratory failure. It works! With anakinra, an IL-1α/β inhibitor, at day 28, the adjusted proportional odds of having a worse clinical status (assessed by the 11-point WHO scale) was only 0.36 (95% confidence interval 0.26–0.50). The clinical benefit with anakinra was already apparent from day 14 and was maintained until day 28. The magnitude of the efficacy was shown in all multivariate analyses.
Epidemiology
Kleynhans J, Tempia S, Wolter N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in a rural and urban household cohort during first and second waves of infections, South Africa, July 2020–March 2021. Emerg Infect Dis September 3, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/12/21-1465_article
The authors assessed SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in 1211 persons living in 2 diverse communities in South Africa and show, not surprisingly, that laboratory-confirmed cases reported from study districts greatly underestimate the actual prevalence. At baseline, seroprevalence was 1% in a rural community and 15% in an urban community, increasing to 7% and 27%, respectively, after the first wave, by March 2021. After the second wave, seroprevalence was 26% (rural) and 41% (urban).
Immunology
Smith N, Goncalves P, Charbit B. et al. Distinct systemic and mucosal immune responses during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Immunol September 1, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-021-01028-7
This study compared systemic and local immune responses during active SARS-CoV-2 infection in a well-characterized COVID-19 cohort. Results demonstrate distinct tissue compartmentalization of SARS-CoV-2 immune responses and highlight a role for the nasopharyngeal microbiome in regulating local and systemic immunity that determines COVID-19 clinical outcomes.
Galván-Peña S, Leon J, Chowdhary K, et al. Profound Treg perturbations correlate with COVID-19 severity. PNAS September 14, 2021, https://www.pnas.org/content/118/37/e2111315118
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are essential in maintaining immunologic homeostasis, self-tolerance, and to prevent runaway immune responses. This study found a unique and striking Treg deviation in COVID-19 patients, which results from the effects of several components of the pro-inflammatory storm.
Pediatrics
Delahoy MJ, Ujamaa D, Whitaker M, et al. Hospitalizations Associated with COVID-19 Among Children and Adolescents — COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1, 2020–August 14, 2021. MMWR September 3, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7036e2.htm?s_cid=mm7036e2_w
Weekly COVID-19–associated hospitalization rates rose rapidly from late June through mid-August 2021 among US children and adolescents aged 0–17 years; by mid-August, the rate among children aged 0–4 years was nearly 10 times the rate 7 weeks earlier (coincident with widespread circulation of Delta). Hospitalization rates were 10 times higher among unvaccinated than among fully vaccinated adolescents.
6 September
Immunology
Israelow B, Mao T, Klein J, et al. Adaptive immune determinants of viral clearance and protection in mouse models of SARS-CoV-2. Science Immunology September 2021, https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.abl4509
More insights into both the immunologic determinants of viral clearance and protection. While T cells were important in the clearance of primary infection, they were not required for protection against reinfection or vaccine-mediated protection, likely due to sufficient antibody-mediated immunity.
Vaccine
Klein NP, Lewis N, Goddard K. Surveillance for Adverse Events After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. JAMA September 3, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2784015?resultClick=1
In this interim analysis of 6.2 million persons who received 11.8 million doses of an mRNA vaccine, event rates for 23 serious health outcomes were not significantly higher for individuals 1 to 21 days after vaccination compared with similar individuals at 22 to 42 days after vaccination.
Feder KA, Patel A, Vepachedu VR, et al. Association of E484K spike protein mutation with SARS-CoV-2 infection in vaccinated persons—Maryland, January – May 2021, Clin Inf Dis September 2, 2021, ciab762, https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab762/6362726
Among 9048 cases, SARS-CoV-2 viruses carrying the spike protein mutation E484K were disproportionately prevalent among persons infected after full vaccination (adjusted OR 1.96).
Collateral damage
Hawrilenko M, Krohus E, Tandon P, et al. The Association Between School Closures and Child Mental Health During COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open September 3, 2021; 4(9):e2124092. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783714?resultClick=1
In this survey study of 2324 adults with at least 1 school-age child, a small association between school closures and worse child mental health outcomes was observed. Children from families with lower income experienced more mental health problems associated with school closures.
Pediatrics
Siegel DA, Reses HE, Cool AJ, et al. Trends in COVID-19 Cases, Emergency Department Visits, and Hospital Admissions Among Children and Adolescents Aged 0–17 Years — United States, August 2020–August 2021. MMWR 3 September 2021. DOI: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7036e1.htm?s_cid=mm7036e1_w
Among US children and adolescents aged 0–17 years, COVID-19 cases and associated ED visits and hospital admissions increased from June 2021 through August 2021. During a 2-week period in August 2021, COVID-19–associated ED visits and hospital admissions for children and adolescents with confirmed COVID-19 were highest in states with the lowest vaccination coverage.
5 September
Epidemiology
Matthias J, Patrick S, Wiringa A, et al. Epidemiologically Linked COVID-19 Outbreaks at a Youth Camp and Men’s Conference — Illinois, June–July 2021. MMWR August 31, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7035e4.htm?s_cid=mm7035e4_w
On June 30, 2021, the Illinois Department of Public Health reported two events sponsored by the same organization: a 5-day overnight church camp for persons aged 14–18 years and a 2-day men’s conference. Believe it or not, neither COVID-19 vaccination nor COVID-19 testing was required before either event. As of August 13, a total of 180 confirmed and probable cases had been identified among attendees at the two events and their close contacts. Among 122 primary cases, 104 (85%) were in persons not fully vaccinated, and 18 (15%) were in fully vaccinated persons. Eight of 38 (21%) close contacts of the 18 fully vaccinated persons subsequently became infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Variants
Strålin K, Bruce D, Wahlsttröm E, et al. Impact of the Alpha VOC on disease severity in SARS-CoV-2-positive adults in Sweden. J Infection August 30, 2021. https://www.journalofinfection.com/article/S0163-4453(21)00448-5/fulltext
Large study from Sweden. Alpha positive individuals had significantly higher rates of hospitalization (2.6% vs. 1.2%) and severe illness than variants of concern negative individuals overall, but the numbers were too small to evaluate differences in severity rate among hospitalized individuals.
Immunology
Baggen J, Vanstreels E, Jansen S, et al. Cellular host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Microbiol September 1, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-021-00958-0
This review summarizes insights into the proviral host factors that are required for SARS-CoV-2 infection that were mainly obtained using functional genetic and interactome screens.
Vaccines
Ben David SSS, Potasman I, Rahamim-Cohen D. Rate of Recurrent Guillain-Barré Syndrome After mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2. JAMA Neurol September 1, 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2783708?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 702 patients, only 1 person needed short medical care for relapse of their previous syndrome, representing a minimal risk.
Marlin R, Godot V, Cardinaud S, et al. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain to cells expressing CD40 improves protection to infection in convalescent macaques. Nat Commun September 1, 2021, 12, 5215. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25382-0
A new generation of subunit vaccines targeting the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen to the CD40 receptor (αCD40.RBD). Immunogenicity is shown in two different animal models. This vaccine may have advantages for a safe and efficient boosting strategy, without requiring an adjuvant.
4 September
Epidemiology
Brooks YM, Gryskwicz B, Sheehan S, Piers S, Mahale P, McNeil S, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater at residential college, Maine, USA, August–November 2020. Emerg Infect Dis August 31, 2021. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/12/21-1199_article
Wastewater surveillance may help to identify outbreaks. Cumulative increases of > 1 log10 SARS-CoV-2 RNA in consecutive 24-hour composite samples preceded outbreaks. For 76% of cases at a school, RNA was identified in grab samples from residence halls < 7 days before case discovery.
Immunology
Loyal L, Braun J, Henze L, et al. Cross-reactive CD4+ T cells enhance SARS-CoV-2 immune responses upon infection and vaccination. Science August 31, https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abh1823
This study highlights the functional contribution of pre-existing spike-cross-reactive T cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Cross-reactive immunity may account for the unexpectedly rapid induction of immunity following primary SARS-CoV-2 immunization and the high rate of asymptomatic/mild COVID-19 disease courses. The S816-830 peptide may serve as a conserved universal coronavirus target in the S2 portion of spike for both B cells and T cells.
Vaccine
Flaxman A, Marchevsky NG, Jenkin D, et al. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity after a late second dose or a third dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 in the UK: a substudy of two randomised controlled trials (COV001 and COV002). Lancet September 01, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01699-8/fulltext
Sub-study of two trials in which the timing of the second dose varied and allowed for comparisons of immunogenicity between the recommended vaccination schedule and a longer interval. Results: the extended interval between the first two doses (44–45 weeks) resulted in higher antibody titers after the second dose than with a shortened interval. A third dose given 28–38 weeks after the second dose increased the antibody titers to above those after the primary (1-2) series.
McQuade ET, Breskin A. Longer intervals and extra doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine. Lancet September 01, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01817-1/fulltext
But what do these data tell us? In their comment, Elizabeth Rogawski McQuade and Alexander Breskin point out that “the total public health impact of the extended prime-boost interval is unclear given the trade-off between a longer period at the lower level of protection afforded by a single dose and the higher level of protection obtained after a delayed second dose”. However, data may assuage concerns about the potential for impaired responses after repeated use of a replication deficient simian adenoviral vector and suggest that a third dose of the AZ/Oxford vaccine could be successful if necessary.
Clinical
Fenton L, Gribben C, Caldwell D, et al. Risk of hospital admission with covid-19 among teachers compared with healthcare workers and other adults of working age in Scotland, March 2020 to July 2021: population based case-control study. BMJ September 2, 2021, 374 https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n2060
The risks of COVID-19 among teachers and their household members: neither was shown to be at increased risk of hospital admission or severe COVID-19 at any time, whether compared with healthcare workers or with adults of working age in the general population.
Treatment
Strich JR, Tian X, Samour M, et al. Fostamatinib for the treatment of hospitalized adults with COVD-19 A randomized trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases September 1, ciab732. https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab732/6358811
Fostamatinib is a novel spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor that could ameliorate Fc activation and attenuate harmful effects of the anti-COVID-19 immune response. In 59 COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization, the addition of fostamatinib to standard of care was safe and patients were observed to have improved clinical outcomes compared to placebo. According to the authors, this warrants further validation in larger confirmatory trials.
3 September
Epidemiology
Soucy JP, Ghasemui A, Sturrock SL, et al. Trends in Interregional Travel to Shopping Malls and Restaurants Before and After Differential COVID-19 Restrictions in the Greater Toronto Area. JAMA Netw Open August 21, 2021; 4(8):e2123139. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783631
Heterogeneous restrictions or partial lockdowns do not make sense: people/viruses just go shopping somewhere else. In this study from Canada, lockdowns in the urban center were associated with reduced overall visits to shopping malls and restaurants by residents but were not associated with decreased travel to these businesses in peripheral regions, where restrictions permitted indoor dining and shopping for non-essential businesses. The authors observed a large increase in visits to shopping malls in the peripheral regions by residents of the urban center in the week following the lockdown.
Keehner J, Horton LE, Binkin NJ, et al. Resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Highly Vaccinated Health System Workforce. NEJM September 1, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2112981?query=featured_home
Rapidly increasing cases among the workforce of the University of California San Diego Health, coinciding with the dominance of the Delta variant, and including cases among fully vaccinated persons. However, the increase was also coincident with the end of California’s mask mandate at the same time.
Transmission
Oster Y, Benenson S, Harpaz LY, et al. Association Between Exposure Characteristics and the Risk for COVID-19 Infection Among Health Care Workers With and Without BNT162b2 Vaccination. JAMA Netw Open September 1, 2021;4(9):e2125394. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783675?resultClick=1
This case-control study found that exposure to SARS-CoV-2–positive household members was a risk factor associated with infection among vaccinated HCWs. Household exposure is usually longer and closer than casual exposure or exposure at work and does not include masking or distancing, exposing one to a higher infectious dose and thus being more contagious.
Clinical
Boehmer TK, Kompaniyets L, Lavery AM, et al. Association Between COVID-19 and Myocarditis Using Hospital-Based Administrative Data — United States, March 2020–January 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 31 August 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7035e5.htm
In this study, the occurrence of myocarditis inpatient encounters was 42% higher in 2020 than in 2019. The risk for myocarditis among patients with COVID-19 during March 2020–January 2021 was nearly 16 times as high as the risk among patients without COVID-19, with the association between COVID-19 and myocarditis being most pronounced among children and older adults. Further, in this cohort, approximately 40% of patients with myocarditis had a history of COVID-19.
Treatment
Marconi VC, Ramanan AV, de Bono S, et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Resp Med September 01, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00331-3/fulltext
Baricitinib “is a potentially effective oral treatment option”. In this huge Phase III trial on 1527 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, the 28-day all-cause mortality was 8% for baricitinib and 13% for placebo (hazard ratio 0.57, 95% CI: 0.41–0.78), a 38% relative reduction in mortality; one additional death was prevented per 20 baricitinib-treated participants.
Kailil AC, Stebbing J. Baricitinib: the first immunomodulatory treatment to reduce COVID-19 mortality in a placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Resp Med September 01, 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(21)00358-1/fulltext
Comment on the above study. According to Andre Kalil and Justin Stebbing, “the clinical benefits and significant reduction in mortality, as well as the absence of safety concerns found by both the COV-BARRIER and ACTT-2 studies, place baricitinib among the few proven treatments of choice for hospitalised patients with COVID-19”.
2 September
Immunology
Lempp FA, Soriaga L, Montiel-Ruiz M, et al. Lectins enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection and influence neutralizing antibodies. Nature August 31, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03925-1
Transmembrane lectins act as attachment receptors, rather than entry receptors for SARS-CoV-2, thus facilitating infection via the canonical ACE2 pathway. This study shows that ranking of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies is highly dependent on the level of ACE2 expression and on the presence of attachment receptors, and identifies a mechanism that possibly results in creation of multinucleate viral factories potentially enhanced by specific antibodies.
Sulaiman I, Chung M, Angel L, et al. Microbial signatures in the lower airways of mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients associated with poor clinical outcome. Nat Microbiol August 31, 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-021-00961-5
This study analyzed lower airway microbiome using a metagenomic and metatranscriptomic approach, along with host immune profiling, in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Data suggest that active lower airway SARS-CoV-2 replication and poor SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody responses (but not secondary respiratory infections) are the main drivers of increased mortality in COVID-19 patients requiring ventilation.
Vaccine
Shavit R, Maoz-Segal R, Iancovici-Kidon M, et al. Prevalence of Allergic Reactions After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination Among Adults With High Allergy Risk. JAMA Netw Open August 31, 2021; 4(8):e2122255. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783626?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of 8102 individuals with a history of allergies, an algorithm was used to define 429 (5%) as “highly allergic”; this group was referred to receive immunization under medical supervision. A total of 98% of the highly allergic individuals had no allergic reaction, 6 (1%) had mild allergic responses, and 3 (0.7%) had anaphylactic reactions.
Deepak P, Kim W, Paley MA. Effect of Immunosuppression on the Immunogenicity of mRNA Vaccines to SARS-CoV-2. Annals Int Med August 31, 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-1757
This study shows that compared with non-users, patients with chronic inflammatory disease treated with glucocorticoids and B cell depletion therapy seem to have lower SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced antibody responses.
Pediatrics
Woolford SJ, Sidell M, Li X, et al. Changes in Body Mass Index Among Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA August 27, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2783690?resultClick=1
Using the huge Kaiser Permanente Southern California (KPSC) electronic health record data, this study revealed a mean gain among 5- through 11-year-olds of 2.30 kg more during the pandemic than during the reference period, 2.31 kg more among 12- through 15-year-olds, and 1.03 kg more among 16- through 17-year-olds.
Davies P, du Pré P, Krishnan H, et al. One-Year Outcomes of Critical Care Patients Post–COVID-19 Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. JAMA Pediatr August 30, 2021. file:///C:/Users/hoffm/AppData/Local/Temp/jamapediatrics_davies_2021_ld_210022_1629993053.04292.pdf
Small study on 68 children. The majority had good outcomes with no significant medium- or long-term sequelae.
1 September
Vaccine
Steensels D, Pierlet N, Penders J, et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response Following Vaccination With BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. JAMA August 30, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2783797?resultClick=1
This large prospective cohort study in Belgian HCWs demonstrated a significantly higher humoral immunogenicity of the mRNA-1273 vaccine (Moderna) compared with the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech), in infected as well as in uninfected participants, and across age categories. According to the authors, the higher mRNA content in mRNA-1273 compared with BNT162b2 and the longer interval between priming (4 weeks vs 3 weeks for BNT162b2) might explain this difference.
Knowlton KU. Insights from a murine model of COVID-19 mRNA vaccination-induced myopericarditis: Could accidental intravenous vaccine injection induce myopericarditis? Clin Inf Dis August 28, 2021, ciab741 https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab741
Kirk Knowlton from Salt Lake City believes that the current data suggest that this is plausible and that it would be appropriate to consider further.
Transmission
Madewell ZJ, Yang X, Longini Jr IM, et al. Factors Associated With Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open August 27, 2021; 4(8):e2122240. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783544?resultClick=1
In this updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 87 studies representing 1,249,163 household contacts from 30 countries, the estimated household secondary attack rate was 19%. The authors observed an increase in household transmission over time, perhaps owing to improved diagnostic procedures and tools, longer follow-up, more contagious variants, and different study locations.
Long COVID
Huang L, Yao Q, Gu X, et al. 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet August 28, 2021. Volume 398, ISSUE 10302, P747-758. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4
The largest cohort study by far, on 1276 COVID-19 survivors who had been hospitalized and who had a follow up of one year. The proportion of patients with at least one sequelae symptom decreased from 68% at 6 months to 49% at 12 months. 88% of patients who were employed before COVID-19 had returned to their original work at 12 months. However, 12% did not (see below). Fatigue or muscle weakness was still present in 20%.
Auwaerter PG. The Race to Understand Post–COVID-19. Ann Int Med August 31, 2021. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-3072
Some thoughts and ideas. “Even if only 10% of patients experience persistent symptoms after COVID-19, the number afflicted will easily be tens of millions.” And, “If science does not move with dispatch in addressing post–COVID-19 care in a multidisciplinary manner, the vacuum will be quickly filled by pseudoscience and quackery.”
31 August
Epidemiology
Kephart JL, Delclòs-Alió X, Rodríguez DA, et al. The effect of population mobility on COVID-19 incidence in 314 Latin American cities: a longitudinal ecological study with mobile phone location data. Lancet Dig Health August 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00174-6
Interventions to promote social distancing that target specific areas within cities might substantially mitigate SARS-CoV-2 transmission while reducing regional or citywide disruption. A 10% lower weekly mobility was associated with 8.6% (95% CI 7.6–9.6) lower incidence of COVID-19 in the following week.
Immunology
Zhang H, Deng S, Ren L, et al. Profiling CD8+ T Cell Epitopes of COVID-19 Convalescents Reveals Reduced Cellular Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Cell Reports August 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109708
Variants are not only resistant to currently available neutralizing antibodies generated against the original variant. According to this study, evading cellular immunity might also contribute to the increased transmissibility and disease severity associated with the new SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Variants
Twohig KA, Nyberg T, Zaidi A, et al. Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study. Lancet Inf Dis August 27, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8
A large national study from England, indicating a higher hospital admission or emergency care attendance risk for patients with COVID-19 infected with the Delta variant compared with the Alpha variant. The HR of hospital admission within 14 days was 2.26 (95% CI 1.32–3.89) after stratification and regression adjustment for confounders.
Lam-Hine T, McCurdy SA, Santora L, et al. Outbreak Associated with SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant in an Elementary School — Marin County, California, May–June 2021. MMWR 27 August 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7035e2.htm?s_cid=mm7035e2_w
Delta is fast. An unvaccinated infected teacher continued to work for 2 days before receiving a test. During those two days, the teacher read aloud (unmasked) to the class despite school requirements to mask while indoors. Results: 26 infections. Students were seated in five rows; despite masking, the attack rate in the two rows closest to the teacher’s desk was 80% (8/10) and was 28% (4/14) in the three back rows.
Treatment
Kosmopoulos A, Bhatt DL, Meglis G, et al. A Randomized Trial of Icosapent Ethyl in Ambulatory Patients with COVID-19. IScience August 26, 2021. https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)01008-7
IPE is believed to afford potent vasculoprotective effects. This small randomized study provides “possible evidence” of an early anti-inflammatory effect of IPE, including an initial loading dose, in symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients. While the difference in change in hs-CRP between groups was not statistically significant, changes in inflammatory biomarker levels were associated with significant improvement in patient-reported symptoms over a 14+3-day period.
30 August
Vaccine
Bates TA, Leier HC, Lyski ZL, et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by convalescent and BNT162b2 vaccinated serum. Nat Commun August 26, 2021, 12, 5135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25479-6
This study indicates that B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and B.1.351 (Beta) are less well neutralized by serum from vaccinated individuals, and that B.1.351, but not B.1.1.7, is less well neutralized by convalescent serum.
Immunology
Sarma A, Christenson SA, Byrne A. et al. Tracheal aspirate RNA sequencing identifies distinct immunological features of COVID-19 ARDS. Nat Commun August 26, 2021. 12, 5152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25040-5
Assessing host gene expression in the lower airways, this study reveals distinct immunological features of COVID-19 ARDS. In contrast to a “cytokine storm,” the authors observed a reduced proinflammatory gene expression in COVID-19 ARDS when compared to ARDS due to other causes.
Co-morbidities
Levy I, Wieder-Finesod A, Litchevsky V, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in people living with HIV-1. Clin Microbiol Infection August 23, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.07.031
A cohort study of 143 PLWH indicating that the Pfizer/BNT vaccine appears immunogenic and safe in those patients who are on ART with unsuppressed CD4 count and suppressed viral load.
Collateral damage
Jarnig G, Jaunig J, van Poppel MN, et al. Association of COVID-19 Mitigation Measures With Changes in Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Body Mass Index Among Children Aged 7 to 10 Years in Austria. JAMA Netw Open August 26, 2021; 4(8):e2121675. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783511?resultClick=1
In this cohort study of Austrian children aged 7 to 10 years, fitness levels decreased and BMI increased from September 2019 to September 2020, most likely in association with COVID-19 mitigation measures. The proportion of overweight or obese children increased by 3.1% among girls and 4.5% among boys.
Nichter B, Hill ML, Na PJ, et al. Prevalence and Trends in Suicidal Behavior Among US Military Veterans During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2783601?resultClick=1
Despite grim forecasts about the COVID-19 pandemic possibly creating a perfect storm for suicidal behavior, the prevalence of suicidality DID NOT increase among military veterans.
Pediatrics
Theuring S, Thielecke M, van Loon W, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission in school settings during the second COVID-19 wave: a cross-sectional study, Berlin, Germany, November 2020. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(34):pii=2100184. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.34.2100184
SARS-CoV-2 infection activity in Berlin schools during peak transmission in November 2020 appeared to be low. Secondary transmission in class did not happen, and in connected households the attack rate was around 1% (remember – this was prior to Delta).
29 August
Virology
Holmes EC, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, et al. The Origins of SARS-CoV-2: A Critical Review. Cell August 18, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.017
A “laboratory escape” scenario or zoonotic emergence? According to this comprehensive review, scientific evidence supports a zoonotic origin.
Vaccine
Uzun G, Althaus K, Bakchoul T. No Correlation between Anti-PF4 and Anti–SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. NEJM August 25, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2111305?query=featured_home
This study does not support the hypothesis that the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 proteins leads to the formation of anti-platelet factor 4 antibodies in patients with vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia.
Immunology
Giovannoni F, Li Z, Remes-Lenicov F, et al. AHR signaling is induced by infection with coronaviruses. Nat Commun August 26, 2021, 12, 5148. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25412-x
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) was recently identified as a host factor for Zika and dengue viruses. This study suggests that AHR activation is a common strategy used by coronaviruses to evade antiviral immunity and promote viral replication, which may also contribute to lung pathology.
Diagnostics
Willeit P, Bernar B, Zurl C, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of the antigen-based anterior nasal self-testing programme for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection in schools, Austria, March 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(34):pii=2100797. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.34.2100797
Data from this nationwide screening program introduced in Austrian schools in January 2021 show that only a (small) subset of infected individuals are detected with antigen-based testing. The authors recommend additional measures such as face masks or ventilation as well as switching to RT-qPCR based approaches.
Treatment
Van Blargan LA, Adams LJ, Liu Z, et al. A potently neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibody inhibits variants of concern by utilizing unique binding residues in a highly conserved epitope. Immunity August 18, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.016
Presentation of a new mAb, SARS2-38, that potently neutralizes all SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern tested and protects mice against challenge by multiple SARS-CoV-2 strains. Structural analysis showed that SARS2-38 engages a conserved epitope proximal to the receptor binding motif.
28 August
Epidemiology
Pei S, Yamana TK, Kandula S, et al. Burden and characteristics of COVID-19 in the United States during 2020. Nature August 27, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03914-4
Roughly one third of the US population has been infected. The national infection fatality rate during the latter half of 2020 hovers around 0.30%, well above estimates for both seasonal influenza (< 0.08%) and the 2009 influenza pandemic (0.0076%).
Transmission
Wang CC, Prather KA, Sznitman J, et al. Airborne transmission of respiratory viruses. Science August 27, 2021. Vol. 373, Issue 6558, eabd9149. https://science.sciencemag.org/content/373/6558/eabd9149
Forget droplets and fomites. According to this comprehensive review, airborne transmission is the dominant form of transmission. The best arguments? The distinct difference between indoor and outdoor transmission (gravity-driven droplets behave identically indoors and outdoors) and the demonstrated role of poor ventilation (droplets and fomite transmission are not affected by ventilation).
Immunology
Sposito B, Broggi A, Pandolfi L, et al. The interferon landscape along the respiratory tract impacts the severity of COVID-19. Cell August 18, 2021. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.016
“Landscape” is the new favorite word of immunologists (for about three years now). This “landscape” study shows that interferons have opposing roles along the respiratory tract, reconciling some of the seemingly contradictory findings on interferons in COVID-19 patients.
Vaccines
Barda N, Dagan N, Ben-Shlomo Y, et al. Safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine in a Nationwide Setting. NEJM August 25, 2021. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2110475?query=featured_home
This observational data set involving more than 2.4 million vaccinated persons from Israel identified an excess risk of lymphadenopathy (78.4 events per 100,000 persons), herpes zoster infection (15.8 events), appendicitis (5.0 events), and myocarditis (2.7 events). Compared to the risk of adverse events associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, this is almost meaningless.
Hippisley-Cox J, Patone M, Mei XW, et al. Risk of thrombocytopenia and thromboembolism after covid-19 vaccination and SARS-CoV-2 positive testing: self-controlled case series study. BMJ August 27, 2021; 374 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1931
Same direction as above. This patient level data obtained for approximately 30 million people vaccinated in England shows that the slightly increased risks of severe hematological and vascular events after the first doses of the Oxford/AZ and Pfizer/BNT vaccines were minimal vs the substantially higher and more prolonged events after SARS-CoV-2 infection in the same population.
Clinical
Ge Y, Martinez L, Sun S, et al. COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics Among Close Contacts of Index Patients With COVID-19A Population-Based Cohort Study in Zhejiang Province, China. JAMA Intern Med August 23, 2021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2783099
Interesting finding: infected contacts of asymptomatic index patients were less likely to present with COVID-19 symptoms, suggesting that amount of exposure may be associated with clinical presentation between close contacts.
27 August
Epidemiology
Petti S. Undetected and relatively sustained SARS-CoV-2 circulation worldwide during the year 2019. Clinical Infectious Diseases August 2021, ciab727, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab727
A brief summary on current data suggesting the hypothesis that in 2019, SARS-CoV-2 circulation was already relatively sustained in Europe and America.
Transmission
Saretzki C, Bergmann O, Dahmann P, et al. Are small airplanes safe with regards to COVID-19 transmission? Journal of Travel Medicine August 20, 2021, taab105, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab105
Yes, they are – if the ventilation system is set on ‘high’. In this simulation study (an externally connected ventilation system was used to simulate the cockpit in-flight airflow for a four-seater general aviation aircraft) the airstream was marked with smoke for visualization.
Vaccine
Baltas I, Boshier FA, Williams CA, et al. Post-vaccination COVID-19: A case-control study and genomic analysis of 119 breakthrough infections in partially vaccinated individuals. Clinical Infectious Diseases, August 19, 2021, ciab714, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab714
This matched control study from the UK describes a cohort of Pfizer/BNT or AZ/Oxford vaccinated multimorbid patients developing COVID-19 predominantly from the B.1.1.7 lineage post first vaccination. One life was saved every four to five vaccinations. As mortality benefit from vaccination occurred immediately after COVID-19 infection, these data indirectly question whether pauci-symptomatic/asymptomatic patients should be offered vaccination.
Clinical
Narayanan S, Chua CV, Baddley JW. COVID-19 associated Mucormycosis (CAM): risk factors and mechanisms of disease. Clin Inf Dis, August 22, 2021, ciab726, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab726
High background prevalence of mucormycosis in India, undiagnosed or poorly controlled diabetes, COVID-19 induced immune dysregulation, and therapies like steroids which cause immune suppression in the setting of limited healthcare access amidst a pandemic surge created a perfect storm. This paper reviews currently identified risk factors and pathogenesis of COVID-19 associated mucormycosis.
Collateral damage (and benefits)
Burdzovic Andreas J, Scott Brunbirg G. Self-reported Mental and Physical Health Among Norwegian Adolescents Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open August 24 2021;4(8):e2121934. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.21934
Most adolescents cope adequately with the pandemic conditions. However, they are at high risk becoming couch potatoes: this large cohort study including 2536 adolescents found that Norwegian adolescents starting high school during the COVID-19 year had lower odds of sports participation than their peers starting high school in preceding years, but no significant differences in depression symptoms, friendships, and physical health.
Ujiie M, Tsuzuki S, Nakamoto T, Iwamoto N. Resurgence of respiratory syncytial virus infections during COVID-19 pandemic, Tokyo, Japan. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Nov [date cited]. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/11/21-1565_article
As of July 2021, however, an unusually high number of respiratory syncytial virus infections were reported in Tokyo. This resurgence (the largest annual increase in cases since monitoring began in 2003) may have resulted from restarting social activities for children.
Pregnancy
Badr DA, Picone O, Bevilacqua E, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and pregnancy outcomes according to gestational age at time of infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Oct [date cited]. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/10/21-1394_article
A large cohort, indicating that SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnant women during the late second and early third trimesters is associated with higher risk for adverse outcomes. Of 10,925 pregnant women, 393 (3.6%) were infected with SARS-CoV-2. After matching for possible confounders, statistically significant increases of adverse obstetric outcomes were seen at > 20 weeks gestation and of composite adverse neonatal outcomes at > 26 weeks gestation.
26 August
Vaccine
Today we have a special on vaccine effectiveness towards the B.1.617.2 (Delta).
Fowlkes A, Gaglani M, Groover K, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Frontline Workers Before and During B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant Predominance — Eight U.S. Locations, December 2020–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 24 August 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7034e4.htm?s_cid=mm7034e4_x
In this cohort of 4217 frontline workers (mainly HCW), the vaccine effectiveness (VE) declined from 91% to 66% when the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant became predominant. However, this trend should be interpreted with caution (increasing time since vaccination, low numbers).
Behrens GM, Cossmann A, Stankov MV, et al. SARS-CoV-2 delta variant neutralisation after heterologous ChAdOx1-S/BNT162b2 vaccination. Lancet August 17, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01891-2
Robust inhibition of variants including Delta by the switch vaccination of AZ then Pfizer/BNT.
Hammerschmidt SI, Bosnjak B, Bernhardt G, et al. Neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant after heterologous and homologous BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination. Cell Mol Immunol August 23, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00755-z
Same group, same direction. This small study indicates an overall robust inhibition of the Delta variant by heterologous boosting with Pfizer/BNT of vaccinees initially primed with AZ. However, in contrast to Alpha, Beta, and Gamma variants, homologous Pfizer/BNT prime-boost vaccination appeared to be even more efficient in neutralizing the Delta variant.
Griffin JB, Haddix M, Danza P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Hospitalizations Among Persons Aged ≥16 Years, by Vaccination Status — Los Angeles County, California, May 1–July 25, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 24 August 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7034e5.htm?s_cid=mm7034e5_w
From May 1–July 25, 2021, among 43,127 SARS-CoV-2 infections in residents of Los Angeles County, 25.3% were in fully vaccinated persons, 3.3% were in partially vaccinated persons, and 71.4% were in unvaccinated persons. On July 25, infection and hospitalization rates among unvaccinated persons were 4.9 and 29.2 times, respectively, those of fully vaccinated persons. Of note, in July, when Delta was predominant, cycle threshold values were similar for unvaccinated and vaccinated persons.
Ong SW, Chiew CJ, Ang LW, et al. Clinical and virological features of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a retrospective cohort study comparing B.1.1.7 (Alpha), B.1.315 (Beta), and B.1.617.2 (Delta). Clin Inf Dis August 23, 2021; ciab721, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab721
Retrospective cohort from Singapore, indicating a signal toward increased severity associated with B.1.617.2 (Delta). The association of B.1.617.2 with lower cycle threshold value and longer viral shedding provides a potential mechanism for increased transmissibility. All of 18 vaccinated patients with Delta had mild disease and none developed pneumonia.
25 August
Transmission
Toumi A, Zhao H, Chhatwal J, et al. Association of Limited In-Person Attendance in US National Football League and National Collegiate Athletic Association Games With County-Level COVID-19 Cases. JAMA Netw Open August 17, 2021;4(8):e2119621. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/article-abstract/2783110
Are football games with limited in-person attendance associated with increased county-level COVID-19 cases? Probably not. This cross-sectional study of US counties that hosted National Football League games suggests that football games held with limited in-person attendance were not associated with increased COVID-19 cases in the counties where they were held.
Vaccine
Ranzani OT, Hitchings MD, Durion M, et al. Effectiveness of the CoronaVac vaccine in older adults during a gamma variant associated epidemic of covid-19 in Brazil: test negative case-control study. BMJ August 20, 2021; 374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n2015
Moderate results with the inactivated whole virus vaccine CoronaVac (from Sinovac Biotech) in older people (> 70 years) in a setting with extensive transmission of the gamma variant: adjusted vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic COVID-19 was 24.7% at 0-13 days and 46.8% at ≥ 14 days after the second dose. Adjusted vaccine effectiveness against hospital admissions was 55.5% (death 61.2%) at ≥ 14 days after the second dose, declining with increasing age.
Wan EY, Chui CD, Lai FT, et al. Bell’s palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested case-control study. Lancet Inf Dis August 16, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00451-5
An additional 4.8 cases of this generally self-limiting adverse event per 100,000 people vaccinated with CoronaVac and 2.0 cases per 100,000 people vaccinated with BNT162b2.
Clinical
Lehmann M, Allers K, Heldt C et al. Human small intestinal infection by SARS-CoV-2 is characterized by a mucosal infiltration with activated CD8+ T cells. Mucosal Immunol August 21, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41385-021-00437-z
Intraepithelial CD8+ T cells are activated upon infection of intestinal epithelial cells with SARS-CoV-2, providing one possible explanation for gastrointestinal symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Treatment
Ehrmann S, Li J, Ibarra-Estrada M, et al. Awake prone positioning for COVID-19 acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: a randomised, controlled, multinational, open-label meta-trial. Lancet Resp Med, August 20, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00356-8
This collaborative meta-trial of six randomized controlled open label superiority trials shows that awake prone positioning of patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19 reduces the need for intubation with no signs of harm. 14 patients treated with awake prone positioning avoids one intubation.
24 August
Epidemiology
Moritz S, Gottschick C, Horn J, et al. The risk of indoor sports and culture events for the transmission of COVID-19. Nat Commun August 2021, 12, 5096. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25317-9
The authors conducted an “experimental” pop concert (music was mainstream) on August 22nd 2020, with a total of 1212 individuals in the Leipzig Arena, Germany. They conclude that with an effective ventilation system, indoor mass gathering events with suitable hygiene practices have a very small, if any, effect on epidemic spread. If you are interested in the ventilation system in the arena: the inlet air is blown in laterally on the east- and west side by jet nozzles. https://static-content.springer.com/esm/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41467-021-25317-9/MediaObjects/41467_2021_25317_MOESM7_ESM.mp4
Transmission
Tinker SC, Szablewski CM, Litvintseva AP, Drenzek C, Voccio GE, Hunter MA, et al. Point-of-care antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 in asymptomatic college students. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Oct [date cited]. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/27/10/21-0080_article
Bad news for the BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card. In this screening study of 1,540 asymptomatic college students, BinaxNOW missed many infections and showed only 20% overall sensitivity (among participants with culturable virus, sensitivity was 60%).
Vaccine
Chung H, He S, Nasreen S, et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 covid-19 vaccines against symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe covid-19 outcomes in Ontario, Canada: test negative design study. BMJ August 20, 2021; 374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1943
Two doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines were observed to be highly effective against symptomatic infection and severe outcomes. Vaccine effectiveness of one dose was observed to be lower, particularly for older adults shortly after the first dose. Of note, a higher effectiveness was seen after one dose of mRNA-1273 (MODERNA) than after one dose of BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer).
Debes AK, Yiao S, Colantuoni E, et al. Association of Vaccine Type and Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection With Symptoms and Antibody Measurements Following Vaccination Among Health Care Workers. JAMA Intern Med August 16, 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2782821
You don’t have to suffer to benefit from COVID vaccination. In this study on HCWs, the vast majority of participants (953 of 954!) developed spike IgG antibodies 14 or more days following dose 2, regardless of vaccine reactions!
Co-morbidities
Foote MB, White JR, Lee J, et al. Association of Antineoplastic Therapy With Decreased SARS-CoV-2 Infection Rates in Patients With Cancer. JAMA Oncol August 20, 2021; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2783284
Interesting finding. After identifying potential ACE2-lowering anti-neoplastic compounds, including mTOR/PI3K inhibitors (like everolimus) and anti-metabolites (like gemcitabine), these were “validated” in a large retrospective cohort: patients who received potential ACE2-lowering anti-neoplastics were nearly half as likely to have positive results for SARS-CoV-2 compared with patients treated with other active anti-neoplastic therapies.
23 August
Vaccines
Eliakim-Raz N, Massarweh A, Stemmer A, Stemmer SM. Durability of Response to SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 Vaccination in Patients on Active Anticancer Treatment. JAMA Oncol. 2021 Aug 11:e214390. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379092. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.4390
Anti-spike (anti-S) IgG antibody response to the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine in 95 patients with solid tumors on active anti-cancer treatment after a median of 4 months from the second vaccination. Eighty-three patients (87%) were seropositive for anti-S IgG antibodies. The median titer levels in patients with cancer was significantly lower than those in the control group. There was a 3.6-fold range in median titer values across tumor types and a wider range (8.8-fold) across treatment types. The only variable significantly associated with lower IgG titers was treatment with chemotherapy plus immunotherapy and immunotherapy plus biological therapy.
Epidemiology
Madsen JR, Nielsen JPS, Fogh K, et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Medical Students in Copenhagen. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021, publshed 19 August. Full text: https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/8/8/ofab273/6354577
“Medical students have the highest reported seropositivity (34.58%) in the Danish health care system. In this cohort of students at University of Copenhagen, seropositivity was associated with social behavior markers and, to a lesser extent, with self-reported contact with SARS-CoV-2-infected patients.”
Transmission
Smith JAE, Hopkins S, Turner C, et al. Public health impact of mass sporting and cultural events in a rising COVID-19 prevalence in England. Public Health England 2021, posted 21 August. Full text: https://khub.net/documents/135939561/338928724/Public+health+impact+of+mass+sporting+and+cultural+events+in+a+rising+COVID-19+prevalence+in+England.pdf/05204895-1576-1ee7-b41e-880d5d6b4f17
“The number of potentially infected persons attending Wembley stadium increased as the [EURO 2020] tournament progressed, reaching more than 2,000 at the EURO 2020 final despite event goers requiring a COVID pass for entry.” In the future, it might be “important to consider including mitigations for spectators to consider such as face coverings when travelling to and from events, minimising crowding in poorly ventilated indoors spaces such as bars and pubs where people may congregate to watch events. It is also important to minimise the risk of transmission from aerosol exposure related to singing and chanting in large groups by improving ventilation in enclosed spaces.” See also the Guardian article: Walker P. 9,000 Covid cases linked to Euro 2020 games in mass events scheme. The Guardian 2021, published 20 August. Full text: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/aug/20/9000-covid-cases-linked-to-euro-2020-games-in-mass-events-scheme
Prevention
Bartels J, Fairfield C, Chen IC, Neu D. Laboratory Study of Physical Barrier Efficiency for Worker Protection against SARS-CoV-2 while Standing or Sitting. medRxiv 2021, posted 29 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.26.21261146
Masks are better than plexiglass barriers. The authors find a more than 70% reduction in exposure to aerosols from simulated coughs, but barriers increase exposure to other people nearby and may impede proper ventilation. Plexiglass barriers divert aerosols, masks remove them.
Collateral Effects
Brink J, Cullen P, Beek K, Peters SAE. Intimate Partner Violence during the Covid-19 pandemic in Western and Southern European countries. Eur J Public Health. 2021 Aug 18:ckab093. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34406373. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckab093
“Six countries showed an increase in domestic violence reports (Austria, Belgium, France, Ireland, Spain, and the UK), two countries a drop (Italy and Portugal), two countries showed no change (the Netherlands and Switzerland), and one country did not provide comparative data (Germany).”
22 August
Vaccines
Gilbert PB, Montefiori DC, McDermott A, et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial. medRxiv 2021, posted 10 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.09.21261290
Antibody levels (measured as IgG bAbs to spike, IgG bAbs to spike RBD, ID50 and ID80 nAb titer) might be able to predict the level of protection provided by the Moderna vaccine. This is the result of a study which compared levels of neutralizing antibodies in 47 vaccinated individuals who developed breakthrough infections with matched controls.
Virology
Resende PC, Naveca FG, Lins RD, et al. The Ongoing Evolution of Variants of Concern and Interest of SARS-CoV-2 in Brazil Revealed by Convergent Indels in the Amino (N)-Terminal Domain of the Spike Protein. Virus Evolution 2021, published 14 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/veab069
The authors identified that SARS-CoV-2 lineages circulating in Brazil independently acquired convergent deletions and insertions in the amino (N)-terminal domain (NTD) of the S protein. They anticipate that ongoing widespread transmission of SARS-CoV-2 will generate new viral lineages that might be more resistant to antibody neutralization.
Prevention
Pagel C. Schools—a gaping hole in the English covid strategy. BMJ Opinion 2021, published 20 August. Full text: https://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/08/20/christina-pagel-schools-a-gaping-hole-in-the-english-covid-strategy
“Schools don’t have to be worse than any other crowded indoor space to be a problem. The problem is simply that they are another crowded indoor space and one where children spend 35 hours a week. We know that Delta spreads easily in such indoor spaces, particular if they are poorly ventilated.”
Hammond PS. Will we ever wash our hands of lubrication theory? Physics of Fluids 2021, published 17 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0060307
The flow physics of hand washing. Why vigorous hand washing for ≥ 20 seconds is optimal. Read more than the abstract, it will be worth your while.
Treatment
Korley FK, Durkalski-Mauldin V, Yeatts SD, et al. Early Convalescent Plasma for High-Risk Outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 18. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34407339. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2103784
Time to close the chapter on convalescent plasma? In this randomized, multicenter, single-blind trial (257 in the convalescent plasma group and 254 in the placebo group), the administration of COVID-19 convalescent plasma to high-risk outpatients within 1 week after the onset of symptoms of COVID-19 did not prevent disease progression.
21 August
Vaccines
Morris J. Israeli data: How can efficacy vs. severe disease be strong when 60% of hospitalized are vaccinated? Covid-19 Data Science 2021, posted 17 August. Full text: https://www.covid-datascience.com/post/israeli-data-how-can-efficacy-vs-severe-disease-be-strong-when-60-of-hospitalized-are-vaccinated
“It is important to use infection and disease rates (per 100k, e.g.) and not raw counts to compare unvaccinated and vaccinated groups to adjust for the proportion vaccinated. Use of raw counts exaggerates the vaccine efficacy when vaccinated proportion is low and attenuates the vaccine efficacy when, like in Israel, vaccines proportions are high.”
Copyright: Jeffrey Morris
Ollila TA, Lu S, Masel R, et al. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccination in Adults With Hematologic Malignant Disease. JAMA Oncol. 2021 Aug 11:e214381. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379085. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.4381
Retrospective study of 160 adults with hematologic malignant disease who were vaccinated with a COVID-19 vaccine. (One hundred and five (66%) patients received a B cell–depleting monoclonal antibody, most commonly rituximab (n = 85)). Sixty-three patients (39%) demonstrated seroconversion. Longer time (greater than or less than 12 months) from last chemotherapy administration to vaccination was associated with increased rates of seroconversion. The quantitative antibody response was also lower among patients with exposure to B cell/plasma cell–depleting antibodies and those with active malignant disease.
Epidemiology
Zhang S. The Coronavirus Is Here Forever. This Is How We Live With It. The Atlantic 2021, published 17 August. Full text: https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2021/08/how-we-live-coronavirus-forever/619783
The path from COVID-19 to the common cold.
Treatment
Crippa JAS, Zuardi AW, Guimarães FS, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Cannabidiol Plus Standard Care vs Standard Care Alone for the Treatment of Emotional Exhaustion and Burnout Among Frontline Health Care Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2120603. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34387679. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20603
Randomized trial of 120 frontline health care professionals. “Emotional exhaustion scores were reduced among participants receiving cannabidiol (CBD) [300 mg] plus standard care compared with those receiving standard care alone. Five participants who received CBD plus standard care experienced serious adverse events, with full recovery after discontinuation.”
Pediatrics and Obstetrics
Chinn J, Sedighim S, Kirby KA, et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Women With COVID-19 Giving Birth at US Academic Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2120456. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379123. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20456
Women with COVID-19 giving birth had increased mortality, need for intubation and ventilation, and intensive care unit admission. This is the result of a cohort study examining 869,079 adult women, including 18,715 women with COVID-19, during 12 months up to February 2021.
20 August
Vaccines
Tan CW, Chia WN, Young BE, et al. Pan-Sarbecovirus Neutralizing Antibodies in BNT162b2-Immunized SARS-CoV-1 Survivors. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 18. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34407341. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2108453
If you had survived SARS-CoV-1 in 2002-2004, the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine would today give you potent cross-clade pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing antibodies. This study (n = 8) is another proof of concept that a pan-coronavirus vaccine is possible. Such a vaccine might cover not only SARS-CoV-2 and its current and future variants but also other coronaviruses with known potential to cause severe human diseases.
Mallapaty S. Delta’s rise is fuelled by rampant spread from people who feel fine. Nature 2021, published 19 August. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02259-2
“People infected with the Delta variant generally do not have COVID-19 symptoms until two days after they start shedding the coronavirus.”
Epidemiology
Kupferschmidt K. Evolving Threat. Science 2021, publshed 19 August. Full text: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/08/new-sars-cov-2-variants-have-changed-pandemic-what-will-virus-do-next
“New SARS-CoV-2 variants have changed the pandemic. What will the virus do next?”
Immunology
Loske J, Röhmel J, Lukassen S, et al. Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Nat Biotechnol (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-021-01037-9
The authors provide evidence that the epithelial and immune cells of the upper airways (nose) of children are pre-activated and primed for virus sensing, resulting in a stronger early innate antiviral response to SARS-CoV-2 infection than in adults.
Transmission
Branswell H. What’s safe to do during summer’s Covid surge? STAT asked public health experts about their own plans. Stat 2021, published 17 August. Full text: https://www.statnews.com/2021/08/17/whats-safe-to-do-during-summers-covid-surge-stat-asked-public-health-experts-about-their-own-plans/
Experts largely stay put.
Paul LA, Daneman N, Schwartz KL, et al. Association of Age and Pediatric Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Aug 16. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34398179. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.2770
In this Ontario study of 6280 households with pediatric index cases, 1717 households (27.3%) experienced secondary transmission.
“Younger children may have greater risk of transmitting SARS-CoV-2 to caregivers and siblings in the household than older children. In this cohort study of 6280 households with pediatric index cases, the adjusted odds of household transmission by children aged 0 to 3 years was 1.43 compared with children aged 14 to 17 years.”
Leibowitz AI, Siedner MJ, Tsai AC, Mohareb AM. Association Between Prison Crowding and COVID-19 Incidence Rates in Massachusetts Prisons, April 2020-January 2021. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Aug 9:e214392. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34369964. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4392
“In this study (…) including all incarcerated persons in 14 Massachusetts state prisons from April 2020 to January 2021 (…), COVID-19 incidence was significantly higher in prisons operating at a higher percentage of their design capacity and was significantly lower in prisons where a higher proportion of incarcerated people were housed in single-cell units.” See also the comment by Clemenzi-Allen AA, Pratt LA. Avoiding COVID-19 Outbreaks in Carceral Settings. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Aug 9. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34369968. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4389
Diagnostics
Congrave-Wilson Z, Lee Y, Jumarang J, et al. Change in Saliva RT-PCR Sensitivity Over the Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA. 2021 Aug 13. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34387653. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.13967
Prospective study to investigate the testing timeframe that optimizes saliva sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 detection. “Saliva was sensitive for detecting SARS-CoV-2 in symptomatic individuals during initial weeks of infection, but sensitivity in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers was less than 60% at all time points. (…) This study suggests saliva-based RT-PCR should not be used for asymptomatic COVID-19 screening.”
19 August
Severe COVID
France 20210817. Triage in Guadeloupe. La Voix du Nord 2021, published 17 August. Full text: https://www.lavoixdunord.fr/1057833/article/2021-08-17/guadeloupe-le-tri-des-patients-covid-en-reanimation-se-fait-desormais-partir-de
Triage in a French overseas territory. French press reports indicate that at the Pointe-à-Pitre hospital in Guadeloupe, “patients over 50 and those below having at least one comorbid factor are no longer intubated.”
Epidemiology
Wadman M. A grim warning from Israel: Vaccination blunts, but does not defeat Delta. Science 2021, published 16 August. Full text: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/08/grim-warning-israel-vaccination-blunts-does-not-defeat-delta
“Israel, which has led the world in launching vaccinations and in data gathering, is confronting a surge of COVID-19 cases that officials expect to push hospitals to the brink. Nearly 60% of gravely ill patients are fully vaccinated.”
Vaccines
Nanduri S, Pilishvili T, Derado G, et al. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Nursing Home Residents Before and During Widespread Circulation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant — National Healthcare Safety Network, March 1–August 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 18 August 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e3
“Two doses of mRNA vaccines were 74.7% effective against infection among nursing home residents early in the vaccination program (March–May 2021). During June–July 2021, when B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant circulation predominated, effectiveness declined significantly to 53.1%.”
Madhi SA, Koen AL, Izu A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in people living with and without HIV in South Africa: an interim analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1B/2A trial. Lancet 2021, published 17 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00157-0
A double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 1B/2A study of the AstraZeneca vaccine in 104 people with HIV and 70 HIV-negative controls. The authors found similar full-length spike (FLS)-binding and receptor-binding domain (RBD)-binding IgG and SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing response patterns in people with HIV and HIV-negative SARS-CoV-2-naive participants.
Schmitz AJ, Turner JS, Liu Z, et al. A vaccine-induced public antibody protects against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Immunity 2021, published 16 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.013
The authors describe an antibody, dubbed 2C08 (a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced mAb cloned from a germinal center B cell isolated from a draining axillary lymph node sampled from a healthy adult after receiving their second dose of an mRNA-based vaccine) which potently neutralizes the Delta, Gamma and Alpha strains and reduces lung viral load and morbidity in hamsters challenged with Delta and Gamma. Clonal analysis identified 2C08-like public clonotypes among B cells responding to SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination in 41 out of 181 individuals. Ergo: SARS-CoV-2 vaccines mitigate resistance by circulating variants of concern. Tell your friends to get vaccinated.
Treatment
Rizk JG, Gupta A, Sardar P, et al. Clinical Characteristics and Pharmacological Management of COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia With Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Aug 10. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34374713. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2021.3444
The recommendations of this review: treatment of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) should consist of therapeutic anti-coagulation mostly with non-heparin products and high-dose intravenous immunoglobin (IVIG). In severe cases, plasma exchange should be used for clearing autoantibodies. Routine platelet transfusions, aspirin, and warfarin should be avoided because of the possibility of worsening thrombosis and magnifying risk of bleeding.
Pediatrics
Dionne A, Sperotto F, Chamberlain S, et al. Association of Myocarditis With BNT162b2 Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccine in a Case Series of Children. JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Aug 10:e213471. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34374740. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2021.3471
A case series of 15 children who were hospitalized with myocarditis after receiving the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine.
18 August
Virology
Liu Y, Liu J, Bryan AJ, et al. Delta spike P681R mutation enhances SARS-CoV-2 fitness over Alpha variant. bioRxiv 2021, posted 12 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.12.456173
The Delta spike mutation P681R could be a key mutation in enhancing Delta variant replication via increased S1/S2 cleavage. The authors suggest that Spike mutations that potentially affect furin cleavage efficiency should be closely monitored for future variant surveillance.
Vaccines
Wadman M. A grim warning from Israel: Vaccination blunts, but does not defeat Delta. Science 2021, published 16 August. Full text: https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2021/08/grim-warning-israel-vaccination-blunts-does-not-defeat-delta
“Israel, which has led the world in launching vaccinations and in data gathering, is confronting a surge of COVID-19 cases that officials expect to push hospitals to the brink. Nearly 60% of gravely ill patients are fully vaccinated.”
Lloyd-Sherlock P, Lasco G, McKee M, Perianayagam A, Sempé L. Does vaccine ageism amount to gerontocide? Lancet. 2021 Aug 11:S0140-6736(21)01689-5. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34390657. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01689-5
“In India, more people younger than 45 years are being vaccinated than those 60 years or older, even though about half of those 60 years or older are yet to receive even a single dose. Unlike age-based triage for acute COVID-19 care, this vaccination policy will not save lives: it will contribute to thousands, potentially millions of avertable deaths. In the Philippines, where only 8·5% of people 60 years or older had been fully vaccinated as of June 29, 2021, the focus of vaccination has now shifted to younger so-called working age adults.”
Transmission
Subbaraman N. How do vaccinated people spread Delta? What the science says. Nature 2021, published 12 August. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02187-1
The Delta seems to be more likely than other variants to spread via vaccinated people. Although vaccinated people are probably infectious for a shorter period, they need to take precautions, especially in indoor settings. If you cannot avoid crowded indoor settings, see here: CDC 20210406. Improve How Your Mask Protects You. Centers for Disease Control 2021 (updated 6 April, accessed 15 August). Full text: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/effective-masks.html
Diagnosis
Snell LB, Cliff PR, Charalampous T, et al. Rapid genome sequencing in hospitals to identify potential vaccine-escape SARS-CoV-2 variants. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, published 13 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00482-5
Music of the future. The authors sequenced and identified 2 cases of the B.1.621 variant in less than 24 hours and reported them to Public Health England within 72 hours of sampling.
Clinical
Liu T, Wu D, Yan W, et al. Twelve-month systemic consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a prospective cohort study in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 14:ciab703. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34390330. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab703
The lives of COVID-19 survivors is not easy, as shown by this 12-month follow up of 594 COVID-19 survivors discharged from Tongji Hospital in Wuhan from February 10 to April 30, 2020. After 3, 6 and 12 months, 257 (51.2%), 169 (40.0%) and 138 (28.4%) patients had at least one symptom. About 5% of patients had restrictions in pulmonary function at 12 months. Electrocardiogram abnormalities occurred in 256 (51.0%) patients at 3 months post-discharge, including arrhythmia, ST-T change and conduction block, which increased to 258 (61.1%) cases at the 6-month visit and were maintained at a high frequency (242; 49.8%) at the 12-month visit. An increased incidence of abnormal liver and renal function was also found. Patients had a median age of 63, had been severe or critically ill originally (88.1%), 36.1% of whom had a history of smoking, and having at least one pre-existing co-morbidity was common.
17 August
Vaccines
Evans SJW, Jewell NP. Vaccine Effectiveness Studies in the Field. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jul 12. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34289274. Full-text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2108891.
“Questions crucial to vaccination policy (…) include the effect of new virus variants, the timing between vaccine doses, the effect of vaccines on asymptomatic infection in contrast to severe disease, the waning of vaccine immunity, and the potentially enhanced effectiveness of mix-and-match strategies that might be used with booster shots.” A comment on the paper we presented on 23 July: Lopez Bernal J, Andrews N, Gower C, et al. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 12;385(7):585-594. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34289274. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2108891
Diaz GA, Parsons GT, Gering SK, Meier AR, Hutchinson IV, Robicsek A. Myocarditis and Pericarditis After Vaccination for COVID-19. JAMA. 2021 Aug 4. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34347001. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.13443
Among 2,000,287 individuals receiving at least 1 COVID-19 vaccination (BioNTech/Pfizer: 52.6%, Moderna: 44.1%, Johnson & Johnson: 3.1%), 20 individuals had vaccine-related myocarditis (1 per 100,000) and 37 had pericarditis (1.8 per 100,000). Myocarditis occurred a median of 3.5 days after vaccination. Fifteen individuals (75%) were male. Four persons (20%) developed symptoms after the first vaccination and 16 (80%) after the second one. Nineteen patients (95%) were admitted to the hospital. All were discharged after a median of 2 days. There were no readmissions or deaths. Find more details about pericarditis in the article.
FDA 20210812. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Vaccine Dose for Certain Immunocompromised Individuals. FDA 2021, published 12 August. Full text: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-additional-vaccine-dose-certain-immunocompromised
The FDA allows a third booster dose in individuals with solid organ transplant or those who have an equivalent level of immunocompromise. The news release also states that “patients should be counseled to maintain physical precautions to help prevent COVID-19. In addition, close contacts of immunocompromised persons should get vaccinated, as appropriate for their health status, to provide increased protection to their loved ones.”
Epidemiology
Khullar D. How Will the Coronavirus Evolve? The New Yorker 2021, published 11 August. Full text: https://www.newyorker.com/science/annals-of-medicine/how-will-the-coronavirus-evolve
A nice read about Lenski’s Long-Term Evolution Experiment and possible SARS coronavirus citrate moments, that exceptionally rare, profoundly consequential evolutionary leaps can happen.
Transmission
Read JM, Green CA, Harrison EM, et al. Hospital-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK’s first COVID-19 pandemic wave. Lancet 20212, published 12 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01786-4
Until the end of July 2020, 6.8% of patients with COVID-19 in 314 UK hospitals may have been infected after hospital admission, with a peak of 8.2% in mid-May. The authors conclusion, “As SARS-CoV-2 is likely to persist as an endemic or seasonal virus in coming years, it is critical to use the lessons learned so far in the pandemic to minimise the burden of hospital-acquired infections.”
16 August
Vaccines
Hillus D, Schwarz T, Tober-Lau P, et al. Safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of homologous and heterologous prime-boost immunisation with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Dis 2021, published 12 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00357-X
A new prospective vaccine mixing study comparing “AstraZeneca (AZ) + BioNTech/Pfizer (BP)” with 2 x AZ and 2 x BP. The authors show “AZ first, BP second” elicited a stronger immune response than two doses of either vaccine. Could these data spur a renaissance for the AstraZeneca vaccine? Not sure. The difference might be explained by the longer (and possibly more effective) immunization interval of AZ+BP compared to the typical 3-week interval of the two BP injections.
Hou X, Zaks T, Langer R, et al. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat Rev Mater (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00358-0
The authors discuss the physiological barriers and possible administration routes for lipid nanoparticle–mRNA systems and highlight preclinical and clinical studies of lipid nanoparticle–mRNA therapeutics for infectious diseases, cancer and genetic disorders.
Immunology
Painter MM, Mathew D, Goel RR, et al. Rapid induction of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells is associated with coordinated humoral and cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Immunity 2021, published 12 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.001
The authors compiled 26 measures of antigen-specific immunity across CD4 and CD8 T cells, antibodies, and memory B cells. After vaccination, the immune response was different for SARS-CoV-2 naive and recovered individuals. Naive people benefit from receiving both doses, while recovered people only need one. The universal CD4 response to the first dose (Th1 and Tfh) may be critical to overall immunity by amplifying responses to the second dose.
Epidemiology
OHA 20210805. COVID-19 Monthly Report | Oregon’s Weekly Surveillance Summary. Oregon Health Authority 2021, published 5 August. Full text: https://www.oregon.gov/oha/covid19/Documents/DataReports/Breakthrough-Report-08-2021.pdf
In Oregon (US), the beginning of the 4th wave of the pandemic is that it is a wave of the unvaccinated. In July 2021, 81% of 12,514 COVID-19 cases were among unvaccinated people, as were 82% of COVID-19-related deaths. Conclusion: “Although the number of vaccine breakthrough cases is increasing, they are very small when compared to the more than 2.3 million people who have completed their COVID-19 vaccination.”
Leatherby L. See How Vaccines Can Make the Difference in Delta Variant’s Impact. The New York Times 2021, published 12 August. Infographic: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/08/12/science/covid-delta-breakthrough.html
As the number of vaccinated people increases, so will the number of breakthrough cases. This doesn’t mean that our vaccines are ineffective. See this very instructional infographic which modeled Delta-driven COVID outbreaks in two communities, one with a high vaccination rate and another with a low rate. Their levels of serious illness and death were starkly different.
15 August
Epidemiology
Rozier G. Guadeloupe. CovidTracker 2021, update 13 August. Web page: https://covidtracker.fr/dashboard-departements/?dep=971
Guadeloupe – and to a lesser extent her sister island Martinique (see Google Maps) – are a telling picture of the Delta variant entering a population where less than 20% had their first COVID-19 vaccine shot. For the week 4-10 August, the cumulative incidence in young adults aged 20 to 29 years was… 4248! For these islands, tourism specialists predict a decline in visitor numbers in the next high season (December 2021 – April 2021).
Copyright: Guillaume Rozier – https://twitter.com/GuillaumeRozier
Yong E. How the Pandemic Now Ends. The Atlantic 2021, published 12 August. Full text: https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2021/08/delta-has-changed-pandemic-endgame/619726/
Just one of several excellent quotes, “Here, then, is the current pandemic dilemma: Vaccines remain the best way for individuals to protect themselves, but societies cannot treat vaccines as their only defense. And for now, unvaccinated pockets are still large enough to sustain Delta surges, which can overwhelm hospitals, shut down schools, and create more chances for even worse variants to emerge.”
Vaccines
Hall VG, Ferreira VH, Ku T, et al. Randomized Trial of a Third Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine in Transplant Recipients. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 11. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379917. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2111462
A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of a third-dose booster of the Moderna vaccine in 120 organ-transplant recipients (median time from transplantation to the third dose was 3.16 years). After four months, an anti–receptor-binding domain (RBD) antibody level of at least 100 U per milliliter was present in 33 of 60 patients (55%) in the mRNA-1273 group and in 10 of 57 patients (18%) in the placebo group. The median percent virus neutralization was 71% in the Moderna group and 13% in the placebo group. The trial was not powered to detect differences in clinical outcomes.
Pathogenesis
Ziegler CGK, Miao VN, Owings AH, et al. Impaired local intrinsic immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection in severe COVID-19. Cell. 2021 Jul 23:S0092-8674(21)00882-5. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34352228. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.023
After single-cell transcriptome sequencing of nasopharyngeal swabs from 58 people, the authors suggests that failed nasal epithelial anti-viral immunity might underlie and precede severe COVID-19.
Clinical
Sah P, Fitzpatrick MC, Zimmer CF, et al. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 24;118(34):e2109229118. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34376550. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2109229118
Systematic review and meta-analysis of over 350 papers. The authors estimate that more than one-third of infections are truly asymptomatic, with greater asymptomaticity in children (46.7%) compared with the elderly (19.7%), and greater asymptomaticity among people with no underlying medical conditions compared with those with co-morbidities.
14 August
Vaccines
Ali K, Berman G, Zhou H, et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 11. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379915. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2109522
Nothing truly new: the Moderna vaccine had an acceptable safety profile in adolescents, the immune response was similar to that in young adults, and the vaccine prevented COVID-19. Interestingly, in the placebo group, after the first and second injections, study participants experienced injection-site pain (in 34.8% and 30.3%, respectively), headache (in 38.5% and 30.2%, respectively), and fatigue (in 36.6% and 28.9%, respectively). It’s fascinating how just the thought of getting a vaccine that might give you headache or fatigue is sufficient to give you… headache fatigue. In this trial, about half of all mild adverse events were probably the product of human imagination.
Pegu A, O’Connell S, Schmidt SD, et al. Durability of mRNA-1273-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, published 12 PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34031659. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abj4176
Most individuals vaccinated with the Moderna vaccine maintained binding and functional antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants for 6 months, including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, B.1.429, and B.1.526. Neutralizing responses were rare after a single Moderna dose, but at the peak of response to the second dose, all individuals had robust responses to all variants. The study included the results from 8 volunteers in each of three age groups: 18-55, 55-70, and 71+ years of age.
Malard F, Gaugler B, Gozlan J, et al. Weak immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 11, 142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00534-z
In patients with hematological malignancies, vaccination with two doses of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine translates into a significant increase in humoral response, allowing almost half of the patients to achieve immune protection against COVID-19 (retrospective study, n = 237). The use of B cell targeting treatment within the previous 12 months before vaccination, and a low CD19+ B cell level predicted failure in achieving immune protection.
Baraniuk C. Covid-19: How effective are vaccines against the delta variant? BMJ. 2021 Aug 9;374:n1960. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34373255. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1960
49% of people in the UK who died from infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant up until 19 July had had two vaccine doses – the author is confident about the protection offered by current vaccines. (He’s probably right!)
Clinical
Pavord S, Scully M, Hunt BJ, et al. Clinical Features of Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 11. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34379914. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2109908
The mortality associated with vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT) was highest among patients with a low platelet count and intracranial hemorrhage. A prospective study of 170 definite and 50 probable cases of VITT (UK, 22 March – 6 June 2021). The overall mortality was 22%, but 73% among patients with platelet counts < 30,000 and intracranial hemorrhage.
13 August
Vaccines
The bad news: Immunity wanes over time
IMH 20210812. Concentration of data on vaccinated in two doses until 31/1/2021 (discussion from 20.7.2021) [ריכוז נתונים על מחוסנים בשתי מנות עד לתאריך 31/1/2021(דיון מ 20.7.2021)]. Israel Ministry of Health (משרד הבריאות) 2021, last modified 12 August. PDF with slides: https://www.gov.il/BlobFolder/reports/vaccine-efficacy-safety-follow-up-committee/he/files_publications_corona_two-dose-vaccination-data.pdf
Effectiveness of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine in Israel by 1) outcome and 2) month vaccinated with second dose (slide 8):
The good news: Waning immunity is better than no immunity
Jeffey N. Among older Israelis, serious COVID rate six times as high if unvaccinated. The Times of Israel 2021, published 10 August. Full text: https://www.timesofisrael.com/among-older-israelis-serious-covid-rate-six-times-higher-if-unvaccinated/
In the new epidemic wave in Israel, the number of severe COVID-19 cases is far higher among unvaccinated people, both old and young.
Van Vinh Chau N, Ngoc NM. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant Among Vaccinated Healthcare Workers, Vietnam. Lancet Preprints 2021, posted 10 August.
In this study of 62 healthcare workers, breakthrough infections with the Delta variant were associated with high viral loads (251 times higher than in people infected with historical strains), prolonged PCR positivity (8–33 days; median: 21), and low levels of vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies. The authors conclude that physical distancing measures will be critical to reduce the transmission of the Delta variant.
Treatment
Yu LM, Bafadhel M, Dorward J, et al. Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet 2021, published 10 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X
Inhaled budesonide, 800 μg twice daily for 14 days, might improve time to recovery and possibly reduce hospital admissions or deaths. In this primary analysis of a randomized trial, time to first self-reported recovery was reduced by almost 3 days with budesonide (11.8 vs 14.7 days). For hospital admissions or deaths, the estimated rate was 6.8% in the budesonide group versus 8.8% in the usual care group. See also comment by Mangin D, Howard M. The use of inhaled corticosteroids in early-stage COVID-19. Lancet 2021, published 10 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01809-2
Tattersall RS, McGonagle D, Manson JJ. A role for interleukin-1 receptor antagonism in severe COVID-19? Lancet Rheumatol 2021, published 9 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00249-6
Dexamethasone and tocilizumab, an interleukin (IL)-6 receptor inhibitor, have an established role in the treatment of hyperinflammatory COVID-19. What about anakinra, a recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist? The authors discuss a paper that finds that anakinra may not be beneficial above and beyond dexamethasone. One possible exception: patients with evidence of a significant inflammatory response, defined as a C-reactive protein concentration higher than 100 mg/L.
Co-morbidities
Klineova S, Harel A, Straus Farber R, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 infection in multiple sclerosis and related conditions: one-year pandemic experience of the multicenter New York COVID-19 Neuroimmunology Consortium (NYCNIC). Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021, published 18 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2021.103153
Anti-CD20 therapies blunt the humoral responses to COVID-19 in patients with multiple sclerosis. Of 474 patients, only 39.5% of patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
12 August
Vaccines
Puranik A, Lenehan PJ, Silvert E, et al. Comparison of two highly-effective mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 during periods of Alpha and Delta variant prevalence. medRxiv 2021, posted 9 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.06.21261707
Data from the Mayo Clinic Health System from January to July 2021 find that the mRNA vaccines produced by BioNTech/Pfizer and Moderna are highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 infection (BioNTech/Pfizer: 76%; Moderna: 86%) and COVID-19 associated hospitalization (85% vs. 91.6%). Surprise in July: while vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization remained high (75% vs 81%), effectiveness against infection was lower for both vaccines (42% vs 76%), with a more pronounced reduction for the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. To be taken with a grain of salt. (BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine administered earlier than the Moderna vaccine?) Note that this is a pre-print paper that has not yet been reviewed.
Hadjadj J, Planas D, Ouedrani A, et al. Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 vaccine Against the Alpha and Delta Variants in Immunocompromised Patients. medRxiv 2021, posted 9 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.08.21261766
Prospective study in 64 patients with systemic inflammatory diseases and 21 controls receiving two doses of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. The Delta variant fully escaped the humoral response of individuals treated with rituximab. See also how they differentially impacted the immunogenicity of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine, by impairing B cell (rituximab) and T cell (methotrexate) responses.
Epidemiology
Rocklöv J, Liu Y. The reproductive number of the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is far higher compared to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 virus. J Travel Med 2021, published 9 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taab124
Don’t throw your masks away, even if you are vaccinated. Here, the authors summarize 5 studies that estimate the basic reproductive number for the Delta variant ranging from 3.2 to 8, with a mean of 5.08. This is almost double the R0 of the historical strain which is 2.79. Vaccination alone may not be sufficient until well into 2022.
Immunology
Vora SM, Lieberman J, Wu H. Inflammasome activation at the crux of severe COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-021-00588-x
Obesity, diabetes, heart disease, hypertension and ageing, which may be etiologically linked through overactive inflammasome signaling, are prognostic of poor COVID-19 outcome. The authors discuss potential mechanisms of inflammasome activation and the implications for therapy.
Beyond COVID
IPCC 20210810. Sixth Assessment Report, Working Group I. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2021, published 9 August. Full text: https://www.ipcc.ch
Infinitely larger than COVID-19. See also the short Nature comment by Tollefson J. IPCC climate report: Earth is warmer than it’s been in 125,000 years. Nature 2021, published 9 August. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02179-1
11 August
Vaccines
Moline HL, Whitaker M, Deng L, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing Hospitalization Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — COVID-NET, 13 States, February–April 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 6 August 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e3
Among adults aged ≥ 65, the effectiveness of full vaccination for preventing hospitalization was 96% for the BioNTech/Pfizer and Moderna vaccines (exception: 91% for the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine in age ≥ 75 years) and 84% for the Janssen vaccine. Note that these data are from the pre-Delta era.
Nirenberg E. Myocarditis and COVID-19 mRNA vaccines. Deplatformdisease.com 2021, published 10 July. https://www.deplatformdisease.com/blog/myocarditis-and-covid-19-mrna-vaccines?format=amp
Not a scientific paper, but worth reading. The author mentions that compared to mRNA vaccine-induced myocarditis, leaving children unprotected or incompletely protected from COVID-19 is currently the bigger risk.
Pepe S, Gregory AT, Denniss AR. Myocarditis, Pericarditis and Cardiomyopathy After COVID-19 Vaccination. Heart Lung Circ. 2021 Jul 30:S1443-9506(21)01156-2. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34340927. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2021.07.011
Among 2,000,287 individuals receiving at least one dose of vaccine, 20 had vaccine-related myocarditis (1.0/100,000; median age: 36) and 37 had pericarditis (1.8/100,000; median age: 59). Myocarditis occurred a median of 3.5 days after vaccination, pericarditis developed after a median of 20 days. All patients were discharged after a median of 1 to 2 days. No one died.
Epidemiology
Wallace-Wells D. Too Many People Are Dying Right Now. “It’s hard to look at these indicators and feel at all optimistic,” explains scientist Eric Topol. Intelligencer 2021, published 8 August. Full text: https://nymag.com/intelligencer/2021/08/too-many-people-are-dying-of-covid-19-right-now.html
There is much uncertainty about how the Delta wave will evolve in the United States. An interview with Eric Topol, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute.
Collateral Effects
Kidman R. Use HIV’s lessons to help children orphaned by COVID-19. Nature 2021, published 9 August. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02155-9
“Young people who have lost parents to the pandemic need urgent support and long-term study to avert the cascade of adversity that can follow. Decades of research into the HIV epidemic provide(s) a solid foundation.”
10 August
Vaccines
Boekel L, Steenhuis M, Hooijberg F, et al. Antibody development after COVID-19 vaccination in patients with autoimmune diseases in the Netherlands: a substudy of data from two prospective cohort studies. Lancet Rheumatology 2021, published 6 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00222-8
Two prospective studies of 3682 patients with rheumatic diseases, 546 patients with multiple sclerosis, and 1147 healthy controls. Seroconversion after first vaccination was significantly lower in patients than in controls, but after the second vaccination, seroconversion exceeded 80% in all patient treatment subgroups, except among those treated with anti-CD20 therapies (three [43%] of seven patients). We all know the final message: don’t delay the second shot in patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs.
Clinical
Chauhan K, Soni D, Sarkar D, et al. Mucormycosis after COVID-19 in a patient with diabetes. Lancet 2021, published 4 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01641-X
Ten days after starting a treatment with supplemental oxygen, intravenous antibiotics, and corticosteroids due to a moderately severe pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2, this patient presents with a blackish patch—extending from just below his left eye to the left side of his face to the level of his mouth—that had developed 2 days earlier. The authors explain that “COVID-19 followed by mucormycosis carries a very high mortality rate and timely detection, antifungal therapy, and aggressive surgical debridement remain key factors in the management.” See also the video at https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)01641-X/fulltext#sec1
Co-morbidities
Jassat W, Cohen C, Tempia S, et al. Risk factors for COVID-19-related in-hospital mortality in a high HIV and tuberculosis prevalence setting in South Africa: a cohort study. Lancet HIV 2021, published 4 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00151-X
In South Africa, between March 5, 2020, and March 27, 2021, increasing age was the strongest predictor of COVID-19 in-hospital mortality. Other factors associated were HIV infection (adjusted odds ratio [OR] 1.34), past tuberculosis (OR 1.26), current tuberculosis (OR 1.42) and both past and current tuberculosis (OR 1.48) compared with never tuberculosis (as well as other common COVID-19 risk factors, such as male sex, non-White race, hypertension, diabetes, chronic cardiac disease, chronic renal disease, and malignancy in the past 5 years). See also the comment by Madhi SA, Nel J. Epidemiology of severe COVID-19 from South Africa. Lancet HIV 2021, published 4 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00183-1
Bitan DT, Kridin K, Cohen AD, Weinstein O. COVID-19 hospitalisation, mortality, vaccination, and postvaccination trends among people with schizophrenia in Israel: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, published 5 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00256-X
A longitudinal cohort study with a year-long estimation of differences in hospitalization and mortality among 25,539 patients with schizophrenia and 25,539 controls. People with schizophrenia showed a higher risk for COVID-19 hospitalization (hazard ratio [HR] 4.81) and mortality (HR 2.52) and showed a sharper decline in survival as time progressed. Diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and ischemic heart disease were significant predictors of vaccination rates among patients with schizophrenia but not among controls. See also the comment by De Picker LJ. Closing COVID-19 mortality, vaccination, and evidence gaps for those with severe mental illness. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, published 5 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00291-1
Severe COVID
Perkins G, Bronwen CJ, Connolly BA, et al. An adaptive randomized controlled trial of non-invasive respiratory strategies in acute respiratory failure patients with COVID-19. medRxiv 2021, posted 4 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.02.21261379
Over 13 months, 1272 participants were randomized to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP; n = 380, 29.9%), high-flow nasal oxygenation (HFNO; n = 417, 32.8%) and conventional oxygen therapy (n = 475, 37.3%). Neither CPAP nor HFNO, when compared with conventional oxygen therapy, reduced mortality at any point. In a comment by Elisabeth Mahase (Covid-19: CPAP reduces need for invasive mechanical ventilation in patients requiring oxygen, study finds. BMJ. 2021 Aug 4;374:n1950. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34353810. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1950), the study’s chief investigator Danny McAuley is cited, saying that “CPAP reduces the pressure on the need for invasive mechanical ventilation and the pressure on intensive care unit beds. HFNO uses a large amount of oxygen and can cause issues with limited oxygen therapy, and we’ve found that it doesn’t really add anything above conventional therapy.”
9 August
Collateral Effects
Sansone A, Mollaioli D, Ciocca G, et al. “Mask up to keep it up”: Preliminary evidence of the association between erectile dysfunction and COVID-19. Andrology. 2021 Jul;9(4):1053-1059. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/33742540. Full text: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/andr.13003 | See also the informal discussion at https://theconversation.com/covid-19-could-cause-male-infertility-and-sexual-dysfunction-but-vaccines-do-not-164139
Erectile dysfunction (ED) could be a short‐ or long‐term complication of COVID‐19. In this analysis of 100 people (25 COVID‐positive and 75 COVID‐negative), the prevalence of ED was significantly higher in the COVID+ group (28% vs. 9.33%; p = 0.027).
Vaccines
Cavanaugh AM, Spicer KB, Thoroughman D, Glick C, Winter K. Reduced Risk of Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 After COVID-19 Vaccination — Kentucky, May–June 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 6 August 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e1
The immunological response elicited by vaccines might be better than the response elicited by natural SARS-CoV-2 infection. In Kentucky residents infected by COVID in 2020, those who were not vaccinated had a 2.34 times higher risk of reinfection than those who were fully vaccinated.
Perry RJ, Tamborska A, Bhagteshwar S, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis after vaccination against COVID-19 in the UK: a multicentre cohort study. Lancet 2021, published 6 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01608-1
An analysis of 95 patients from more than 40 hospitals across the UK. Seventy patients had vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) and 25 did not. Patients with VITT-associated cerebral venous thrombosis had more intracranial veins thrombosed than non-VITT patients; they also more frequently had extracranial thrombosis. Death or dependency occurred in 47% of patients with VITT-associated cerebral venous thrombosis. Non-heparin anticoagulants and immunoglobulin treatment might improve VITT outcome.
Callaway E. COVID vaccine boosters: the most important questions. Nature 2021, published 5 August. Full text: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02158-6
“Concerns over waning immunity and SARS-CoV-2 variants have convinced some countries to deploy extra vaccine doses — but it’s not clear to scientists whether most people need them.”
Immunology
Ortega N, Ribes M, Vidal M, et al. Seven-month kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and role of pre-existing antibodies to human coronaviruses. Nat Commun 12, 4740 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24979-9
Many studies have reported a lack of protection from infection with human coronaviruses causing common cold (HCoVs). The authors don’t agree. They analyzed data from a cohort of 578 health care workers followed up to 7 months and found that IgG and IgA to HCoV were significantly higher in asymptomatic than symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 seropositive individuals.
8 August
Vaccines
Public Health England 202100806. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England | Technical briefing 20. UK Government 2021, 6 August. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/investigation-of-novel-sars-cov-2-variant-variant-of-concern-20201201 | PDF: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1009243/Technical_Briefing_20.pdf
Again, for Delta variant infections, the viral load cycle threshold (Ct) is described as being similar for unvaccinated individuals (17.8) and those with a full vaccination schedule (18.0). The authors conclude that “similar Ct values (…) suggest limited difference in infectiousness.” Note that there is still the possibility that vaccinated people shed the virus for a shorter period of time. Vaccination may also reduce an individual’s overall risk of becoming infected. In any case, vaccination should be expected to reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission, even of the Delta variant. Interesting discussions ahead.
Liu X, Shaw RH, Stuart ASV, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous versus homologous prime-boost schedules with an adenoviral vectored and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Com-COV): a single-blind, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2021, published 6 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01694-9
BioNTech/Pfizer vs AstraZeneca – the first immunogenicity comparison of heterologous vaccine schedules. After measuring the SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike IgG concentrations (measured by ELISA) at 28 days after the vaccine boost, the authors find the following values for homologs and heterologs schedules (BNT: BioNTech/Pfizer; AZ: AstraZeneca):
BNT/BNT: 14,080 ELU/mL
AZ/BNT: 12,906 ELU/mL
BNT/AZ: 7133 ELU/mL
AZ/AZ: 1392 ELU/mL
Bok K, Sitar S, Graham BS, Mascola JR. Accelerated COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons, and prospects. Immunity. 2021 Aug 3:S1074-7613(21)00303-4. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34348117. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.07.017
SARS-CoV-2 vaccines have been developed and approved in time frames never before seen, a feat that bodes well for future advancements in medicine, not only in infectious diseases. The authors review the milestones, methods and outcomes of this effort and provide a perspective for how partnership and preparedness can be better utilized in response to future public-health pandemic emergencies.
Transmission
Chen PZ, Koopmans M, Fisman DN, Gu FX. Understanding why superspreading drives the COVID-19 pandemic but not the H1N1 pandemic. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, published 2 August. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(21)00406-0/fulltext
With SARS-CoV-2, fewer cases cause the majority of infections, and a greater proportion of infections tend to be linked to large clusters via superspreading events. Why is this phenomenon, called over-dispersion in transmissibility (k), a characteristic of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, not part of the 2009 influenza H1N1 pandemic? The authors discuss which virological factors mediate k.
Pediatrics
Molteni E, Sudre CH, Canas LS, et al. Illness duration and symptom profile in symptomatic UK school-aged children tested for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2021, published 3 August. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00198-X
In this study of more than 1700 children age 5-17 that analyzed data reported by an adult proxy via a mobile application, 62% of children suffered from headaches and 55% from exhaustion. Among the younger children (5 to 11 years old), fever (44%), sore throat (36%) and stomach pain (28%) were also common. Among the older children, other symptoms included sore throat (51%), anosmia (48%), fever (35%) and persistent cough (26%). Younger and older children were sick for a median of five and seven days, respectively. 4.4% of the children had symptoms for at least 28 days; this was more commonly in older than younger children (5.1% and 3.1%, respectively).
7 August
Vaccines
Israel A, Merzon E, Schäffer AA, et al. Elapsed time since BNT162b2 vaccine and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in a large cohort. medRxiv 2021, posted 5 August. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.03.21261496
A retrospective study from Israel describing 33,993 fully vaccinated adults tried to answer one of the bigger questions these days: is the amount of time since the second injection of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine significantly associated with a risk of post-vaccination COVID-19 infection? Yes, it is. Those who received their second dose of vaccine at least 146 days before a new RT-PCR test (Group 1) had a higher risk of infection that those who received their vaccine less than 146 days before (Group 2). The absolute numbers are somewhat less scary: among people older than 60, 182/7021 (2.6%) tested positive in Group 1 and 19/2164 (0.9%) in Group 2.
Elliott P, Haw D, Wang H, et al. REACT-1 round 13 final report: exponential growth, high prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and vaccine effectiveness associated with Delta variant in England during May to July 2021. Imperial College London 2021, published 4 August. https://spiral.imperial.ac.uk/handle/10044/1/90800
First, the good news: fully vaccinated people have lower viral loads (median Ct: 27.6) than unvaccinated or partially vaccinated people (23.1), so vaccines are likely to decrease the potential for the transmission of the Delta variant. Now, the bad news: between 24 June and 12 July 2021, with the Delta variant already firmly established in the UK, 44% of infections occurred in fully vaccinated individuals. The authors estimate vaccine effectiveness against infection to be 49%. Sex, ethnicity, household size and local levels of economy also jointly contributed to the risk of higher prevalence. The authors anticipate that increased mixing during the autumn in the presence of the Delta variant may lead to a new wave of the pandemic, even at high levels of vaccination. [Note that men had higher odds of infection than women, a finding not seen in a previous analysis (20 May and 7 June). The reason? Increased social mixing during England’s progression in the Euro 2020 football competition during June and July 2021…]
Clinical
Hakimian S, Raines D, Reed G, et al. Assessment of Video Capsule Endoscopy in the Management of Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 1;4(7):e2118796. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34328500. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18796
The authors suggest that “video capsule endoscopy can serve as a safe alternative to the standard endoscopic evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding because it reduces the number of invasive procedures, personnel involved, and use of personal protective equipment.”
Co-morbidities
Corey L, Beyrer C, Cohen MS, Michael NL, Bedford T, Rolland M. SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Patients with Immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 5;385(6):562-566. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34347959. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsb2104756
Is viral evolution in immunocompromised patients an important factor in the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern? Read this nice summary of our current knowledge.
Treatment
O’Brien MP, Forleo-Neto E, Musser BJ, et al. Subcutaneous REGEN-COV Antibody Combination to Prevent Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 4. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34347950. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2109682
Normally, articles published in the New England Journal of Medicine provide relevant and important information for the improvement of medical care. This one might fail to reach that benchmark. You would need to treat 753 people to prevent 48 household infections with SARS-CoV-2. That is, 16 people treated to prevent one infection. Disappointingly, apart from the ‘duration of symptoms’, this study doesn’t present any clinical data on the 70 people who got infected. The combination of vaccines and – later on – cheap antiviral drugs will help combat the COVID-19 pandemic, monoclonal antibodies won’t.
6 August
Vaccines
Zhang H, Liu Y, Liu D, et al. Time of day influences immune response to an inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2021 Aug 2. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34341489. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-021-00541-6
Should you better go early in the morning to get your vaccine shot? The authors analyzed 63 health care workers who received the inactivated BBIBP-CorV vaccine (Sinopharm) either between 9 and 11 o’clock in the morning or between 3 and 5 o’clock in the afternoon. Strikingly, participants vaccinated in the morning showed significantly higher level of NAbs in the sera, 34.70 vs 19.35. Early birds also had stronger B cell and Tfh responses. Interesting path to follow.
Keeton R, Richardson SI, Moyo-Gwete T, et al. Prior infection with SARS-CoV-2 boosts and broadens Ad26.COV2.S immunogenicity in a variant dependent manner. medRxiv 2021, posted 28 July. Full text: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.24.21261037v1
Therefore, vaccination with the J&J vaccine following previous infection, even > 6 months previously, may result in substantially enhanced protection against COVID-19. The authors conclude that this finding may be of particular relevance in settings of high SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence.
Emanuel EJ, Skorton DJ. Mandating COVID-19 Vaccination for Health Care Workers. Ann Intern Med. 2021 Jul 30. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34328365. Full text: https://doi.org/10.7326/M21-3150
The Delta variant is paving the way for mandating COVID-19 vaccination, not only for health care workers.
Variants
Kimura I, Kosugi Y, Wu J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant exhibits higher infectivity and immune resistance. bioRxiv 2021, posted 28 July. Full-text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.454085
More about the Lambda variant (also known as the C.37 lineage which is now spreading in South American countries such as Peru, Chile, Argentina, and Ecuador).
The authors describe three mutations or variants, the RSYLTPGD246-253N, L452Q and F490S mutations, which respectively confer resistance to vaccine-induced antiviral immunity. Additionally, the T76I and L452Q mutations contribute to enhanced viral infectivity.
Clinical
Vousden N, Ramakrishnan R, Bunch K, et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant on the severity of maternal infection and perinatal outcomes: Data from the UK Obstetric Surveillance System national cohort. medRxiv 2021, posted 25 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.22.21261000
In this prospective cohort study on 3371 hospitalized pregnant women with symptoms of confirmed SARS-CoV-2, the proportion of pregnant women with moderate to severe COVID has increased with each successive appearance of new variants: 24% during the ‘wild-type period’ (1st March to 30th November 2020); 36% during the ‘Alpha period’ (1 December 2020 to 15 May 2021); and 45% during the ‘Delta period’ (16 May to 11 July 2021).
Treatment
REMAP-CAP, et al. Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021, published 4 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2103417
No benefit for critically ill patients with COVID-19 from routine therapeutic-dose anticoagulation with unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin. See also the comment by ten Cate H. Surviving Covid-19 with Heparin? N Engl J Med 2021, published 4 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe2111151
5 August
Vaccines
Hause AM, Gee J, Baggs J, et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Safety in Adolescents Aged 12–17 Years — United States, December 14, 2020–July 16, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 30 July 2021. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7031e1
As of July 16, 2021, almost 9 million US adolescents aged 12–17 years had received the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine. The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) received 9246 reports, 90.7% of which were for non-serious adverse events while 9.3% were for serious adverse events, including around 400 cases of myocarditis (4.3%; about 1:25,000 vaccinees; see also https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/70/wr/mm7027e2.htm). Systemic reactions were more common after the second dose.
Pinto D, Sauer MM, Czudnochowski N, et al. Broad betacoronavirus neutralization by a stem helix–specific human antibody. Science 2021, 3 August. Full text: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2021/08/03/science.abj3321
On our way to a universal betacoronavirus vaccine? The authors describe 5 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) cross-reacting with the stem helix of multiple β coronavirus spike glycoproteins isolated from COVID-19 convalescent individuals.
Immunology
Hasenkrug KJ, Feldmann F, Myers L, et al. Recovery from Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Development of Anamnestic Immune Responses in T Cell-Depleted Rhesus Macaques. mBio. 2021 Jul 27:e0150321. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34311582. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01503-21
What is the role of T cells in protection against SARS-CoV-2 reinfection? The authors inoculated macaques and rechallenged them 6 weeks later. Their conclusion: T cells might not be critical for recovery from acute SARS-CoV-2 infections while B cell responses and antibodies could be the essential mediators of protection from re-exposure. The discussion about the importance of T cells continues.
Virology
Mendonça L, Howe A, Gilchrist JB, et al. Correlative multi-scale cryo-imaging unveils SARS-CoV-2 assembly and egress. Nat Commun 12, 4629 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24887-y
The authors report a multi-modal, multi-scale cryo-correlative platform to image SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero cells, describing viral RNA transport portals, virus assembly intermediates, viral egress pathway, and native virus spike structures, in the context of whole cell volumes revealing drastic cytopathic changes.
Pathogenesis
Xydakis MS, Albers MW, Holbrook EH, et al. Post-viral effects of COVID-19 in the olfactory system and their implications. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Jul 30:S1474-4422(21)00182-4. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34339626. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00182-4
Why do we lose our smell with COVID-19? And what might be the consequences? The authors postulate that, “in people who have recovered from COVID-19, a chronic, recrudescent, or permanent olfactory deficit could be prognostic for an increased likelihood of neurological sequelae or neurodegenerative disorders in the long term.” See also the comment by Doty RL. The mechanisms of smell loss after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Jul 30:S1474-4422(21)00202-7. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34339627. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00202-7
4 August
Vaccines
Chia PY, Ong S, Chiew CJ, et al. Virological and serological kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant vaccine-breakthrough infections: a multi-center cohort study. medRxiv 2021, posted 31 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261295
Singapore, 218 patients admitted to hospital with Delta (B.1.617.2) SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vaccination (mostly with the BioNTech/Pfizer or Moderna vaccines) was associated with a faster decline in RNA viral load. The odds of severe COVID-19 requiring oxygen supplementation was significantly lower following vaccination (adjusted odds ratio 0.07, p = 0.001). PCR cycle threshold (Ct) values were similar between vaccinated and unvaccinated groups at diagnosis, but viral loads decreased faster in vaccinated individuals.
Parry H, McIlroy G, Bruton R, et al. Antibody responses after first and second Covid-19 vaccination in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Blood Cancer J. 11, 136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00528-x
In 267 patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), one dose of vaccine generated detectable spike-specific antibody responses in 34% of patients with CLL compared to 94% of healthy donors. After the second dose of vaccine, antibody responses increased to 75% (n = 55), but titers remained lower than in controls. Current treatment with Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors or IgA deficiency were independently associated with failure to generate an antibody response after the second vaccine.
Medeiros-Ribeiro AC, Aikawa NE, Saad CGS, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the CoronaVac inactivated vaccine in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a phase 4 trial. Nat Med (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01469-5
In 910 adults with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD) vaccinated with the Chinese CoronaVac vaccine, all had lower IgG seroconversion rates, and lower neutralizing antibody titers were lower than in 182 age- and sex-matched healthy adults.
Immunology
Muecksch F, Weisblum Y, Barnes CO, et al. Affinity maturation of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies confers potency, breadth, and resilience to viral escape mutations. Immunity. 2021 Jul 29:S1074-7613(21)00294-6. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34331873. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2021.07.008
The authors suggest that “increasing antibody diversity through prolonged or repeated antigen exposure may improve protection against diversifying SARS-CoV-2 populations, and perhaps against other pandemic threat coronaviruses.”
Pathogenesis
Chen KG, Park K, Spence JR. Studying SARS-CoV-2 infectivity and therapeutic responses with complex organoids. Nat Cell Biol (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00721-x
A review of the roles of complex organoids in the study of SARS-CoV-2 infection, modeling of COVID-19 disease pathology and of drug, antibody and vaccine development. The authors anticipate valuable lessons for the study of other viral diseases as well.
3 August
Vaccines
DREES 20210729. Entrées hospitalières et décès de patients Covid-19 selon le statut vaccinal et la présence de la mutation L452R. DREES 2021 (Direction de la recherche, des études, de l’évaluation et des statistiques), published 29 July. Full text : https://solidarites-sante.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/2021-07-23_-_sivic-sidep-vacsi_premiers_resultats_-_drees-2.pdf
In France, between 31 May and 11 July 2021, unvaccinated people represented around 85% of COVID-19 patients hospitalized, both in ICU units and non-ICU units. Fully vaccinated patients made up only 7% of admissions.
Merrill ED, Kashem SW, Amerson EH, et al. Association of Facial Pustular Neutrophilic Eruption With Messenger RNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. JAMA Dermatol. 2021 Jul 28. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34319363. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2474
The authors report a facial eruption that developed within 24 hours after receiving the Moderna vaccine in 2 patients without a history of known allergies, rosacea, facial/dental fillers, or prior SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Transmission
Sikkens JJ, Buis DTP, Peters EJG, et al. Serologic Surveillance and Phylogenetic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Hospital Health Care Workers. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 1;4(7):e2118554. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34319354. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18554
In this cohort study of 801 hospital health care workers (HCWs), the risk of getting infected with SARS-CoV-2 was nearly 4-fold higher among HCWs on COVID-19 wards compared with HCWs not in patient care. There was no evidence for patient-to-HCW transmission but several occurrences of HCW-to-HCW transmission.
Diagnosis
Schuit E, Veldhuijzen IK, Venekamp RP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and presymptomatic close contacts of individuals with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection: cross sectional study. BMJ. 2021 Jul 27;374:n1676. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34315770. Full-text: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n1676
The sensitivities of the Veritor and Biosensor lateral flow rapid antigen tests in asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic close contacts tested on day 5 onwards after close contact with an index case were more than 85% after a viral load cut-off was applied as a proxy for infectiousness.
Treatment
Abbasi J. Überantibodies From Recovered COVID-19 Patients Could Spur New Therapeutics and Vaccines. JAMA. 2021 Jul 28. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34319350. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.12915
A comment on the Wang paper that described antibodies with sub-nanomolar neutralization titers: Wang L, Zhou T, Zhang Y. Ultrapotent antibodies against diverse and highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 01 Jul 2021: eabh1766. https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2021/06/30/science.abh1766
2 August
Vaccines
Corbett KS, Nason MC, Flach B, et al. Immune Correlates of Protection by mRNA-1273 Immunization against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Nonhuman Primates. Science 2021, published 29 July. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/33907752. Full text: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2021/07/29/science.abj0299
In Rhesus macaques, viral replication was significantly reduced in bronchoalveolar lavages and nasal swabs following a SARS-CoV-2 challenge in vaccinated animals and strongly correlated with levels of anti-S antibody and neutralizing activity. Lower antibody levels were needed for reduction of viral replication in the lower airway than in the upper airway.
Fallah M. Remember Ebola: stop mass death in Africa. Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7869):627. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34316054. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-01964-2
“Rich countries are hoarding vaccines, allowing doses to expire while unvaccinated people who want to be immunized die.”
Clinical
Araujo-Silva CA, Marcos AAA, Marinho PM, et al. Presumed SARS-CoV-2 Viral Particles in the Human Retina of Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021 Jul 29. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34323931. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.2795
Post-mortem analysis of enucleated eyes of three patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection revealed presumed S and N COVID-19 proteins within endothelial cells close to the capillary flame and cells of the inner and the outer nuclear layers. This finding may explain some of the infection’s ocular clinical manifestations.
Treatment
Butler CC, Yu LM, Dorward J, et al. Doxycycline for community treatment of suspected COVID-19 in people at high risk of adverse outcomes in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet Resp Med 2021, published 27 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00310-6
Don’t use doxycycline as a routine treatment for COVID-19! In patients with suspected COVID-19 who were at high risk of adverse outcomes, treatment with doxycycline was not associated with clinically meaningful reductions in time to recovery, hospital admissions or deaths related to COVID-19.
Collateral Effects
Burki K. Tobacco industry capitalises on the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Resp Med 2021, published 29 July. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00361-1
“Ever since the tobacco industry started marketing its products, it has attempted to hitch them to key trends and events. Adverts during World War One associated tobacco with victory. The industry would subsequently deploy the rhetoric of the suffragette movement with the “torches of freedom” campaign. Virginia Slims introduced the tagline “you’ve come a long way, baby” in the late 1960s, playing on the feminist themes of the era. “Today, we see the industry paying influencers on social media to push e-cigarettes, which they claim are harmless and cool, when in fact the whole point is to get a new generation addicted to nicotine. (…) As soon as COVID-19 arrived, they recognized the opportunity that the pandemic presented.”
1 August
Vaccines
Krantz MS, Kwah JH, Stone CA Jr, et al. Safety Evaluation of the Second Dose of Messenger RNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Patients With Immediate Reactions to the First Dose. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Jul 26. PubMed: https://pubmed.gov/34309623. Full text: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3779
All 159 patients with an immediate allergic reaction to the first dose of the Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna vaccine, including 19 individuals with first-dose anaphylaxis, tolerated the second dose. (Antihistamine pre-medication had been given to 47 patients [30%] before the second dose). Thirty-two patients (20%) reported immediate and potentially allergic symptoms that were associated with the second dose that were self-limiting, mild, and/or resolved with antihistamines alone.
Stampfer SD, Goldwater MS, Jew S, et al. Response to mRNA vaccination for COVID-19 among patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-021-01354-7
Study of 103 multiple myeloma (MM) patients (96 patients with active MM and 7 with smoldering (asymptomatic) disease). Smoldering MM patients responded better than those with active disease. Only 45% of active MM patients developed an adequate response, while 22% had a partial response. Lower spike antibody levels were associated with older age, impaired renal function, low lymphocyte counts, reduced uninvolved immunoglobulin levels, > second line of treatment, and among those not in complete remission.
Pathogenesis
Cohen CA, Li APY, Hachim A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell responses are lower in children and increase with age and time after infection. Nat Commun 12, 4678 (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24938-4
Could a reduced prior β coronavirus immunity and reduced T cell activation in children drive a milder COVID-19 pathogenesis? The authors found that infected children have lower CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 structural and ORF1ab proteins compared to infected adults.
Prevention
Schooley RT. Introduction to the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2) Supplement, Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 73, Issue Supplement_2, 1 August 2021, Page S119, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab524
Eight manuscripts about the scientific underpinning of non-biological interventions. Among other topics: 1) the importance of aerosols and pre-symptomatic shedding; 2) the impact of distancing and masking on preventing ongoing viral transmission; 3) initial overestimation of the role of fomites and of droplets in viral transmission.
Chowell G, Dahal S, Bono R, et al. Harnessing testing strategies and public health measures to avert COVID-19 outbreaks during ocean cruises. Sci Rep 11, 15482 (2021). Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95032-4
A cruise ship is not a good place to be during a pandemic of a respiratory pathogen. This study finds that PCR testing at embarkation and daily testing of all individuals aboard, together with increased social distancing, might be able to reduce the probability of onboard COVID-19 community spread. At the personal level, there might be an even more promising strategy: avoid cruise ships until the pandemic is under control.
Home | Top Papers | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12
2021: 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07
By Christian Hoffmann &
Bernd S. Kamps